How Do Vegetarians Get Protein
How do vegetarians get protein? Despite popular belief, a plant-based diet has lots of protein-rich foods! Legumes, tofu, quinoa, almonds, seeds, and dairy substitutes are essential for muscle building and general health.
A balanced diet can help you satisfy your protein needs, regardless of whether you choose vegetarianism for ethical, health, or environmental reasons. This article explores the best vegetarian protein sources to keep you strong and energized!
Why Protein Is Important
Protein consists of amino acids, which serve as the fundamental components essential for life. Since the body cannot independently generate nine of the twenty amino acids, they are considered crucial. These must be obtained through diet. Protein is vital for:
1. Builds And Repairs Muscles
Protein is the building block of muscles, helping in growth, repair, and recovery. Athletes and active individuals must prevent muscle loss and enhance strength, endurance, and overall physical performance. It also helps repair tissues after injuries.
2. Supports Enzyme And Hormone Production
Proteins form enzymes that facilitate digestion, metabolism, and energy production. They also aid in hormone production and regulate bodily functions like mood, stress response, and reproductive health. Without adequate protein, these functions are deficient, leading to health issues.
3. Boosts Immune Function
Antibodies, which help fight infections and diseases, are made of proteins. A protein-rich diet strengthens immune defences, allowing the body to respond effectively to viruses and bacteria. Low protein intake can weaken immunity, making you more vulnerable to illness.
4. Aids In Weight Management
Protein keeps you full longer, reducing hunger and cravings. It also boosts metabolism, helping burn more calories. High-protein diets help people lose fat while maintaining muscle mass, which makes it a vital food for managing weight and maintaining good body composition.
5. Maintains Skin, Hair, And Nails
Proteins like collagen and keratin support skin elasticity, hair strength, and nail growth. They help prevent wrinkles, hair loss, and brittle nails. A protein deficiency can lead to premature aging, weak hair, and dull skin, affecting overall appearance.
6. Supports Bone Health
Protein is vital in maintaining strong bones by aiding calcium absorption and supporting bone remodelling processes. Its contribution is essential for overall bone health and strength.
It helps prevent osteoporosis and fractures, especially in older adults. A protein-rich diet supports overall skeletal strength, reducing the risk of bone-related issues.
7. Regulates Metabolism
Protein is essential for metabolic processes, supporting energy production and nutrient absorption. It encourages muscular contraction and helps keep blood sugar levels steady.
A healthy metabolism ensures efficient digestion, better energy levels, and reduced risks of metabolic disorders like diabetes.
8. Enhances Oxygen Transport
Hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells, carries oxygen throughout the body. This ensures proper organ function, muscle performance, and overall vitality.
Low protein intake can hinder oxygen supply, resulting in weakness, exhaustion, and a decline in mental and physical function.
9. Improves Recovery
The protein ring damages tissues by repairing them, and the protein accelerates recovery after death. The healing process accelerates, and muscle pain decreases. Consuming adequate protein ensures the body can quickly rebuild and maintain optimal strength and functionality.
10. Essential For Overall Growth
Protein is vital for children’s growth, ensuring the proper development of bones, muscles, and organs. In adults, it supports cell regeneration and body maintenance. A lack of protein can result in delayed growth, muscle loss, and weakened general health.
How Much Protein Do You Need?
Protein requirements vary based on lifestyle, age, and health goals. The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for a typical adult is 0.8g of protein per kilogram of body weight. However, this amount may not be sufficient for everyone.
For sedentary adults, 0.8g/kg is adequate for essential bodily functions. However, active individuals need more protein for muscle repair and energy levels, requiring around 1.2–1.4g/kg.
Those engaged in intense training, such as athletes or bodybuilders, benefit from 1.6–2.0g/kg to aid muscle growth and recovery.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women need extra protein, typically 1.1–1.3g/kg, for fetal development and milk production. Your daily protein requirements can be calculated by multiplying your body weight in kilograms by the relevant factor.
For example, an active adult weighing 70 kg (154 lbs) requires approximately 84–98g of protein daily to maintain muscle health and overall well-being.
Consuming sufficient protein from diverse sources—such as legumes, nuts, tofu, and whole grains—ensures optimal body function. For sustained well-being, modify your intake according to your activity level and health.
Top Plant-Based Protein Sources For Vegetarians
The top vegetarian-friendly protein sources and their protein amount per serving are listed below:
Legumes
Legumes, including beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas, are a staple in vegetarian diets. They are high in protein and fibre, iron, and folate.
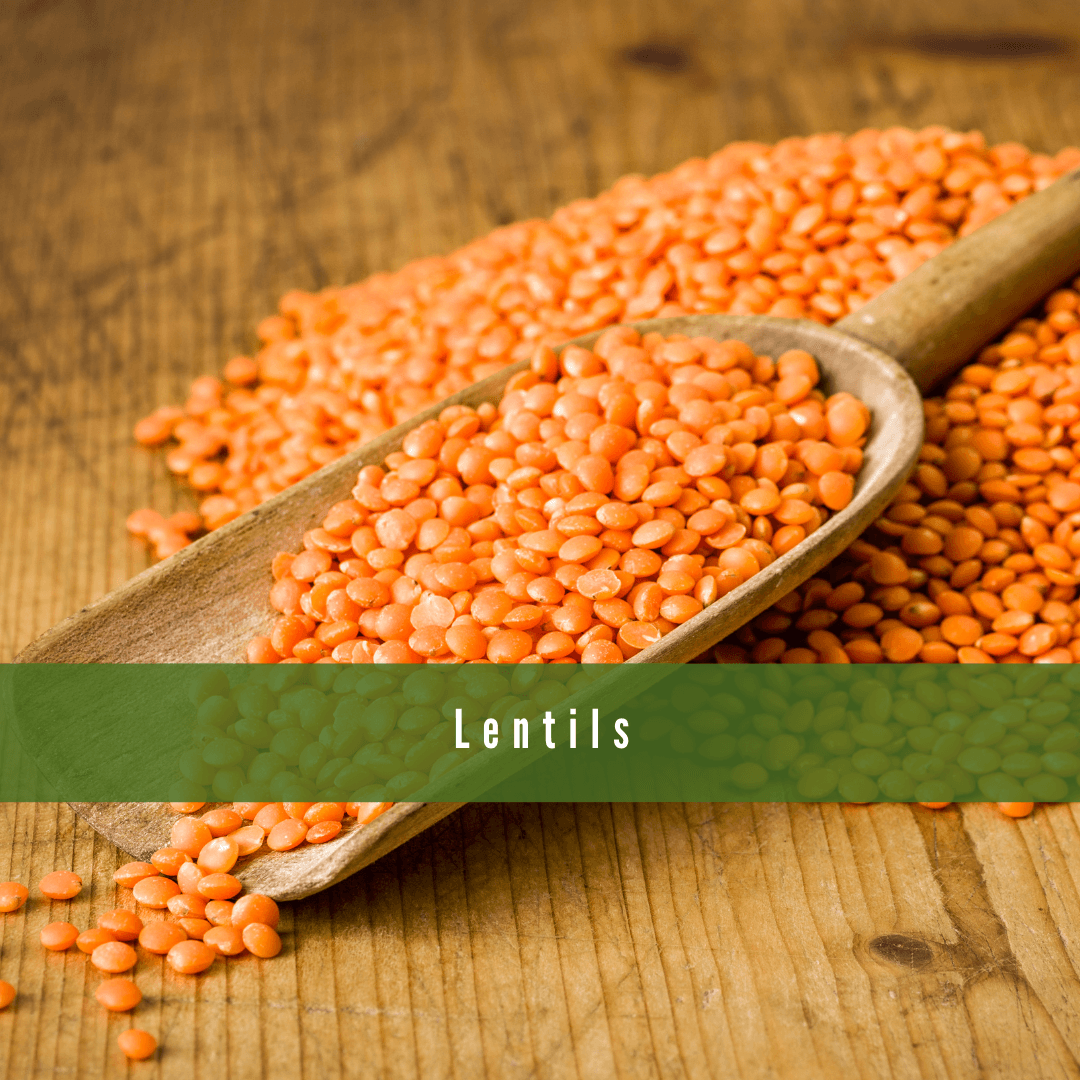
1. Lentils (18g protein per cup, cooked)
Lentils are a nutrient-dense food, offering a rich combination of protein, fibre, and vital minerals. Because of their remarkable nutritional profile, lentils are a beneficial complement to any diet.
They support muscle growth, aid digestion, and help regulate blood sugar levels. Their rich iron content makes them especially beneficial for vegetarians and vegans to prevent deficiencies.
How To Use
Lentils can be added to soups, stews, curries, or salads. They also make excellent veggie burger patties and protein-packed lentil dips.
2. Chickpeas (15g protein per cup, cooked)
Chickpeas offer 15g of protein per cooked cup, making them a great plant-based source. Their high fibre content also supports heart health, controls blood sugar, and extends sensations of fullness.
Rich in folate and iron, they boost energy and overall well-being while reducing cholesterol. They are a nutritious and delicious addition to any diet!
How To Use
Chickpeas can be used in hummus, salads, stir-fries, or curries. They can also be pureed or roasted for a crispy snack or soup.
3. Black Beans (15g protein per cup, cooked)
Black beans are a nutrient-rich food that contains protein, fibre, and antioxidants. They are a healthy complement to any diet because they help reduce inflammation and promote digestive health.
Their high folate content supports brain function, while their slow-digesting carbs provide long-lasting energy, making them great for active individuals.
How To Use
Add black beans to tacos, burritos, soups, or salads. Mash them for veggie burgers, dips, or a protein-rich pasta sauce.

Soy Products
Soy is an uncommon plant-based protein source that is complete since it contains all nine essential amino acids.
1. Tofu (10g protein per ½ cup)
A versatile plant protein high in calcium and iron, tofu (10g protein per ½ cup) promotes bone health and vitality. Its mild taste absorbs flavours, making it a great meat alternative.
Packed with isoflavones, tofu encourages heart health and hormone balance, making it a nutritious addition to any diet.
How To Use
Stir-fry, grill, or bake tofu for a crispy texture, blend it into smoothies, or use it in soups, scrambles, and curries.
2. Tempeh (15g protein per ½ cup)
Tempeh (15g protein per ½ cup) is a fermented soybean product rich in protein, probiotics, and fibre. It supports digestion and gut health.
Due to its complex structure and nutty taste, tempeh is an excellent meat substitute. Fermentation boosts nutrient absorption, enhancing overall health and making tempeh a nutritious addition to any meal.
How To Use
Slice and sauté tempeh for sandwiches, crumble it into stir-fries or tacos or marinate and grill it for a hearty dish.
3. Edamame (17g protein per cup, cooked)
Edamame, young soybeans, are a complete protein source with all essential amino acids. They are also rich in fibre, vitamins, and antioxidants that support muscle recovery, heart health, and immune function, making them a perfect snack or meal addition.
How To Use
Toss into rice dishes, stir-fries, or salads, incorporate into hummus for added protein, or steam and season with sea salt.

4. Soy Milk (7g protein per cup)
Soy milk (7g protein per cup) is a dairy-free alternative packed with calcium, vitamin D, and essential amino acids. It supports bone and muscle growth and heart health while being lower in saturated fat than dairy milk. Nutritious and versatile, soy milk is an excellent addition to a balanced diet.
How To Use
You can pour it into coffee, smoothies, or cereal, use it in baking, or enjoy it as a refreshing drink with added flavours like vanilla.
Whole Grains
A good source of complex carbs, whole grains also offer a respectable amount of protein.
1. Quinoa (8g protein per cup, cooked)
Quinoa has all the necessary amino acids, making it a complete protein. It’s gluten-free, fibre-rich, and packed with iron, magnesium, and antioxidants. This superfood supports muscle growth, digestion, and sustained energy levels, making it a perfect meal addition.
How To Use
Cook and add to salads, grain bowls, stir-fries, or soups. Enjoy as a side dish with vegetables, tofu, or beans for a nutritious meal.

2. Brown Rice (5g protein per cup, cooked)
Brown rice, with 5g of protein per cooked cup, is a nutrient-rich whole grain packed with fibre, magnesium, and manganese.
It supports digestion, promotes heart health, and provides steady energy. It is a nutritious option for well-balanced diets because it is versatile, filling, and an excellent foundation for vegetarian and vegan dishes.
How To Use
Serve as a side dish, mix into stir-fries, make grain bowls, use in stuffed peppers, or prepare as wholesome porridge.
3. Oats (6g protein per cup, cooked)
Oats provide 6g of protein per cooked cup and are rich in fibre and beta-glucans, which support heart health, digestion, and steady energy.
Oats are a versatile whole grain that is perfect for a balanced and nutritious diet. They can control blood sugar and decrease cholesterol, making them a healthy option for breakfast or snacks.
How To Use
Make oatmeal, blend it into smoothies, bake it into granola bars, or use it in overnight oats for extra nutrition.
4. Whole Wheat Bread (4g protein per slice)
Whole wheat bread has 4g of protein per slice, plus fibre and B vitamins for digestion and energy. Unlike refined bread, it keeps the bran and germ, offering more nutrients.
A wholesome choice, it’s great for sandwiches, toast, or meals, promoting steady energy and overall health while adding heartiness to your diet.
How To Use
It can be used in handmade croutons for salads, avocado toast, sandwiches, French toast, and soup pairings.
Want to Share Your Passion for Vegan Living?
Discover how easy and fulfilling vegan living can be —
from recipes and travel to lifestyle and sustainability tips.
Read this blog post next:
How to Start a Vegan Blog (and Turn Your Passion into Purpose).
Nuts And Seeds
Nuts and seeds are nutrient-dense and provide healthy fats, fibre, and protein.
1. Almonds (6g protein per ounce, 28g)
Almonds are rich in protein, good fats, and vitamin E and promote heart health, brain function, and skin nourishment. They are a great supplement to meals or snacks since they help regulate hunger, encourage muscle regeneration, and provide steady energy.
How To Use
Eat raw, roast for a crunchy snack, blend into almond butter, sprinkle over salads, or add to oatmeal and smoothies.

2. Peanuts (7g protein per ounce, 28g)
Peanuts provide 7g of protein per ounce and are rich in heart-healthy monounsaturated fats, folate, and magnesium. These affordable legumes promote muscle building, help manage weight, and keep you feeling fuller for longer.
A nutritious snack, peanuts offer essential nutrients while supporting overall health and providing a satisfying, protein-packed option for your diet.
How To Use
Enjoy as peanut butter, sprinkle over stir-fries, mix into trail mixes, add to smoothies, or use in sauces like satay.
3. Chia Seeds (4g protein per ounce, 28g)
Chia seeds offer 4g of protein per ounce and omega-3 fatty acids, fibre, and antioxidants. They absorb liquid to form a gel-like texture, supporting digestion, hydration, and heart health.
Chia seeds are rich in vital nutrients and offer a sustained energy boost. They are a potent and adaptable supplement to any diet.
How To Use
You can mix chia seeds into smoothies, make chia pudding, stir it into yogurt, add it to oatmeal, or sprinkle it on salads and baked goods.
Dairy And Eggs (For Lacto-Ovo Vegetarians)
Dairy and eggs are excellent sources of high-quality protein for vegetarians who consume them.

1. Greek Yogurt (10g protein per 100g)
Greek yogurt is abundant in probiotics, calcium, and protein, with 10g of protein per 100g. It promotes healthy bones, digestion, and muscle growth.
With its creamy texture and mildly tangy flavour, Greek yogurt is a versatile, nutritious choice for snacks or meals. It gives your diet the right amount of protein and healthful elements.
How To Use
Eat plain, mix with fruit and honey, blend into smoothies, use as a base for dips, or substitute for sour cream.
2. Cottage Cheese (11g protein per ½ cup)
Cottage cheese provides 11g of protein per ½ cup and is rich in casein protein, which promotes muscle recovery and more prolonged satiety.
Packed with calcium and B vitamins, it supports bone health and energy metabolism. This nutrient-dense dairy product is a versatile and nutritious addition to any diet, promoting muscle growth, recovery, and overall well-being.
How To Use
For a nutritious, protein-packed boost, eat plain, mix with fruit and nuts, spread on toast, add to scrambled eggs, or blend into smoothies.
Meat Alternatives
Many plant-based meat alternatives are now available, offering a convenient way to boost protein intake.
1. Seitan (21g protein per 3 ounces, 85g)
Seitan, made from wheat gluten, is a dense, chewy meat alternative packed with protein. It absorbs flavours well, making it an excellent option for savoury dishes. However, it's unsuitable for those with gluten intolerance or celiac disease.
How To Use
Stir-fry with vegetables, grill as steaks, use in burgers, slice for sandwiches, add to curries or use in stir-fry noodle dishes.

2. Plant-Based Burgers (15–20g protein per patty)
Plant-based burgers from soy, pea protein, or other plant ingredients provide 15–20g of protein per patty. They offer a satisfying meat-like texture and are rich in minerals, enhancing their nutritional value.
These burgers are a great protein source and perfect for those seeking a meat alternative. They support a balanced, plant-based diet while delivering flavour and nutrients.
How To Use
Grill or pan-fry, serve on a bun with toppings, crumble into pasta dishes, chop into salads, or add to wraps.
Vegetables
While not as protein-dense as other sources, some vegetables increase protein intake.
1. Broccoli
Broccoli provides 3g of protein per cooked cup and is packed with antioxidants, fibre, and vitamins C and K. It strengthens the immune system, promotes digestive health, and aids in general well-being maintenance.
This nutrient-rich vegetable is essential to a balanced diet. It promotes vitality and offers numerous health benefits with every serving.
How To Use
Add cooked broccoli to stir-fries or soups, or toss it in pasta for a nutritious boost that enhances flavour and health benefits.

2. Spinach
A cooked cup of spinach has 5g of protein and vital vitamins A, C, and K, which promote healthy bones, skin, and immunity.
Rich in iron, spinach helps improve energy levels, prevent anemia, and boost vitality. This powerhouse green is an excellent choice for maintaining healthy body functions, making it a nutrient-packed addition to your diet.
How To Use
Sautéed spinach can be added to omelets, sandwiches, or smoothies for an easy nutrient boost, enhancing your meals' flavour and nutritional value.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the answer to how do vegetarians get protein lies in a diverse and balanced diet. Protein is easy for vegetarians to get from nutrient-dense foods, including beans, tofu, quinoa, almonds, and dairy alternatives.
Plant-based protein sources provide all the necessary elements for a robust and invigorated body, whether for ethical, health, or fitness purposes. The secret to maintaining a sustainable and healthy vegetarian lifestyle is embracing variation!
I trust you enjoyed this article on How Do Vegetarians Get Protein. Please stay tuned for more plant-based recipes, vegan travel tips, and lifestyle inspiration.
Take care!
— JeannetteZ 🌿
💬 Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I’d love to hear from you. Please leave your comments below, or email me directly at Jeannette@LivingTheVeganLifestyle.org.
📚 More Vegan Lifestyle Reads
🌱 My #1 Recommendation for Online Success
Sharing my passion for vegan living — from food to fashion — has been such a rewarding journey.
If you’ve ever dreamed of building your own ethical lifestyle brand or blog, this is the best place to start.
🌟 See How Vegan Bloggers Build Online Income — Try WA Free (No Credit Card Needed)
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate and participant in other affiliate programs, I earn from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you. Please read my full affiliate disclosure.