Best Nonmeat Sources Of Vitamin B12

Best Nonmeat Sources Of Vitamin B12
In today's health-conscious world, more people are exploring vegetarian and vegan lifestyles for ethical, environmental, and health reasons.
However, one common concern among individuals following plant-based diets is obtaining adequate Vitamin B12, an essential nutrient primarily found in animal products.
Fortunately, numerous non-meat sources of vitamin B12 are available to address this concern, ranging from fortified plant-based foods to natural sources like certain seaweeds and mushrooms.
From fortified plant-based foods to natural sources like certain seaweeds and mushrooms, vegetarians and vegans have various options to ensure they meet their B12 requirements without compromising their dietary preferences.
For those who follow a plant-based lifestyle and want to preserve optimal health and well-being, it is imperative that they comprehend and include these non-meat sources of Vitamin B12.
This article will examine the wide range of plant-based sources of vitamin B12 and offer helpful advice on how people can successfully include them in their regular meals to meet their dietary requirements.
Introduction To Vitamin B12
Water-soluble vitamin B12, often known as cobalamin, is necessary for several physiological processes in the body.
It's essential for DNA synthesis, red blood cell production, neuron function, and the metabolism of lipids and amino acids.
Vitamin B12 is very important for vegetarians and vegans. Vitamin B12's primary sources are foods derived from animals, including meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products.
Therefore, individuals whose diets exclude or restrict animal products may be at a higher risk of developing a vitamin B12 deficiency.
Ensuring you get enough vitamin B12 is essential for preserving general health and well-being. A lack of vitamin B12 can cause many health concerns, such as anemia, neurological conditions like tingling and numbness in the extremities, weariness, cognitive decline, and mood swings.
Given the potential health consequences of vitamin B12 deficiency, it is essential for individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets to ensure they obtain an adequate intake of this nutrient through fortified foods, supplements, or fortified beverages to support optimal health and prevent deficiency-related complications.
Health Benefits Of Vitamin B12
Nonmeat sources of vitamin B12 provide essential nutrients like cobalamin, playing multiple crucial roles in the body.
1. Energy Production
Vitamin B12 is key in metabolizing carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, the body's primary energy sources.
It helps convert these nutrients into glucose, which cells produce for energy. Adequate vitamin B12 is essential for maintaining optimal energy levels and preventing fatigue.
2. Nervous System Health
Vitamin B12 is crucial for properly functioning the nervous system. It helps maintain the integrity of myelin, the protective sheath surrounding nerve fibres and facilitates the transmission of nerve impulses.
Vitamin B12 contributes to cognitive function, mood regulation, and overall neurological health by supporting nerve function.
3. Red Blood Cell Formation
Vitamin B12 is necessary to produce red blood cells in the bone marrow. Red blood cells remove carbon dioxide for excretion and carry oxygen from the lungs to all bodily tissues.
Adequate vitamin B12 levels are necessary to prevent anemia and ensure optimal oxygen delivery to cells and tissues.
4. Heart Health
When homocysteine levels are high, it is linked to a higher risk of cardiovascular disease. Vitamin B12 is involved in the breakdown of homocysteine.
Vitamin B12 may support heart health and lessen the risk of heart disease and stroke by reducing homocysteine levels in the blood.
5. Brain Function
Nonmeat sources of vitamin B12 are crucial for maintaining cognitive function, aiding in improved memory, concentration, and overall brain health.
At the same time, deficiency in this nutrient has been associated with cognitive decline and neurological disorders.
Adequate levels of vitamin B12 have been linked to improved memory, concentration, and overall brain health.
Deficiency in vitamin B12 has been associated with cognitive decline, dementia, and neurological disorders.
6. Mood Regulation
Neurotransmitters, including dopamine and serotonin, which impact mood regulation and emotional health, are made by vitamin B12.
Sufficient intake of vitamin B12 may lower the chance of mood disorders, anxiety, and depression.
7. Healthy Skin, Hair, And Nails
Vitamin B12 is essential for regenerating and maintaining skin cells, hair follicles, and nail beds. It promotes healthy skin, hair growth, and nail strength, contributing to overall appearance and vitality.
Overall, vitamin B12 is required to produce energy, improve the health of the neurological system, develop red blood cells in the heart and brain, improve mood control, and preserve healthy skin, hair, and nails.
To maintain general health and well-being, it's critical to ensure you get enough vitamin B12 via your diet or supplements.
Exploring The Nonmeat Sources Of Vitamin B12
A universe of non-meat sources is waiting to give you this vital nutrient, whether you're a committed vegan, a seasoned vegetarian, or just trying to switch things up in your diet.
The alternatives are as delicious as they are varied, ranging from savoury plant-based cheeses that melt in your mouth while offering a B12 boost to fortified plant-based milk that turns your morning cereal into a nutritious powerhouse. Now, let's take a tasty tour of the vibrant world of vitamin B12-containing plant-based foods:
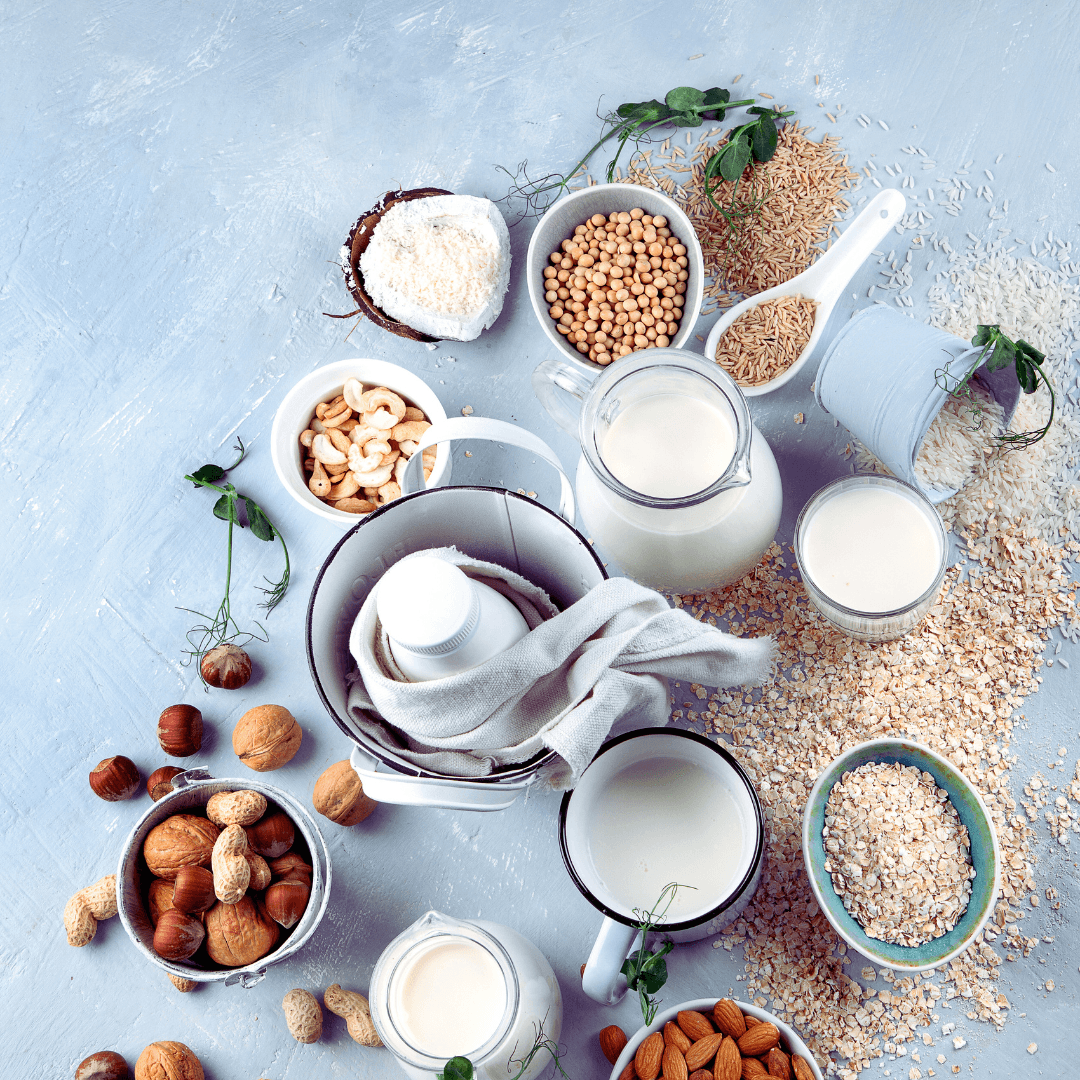

1. Fortified Plant-Based Milk
Fortified plant-based milk offers a convenient and versatile way to incorporate vitamin B12 into a vegetarian or vegan diet.
Popular options like soy, almond, coconut, and oat milk are fortified with vitamin B12, making them suitable alternatives for individuals looking to boost their intake of this essential nutrient.
Make sure the plant-based milk you choose is fortified with vitamin B12 by carefully reading the label.
Typically, manufacturers fortify plant-based milk with vitamin B12 to levels comparable to those found in dairy milk, providing a reliable source of this nutrient for those who do not consume animal products.
Whether enjoyed on its own, poured over cereal, blended into smoothies, or used in cooking and baking, fortified plant-based milk offers a delicious and accessible way to meet daily vitamin B12 needs while enjoying the benefits of a dairy-free lifestyle.
Incorporating fortified plant-based dairy into your diet can contribute to overall health and well-being, ensuring adequate nutrient intake without compromising taste or convenience.
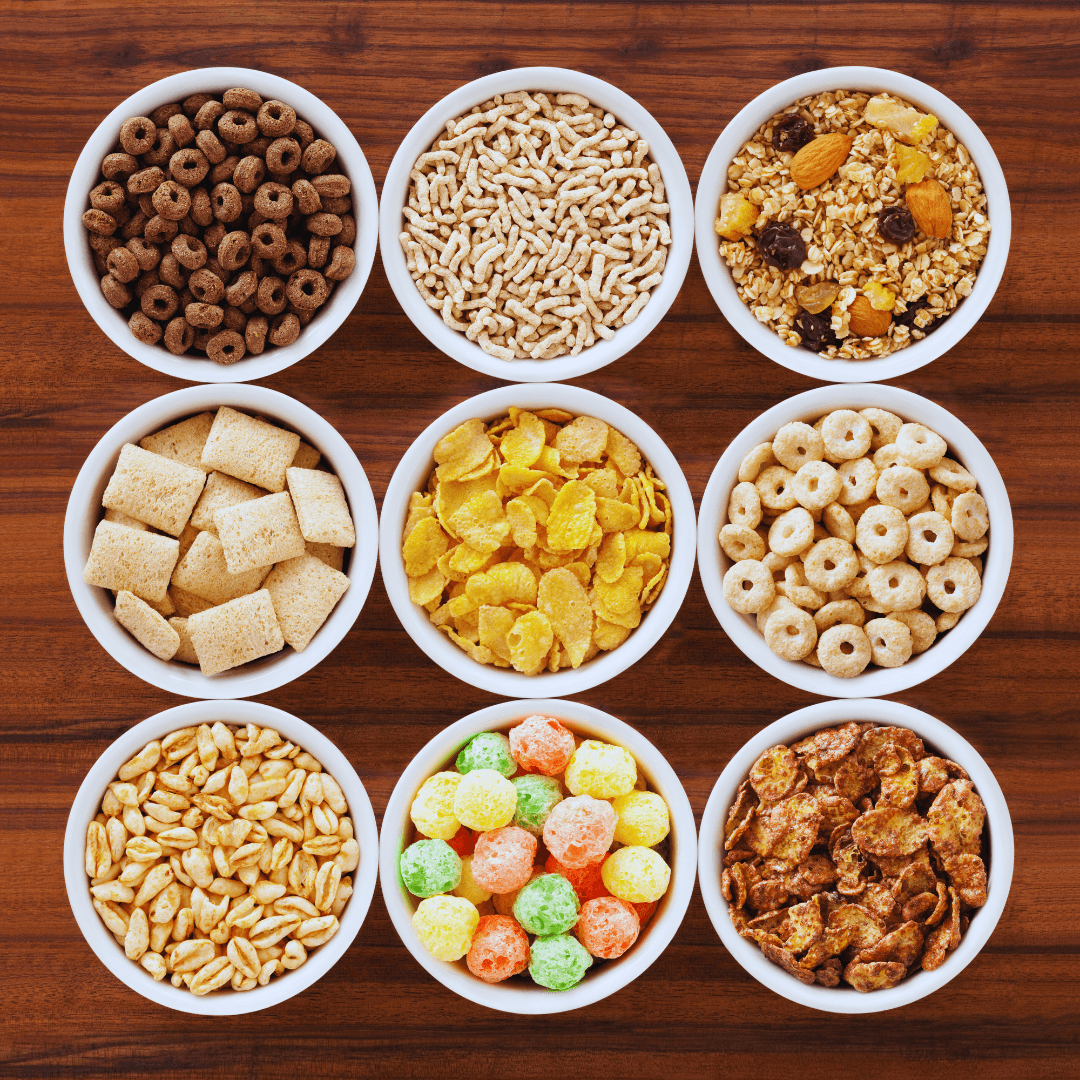

2. Fortified Breakfast Cereals
Fortified breakfast cereals provide a convenient and tasty way to increase your intake of vitamin B12, particularly for individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets.
Due to their unique formulation that includes extra vitamin B12, these cereals are a great option for people who want to ensure they get all the nutrients they need daily.
When shopping for breakfast cereals, looking for products labelled as “fortified” or “enriched” with vitamin B12 on the packaging is important.
These labels indicate that the cereal has been supplemented with vitamin B12 to provide a significant portion of the recommended daily intake.
Fortified breakfast cereals come in various flavours and styles, catering to different tastes and preferences.
Whether you prefer classic flakes, crunchy clusters, or fruity loops, there's likely a fortified cereal option to suit your breakfast routine.
By starting your day with a bowl of fortified breakfast cereal, you can enjoy a delicious and nutritious meal while ensuring you get the vitamin B12 your body needs to function optimally.
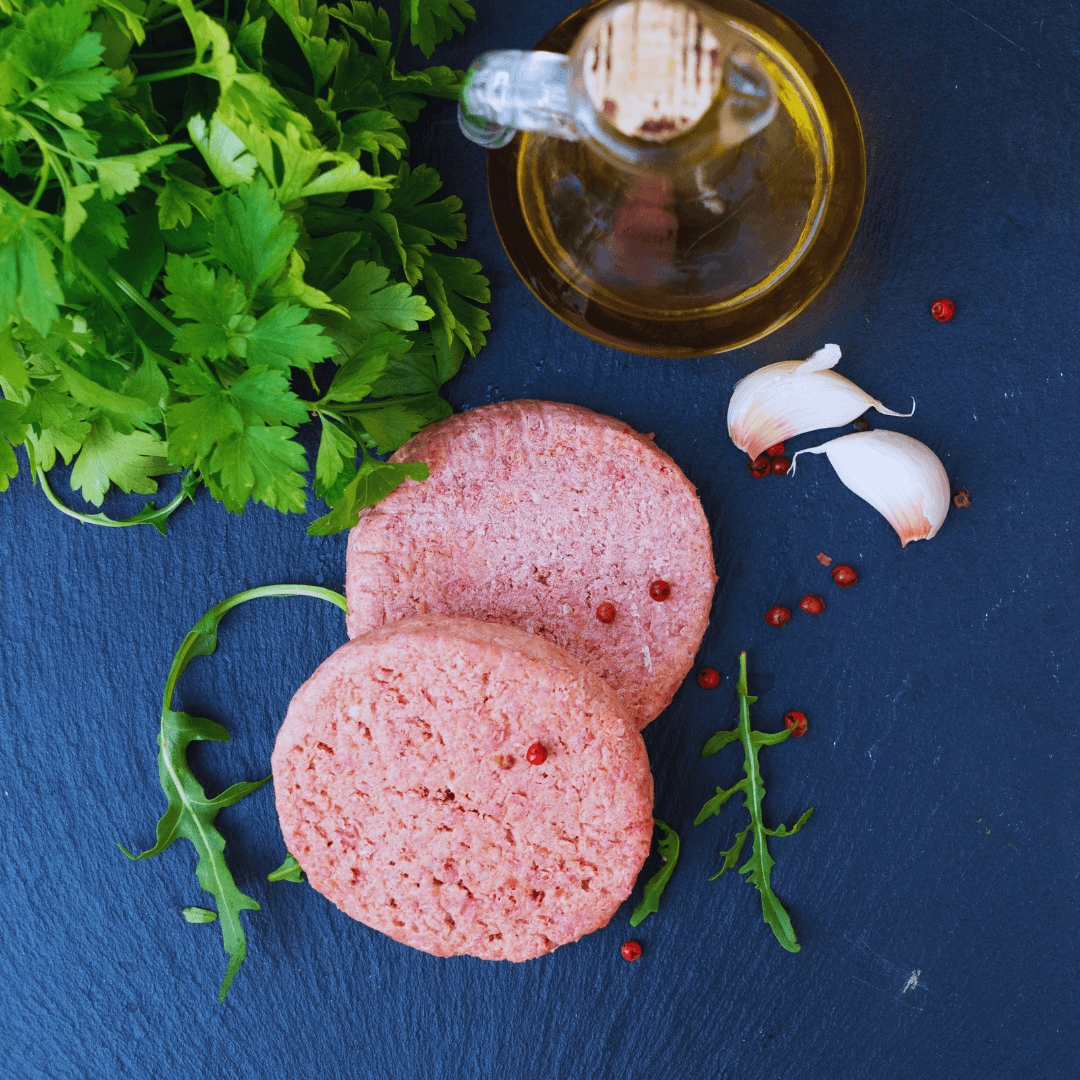

3. Fortified Meat Substitutes
Nonmeat sources of vitamin B12, such as fortified meat substitutes like tofu, tempeh, and seitan, provide essential nutrients for individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets, ensuring they receive added nutritional benefits.
Options like tofu, tempeh, and seitan are rich in plant-based protein and fortified with vitamin B12 to provide an added nutritional boost.
Verifying the label while choosing fortified meat alternatives ensures the product has extra vitamin B12.
This information is typically clearly displayed on the packaging, ensuring consumers can make informed choices about their dietary intake.
Fortified meat substitutes can be used in various culinary applications, from stir-fries and salads to sandwiches and stews, offering a flavourful and nutritious alternative to traditional meat-based dishes.
By incorporating fortified meat substitutes into their meals, individuals can enjoy the benefits of vitamin B12 without compromising on taste, texture, or dietary preferences.
This makes it easier than ever to meet their nutritional needs while following a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle.
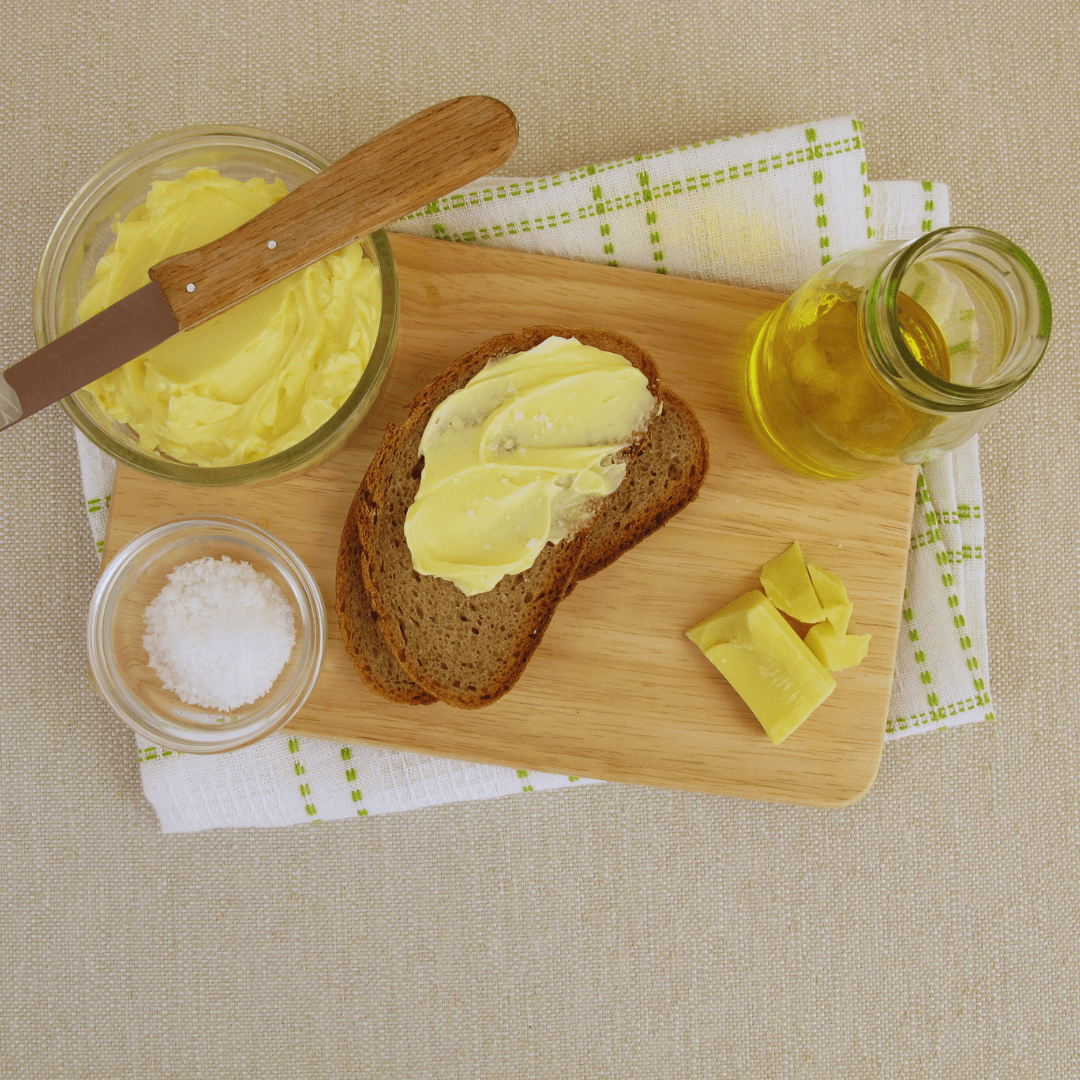

4. Fortified Plant-Based Spreads
Fortified plant-based spreads, such as margarine, offer a convenient way for individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets to incorporate vitamin B12 into their daily routine.
These spreads are specially formulated to contain added vitamin B12, making them an excellent choice for those looking to ensure they meet their nutritional requirements.
When shopping for plant-based spreads, it is important to look for products labelled “fortified” with vitamin B12 on the packaging.
This label indicates that the spread has been supplemented with vitamin B12 to provide an additional source of this essential nutrient.
Fortified plant-based spreads can be used in various ways, including spreading on toast, crackers, or sandwiches or in cooking and baking recipes.
By choosing fortified plant-based spreads, individuals can enjoy the benefits of vitamin B12 while adding flavour and versatility to their meals.
This makes maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet easier while following a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle.
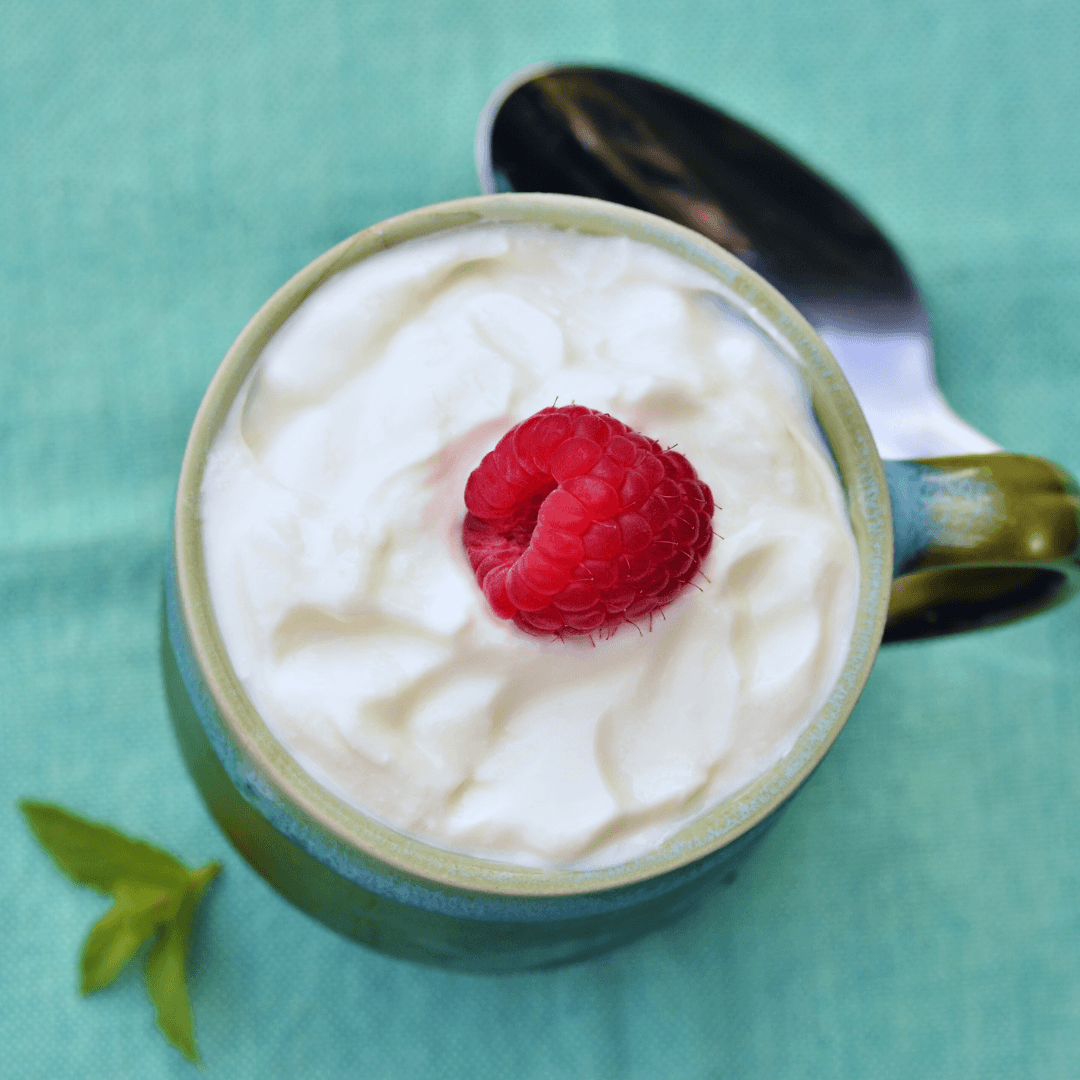

5. Fortified Plant-Based Yogurts
Fortified plant-based yogurts provide a convenient and delicious way for individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets to incorporate vitamin B12 into their daily meals.
Varieties such as soy yogurt and almond yogurt are often fortified with vitamin B12, offering a reliable source of this essential nutrient.
It's important to verify on the label whether plant-based yogurts include additional vitamin B12 when choosing.
Customers can choose their dietary intake with knowledge because this information is usually clearly visible on the box.
Plant-based yogurts with added nutrients can be consumed as a healthy snack or mixed into smoothie bowls, parfaits, and desserts.
By including fortified plant-based yogurts in their diet, individuals can ensure they meet their vitamin B12 needs while enjoying yogurt's creamy texture and tangy flavour without compromising their dietary preferences.

6. Fortified Nutritional Beverages
Nonmeat sources of vitamin B12, such as fortified nutritional beverages like protein shakes and meal replacement shakes, offer individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets a comprehensive source of essential nutrients, including added vitamin B12, ensuring their dietary needs are met.
These beverages are often enriched with added nutrients, including vitamin B12, to provide a comprehensive source of essential vitamins and minerals.
When selecting nutritional beverages, it's essential to check the label to ensure the product contains added vitamin B12.
Look for labels indicating the beverage is “fortified” or “enriched” with vitamin B12, which signifies that the nutrient has been deliberately added to the product.
Fortified nutritional beverages can be consumed as a quick and convenient meal replacement or post-workout recovery drink.
They include a combination of protein, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals to promote general health and well-being.
By incorporating fortified nutritional beverages into their diet, individuals can easily meet their vitamin B12 needs while enjoying the convenience and versatility of these on-the-go options.
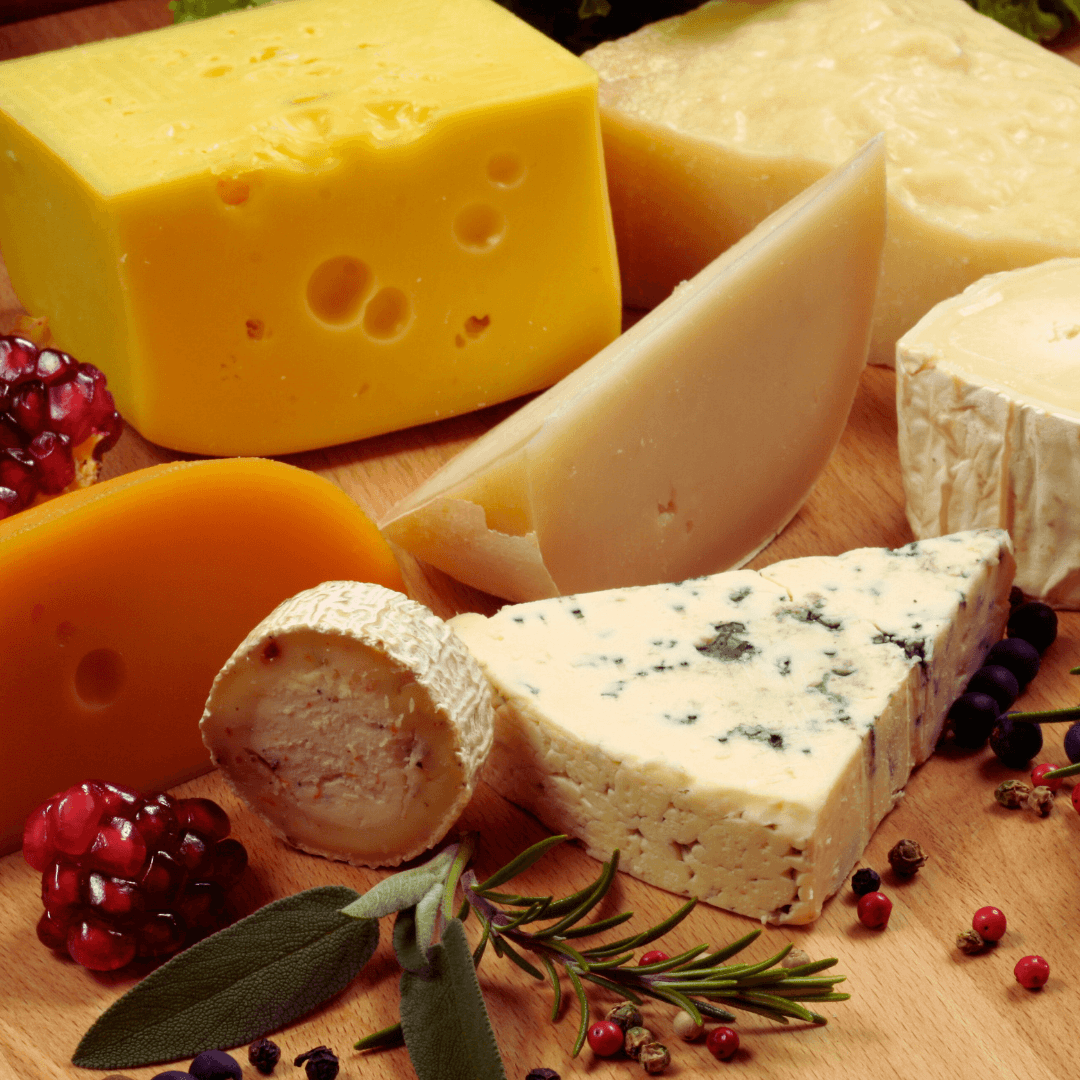

7. Fortified Plant-Based Cheeses
Vegans and vegetarians can ensure they get enough vitamin B12 in their diets by eating fortified plant-based cheeses, which are tasty and easy to make.
These plant-based cheeses made from nuts, seeds, or soy are fortified with extra B12 to give an extra dose of this vital vitamin.
When perusing your selections, it's important to verify on the label whether a plant-based cheese choice includes additional vitamin B12.
Examine the labels for any indications of intentional supplementation, such as “fortified” with vitamin B12.
Fortified plant-based cheeses come in various flavours and textures, from creamy cashew-based spreads to tangy almond milk-based blocks, offering a versatile option for cheese lovers.
Whether enjoyed sliced on crackers, melted over pizza, or crumbled onto salads, fortified plant-based cheeses add flavour to any meal while ensuring individuals maintain optimal vitamin B12 levels without relying on animal-derived products.
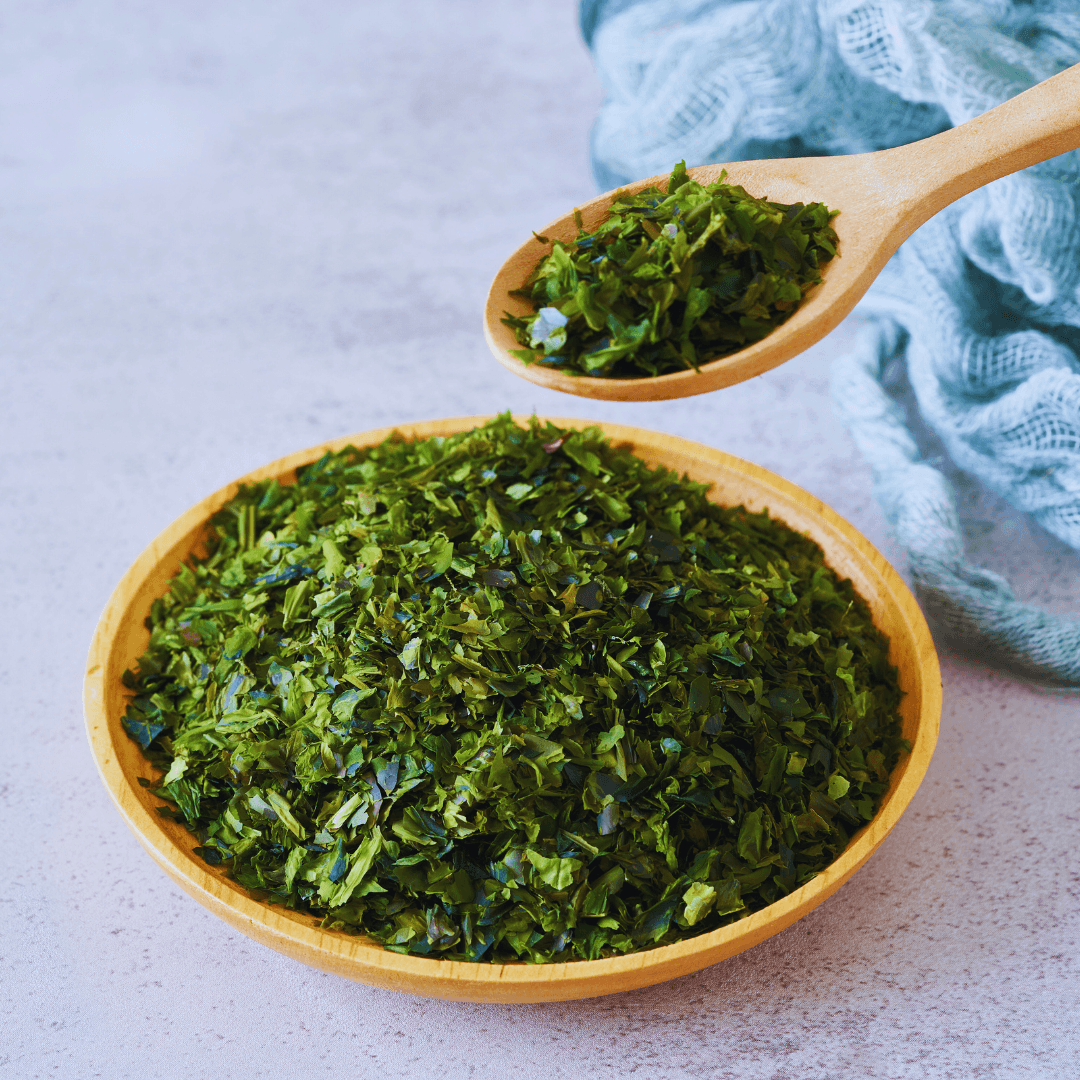

8. Algae And Seaweed
Certain algae and seaweed serve as nonmeat sources of vitamin B12, offering a natural alternative for individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets, although their levels may not always meet daily requirements.
Certain types of algae, including nori, spirulina, and chlorella, contain small amounts of vitamin B12. However, these sources may need to provide higher levels to meet daily requirements.
Seaweed varieties such as kelp and wakame may contain some vitamin B12, but the concentration can vary depending on growing conditions and processing methods.
Even though algae and seaweed might increase your consumption of vitamin B12 overall, they shouldn't be your only source of the vitamin, especially if you're a committed vegetarian or vegan.
However, incorporating algae and seaweed into meals, such as sushi rolls, salads, and soups, can add nutritional diversity and flavour while offering a modest boost of vitamin B12 and other essential nutrients.
9. Fortified Plant-Based Protein Bars
Fortified plant-based protein bars provide a convenient and on-the-go option for individuals seeking to increase their intake of vitamin B12, particularly those following vegetarian or vegan diets.
These protein bars are specially formulated with added vitamin B12 to offer an additional source of this essential nutrient.
When selecting plant-based protein bars, it's important to check the label to confirm whether the product contains added vitamin B12.
Look for labels indicating that the protein bar is “fortified” with vitamin B12, which signifies intentional supplementation.
Fortified plant-based protein bars come in various flavours and textures, from nutty and crunchy to sweet and chewy, catering to different tastes and preferences.
Whether enjoyed as a pre-workout snack, a post-workout recovery fuel, or a convenient meal replacement, fortified plant-based protein bars provide a satisfying and nutritious option.
At the same time, ensuring individuals meet their vitamin B12 needs without relying on animal-derived products.
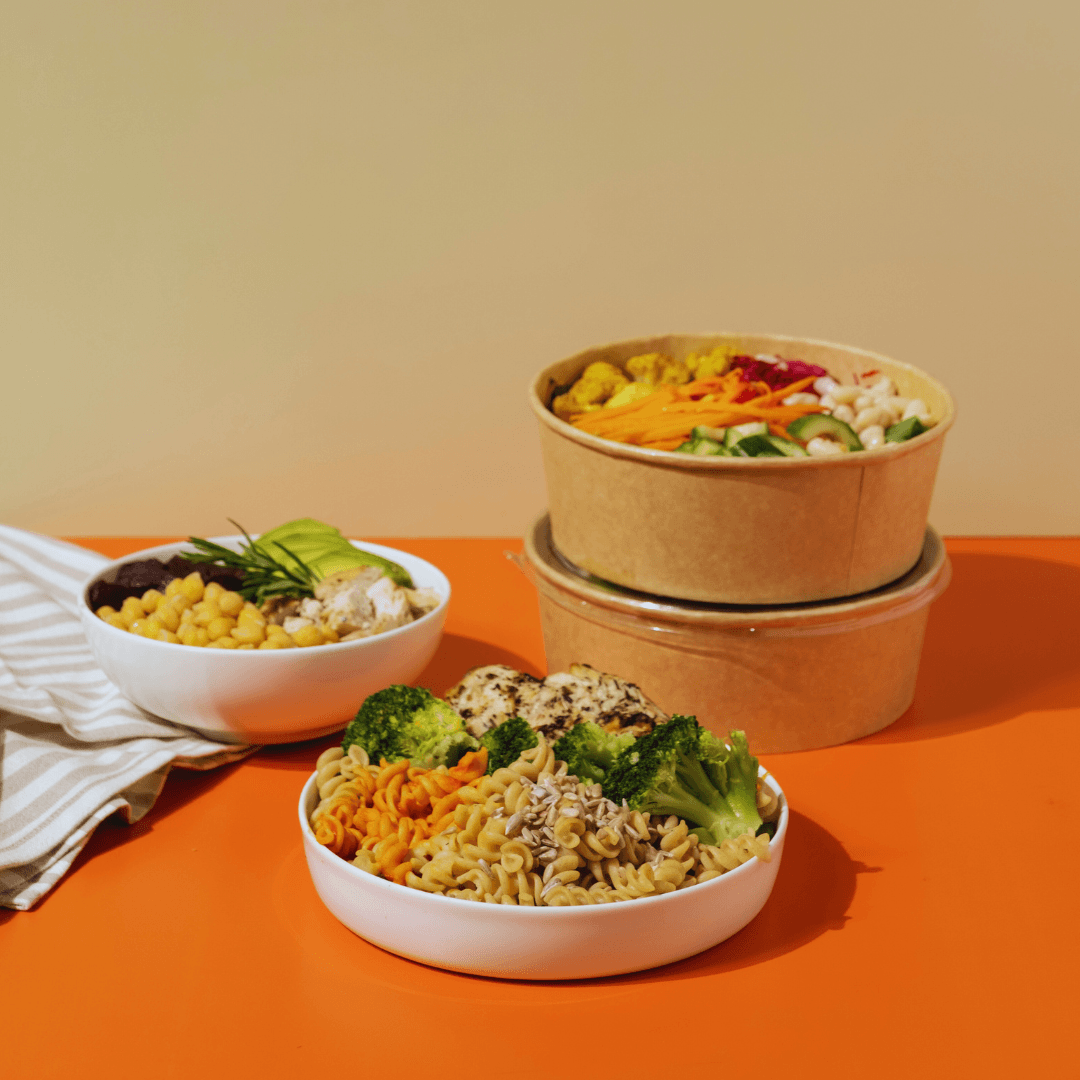

10. Fortified Plant-Based Ready Meals
Fortified plant-based ready meals offer a convenient and hassle-free option for individuals looking to incorporate vitamin B12 into their diet, particularly those following vegetarian or vegan lifestyles.
These meals, available in various formats, such as frozen dinners and microwaveable options, are specially fortified with added vitamin B12 to provide an extra source of this essential nutrient.
Verifying the label while choosing plant-based ready meals is crucial to ensure that extra vitamin B12 is included.
Look for labels indicating that the meal is “fortified” or “enriched” with vitamin B12, which indicates intentional supplementation.
Fortified plant-based ready meals come in diverse cuisines and flavours, from hearty pasta dishes to flavorful stir-fries, offering something for every palate.
Whether enjoyed as a quick lunch at work or a convenient dinner option after a busy day, fortified plant-based ready meals provide a tasty and nutritious way to meet vitamin B12 needs without sacrificing convenience or flavour.
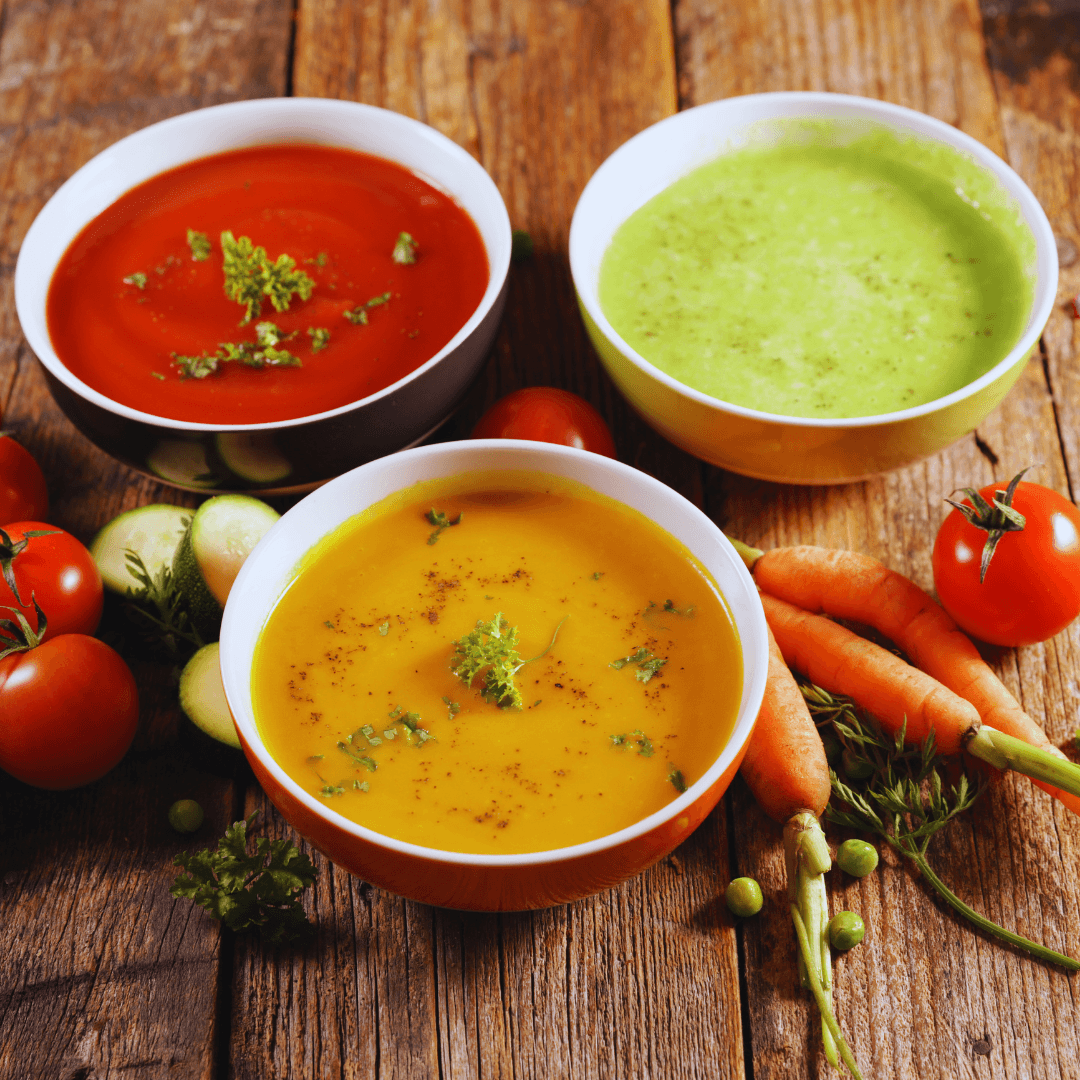

11. Fortified Plant-Based Soups
Fortified plant-based soups serve as non-meat sources of vitamin B12, offering individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets a convenient way to ensure their dietary intake meets essential nutrient requirements.
To offer an extra supply of this vital ingredient, these soups—which include variations including lentil, vegetable, and tomato soup—may be fortified with extra vitamin B12.
It's important to verify on the label whether plant-based soups have additional vitamin B12. Look for labels indicating that the soup is “fortified” with vitamin B12, which signifies intentional supplementation.
Fortified plant-based soups come in various flavours and styles, from hearty and comforting to light and refreshing, catering to various preferences and dietary needs.
Whether enjoyed as a warming meal on a chilly day or as a light lunch option, fortified plant-based soups offer a convenient and delicious way to meet vitamin B12 needs while enjoying the wholesome goodness of plant-based ingredients.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the availability of non-meat sources of vitamin B12 offers many options for individuals seeking to maintain adequate levels of this essential nutrient, particularly those following vegetarian or vegan diets.
The availability of nonmeat sources of vitamin B12 provides diverse options for individuals, particularly those on vegetarian or vegan diets, ensuring they can maintain adequate nutrient levels while enjoying a varied and satisfying diet.
Plant-based ready meals and soups offer further convenience, allowing individuals to enjoy flavorful and nutritious meals without compromising their dietary preferences.
By carefully reading labels and choosing fortified products, individuals can ensure they meet their vitamin B12 needs while enjoying a diverse and satisfying diet.
But it's important to remember that while vitamin B12 from non-meat sources can increase consumption overall, supplementation might be required for some people, particularly those with certain dietary limitations or health issues.
Incorporating various non-meat sources of vitamin B12 into one's diet can support overall health and well-being, making it easier than ever to thrive on a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle.
I trust you enjoyed this article about the Best Nonmeat Sources Of Vitamin B12. Please stay tuned for more blog posts soon. Take care!
JeannetteZ
>>>Please click here to read my Vegan Travel Guides To World Destinations<<<
>>>Want To Learn How To Create Delicious, Cruelty-Free, Healthy AND 100% Vegan Meals? Try These Awesome Vegan Cooking Courses With A Free 7-DAY MEMBERSHIP<<<
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I would love to hear from you. Please leave me your questions, experiences, and remarks about the article on the Best Nonmeat Sources Of Vitamin B12 in the comments section below. You can also email me at Jeannette@LivingTheVeganLifestyle.org.
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. I earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate and other affiliate programs. Please read my full disclosure.
Here are links to some of my favourite articles:
Best Vegan Barbecue Foods For Your Next Cookout
Animal Rights vs Animal Welfare
Environmental Benefits Of A Plant-Based Diet