Do Vegans Eat Honey

Do Vegans Eat Honey?
Whether vegans consume honey sparks a significant debate within the vegan community and beyond.
As a dietary and lifestyle choice that avoids all animal-derived products, veganism raises questions about the ethical and practical considerations surrounding honey consumption.
While some vegans embrace honey as a natural sweetener with health benefits, others abstain from it due to concerns about beekeeping practices and the ethical implications of exploiting bees for their labour.
This article explores the complexities of the honey debate within the vegan movement, shedding light on different perspectives and the reasons behind each stance.
By delving into the various aspects of honey production, its nutritional value, and the moral dilemmas vegans face, we can better understand why this seemingly innocent bee-made product remains a contentious topic among those who follow a plant-based lifestyle. So, let’s get started !!
What Exactly is Honey?
Honey is a natural and complex substance created by honeybees through a remarkable collection, transformation, and storage process.
The journey of honey begins with foraging worker bees who visit flowers and collect nectar, a sugary liquid secreted by the glands of plants.
These bees use their long, tube-like tongues to suck the nectar from flowers, storing it in a specialized honey stomach.
Back at the hive, the forager bees transfer the nectar to receiver bees, which then ingest and regurgitate it multiple times.
This process introduces enzymes into the nectar, breaking the complex sugars into simpler forms and adding the bees' enzymes for further transformation. The nectar is then deposited into wax cells within the hive's honeycomb.
To further reduce the water content and increase the viscosity, worker bees fan their wings over the open honeycomb cells, creating an airflow that helps evaporate excess water from the nectar.
When the moisture content reaches around 18%, the bees seal the cells with wax to preserve the concentrated substance.
The enzymes introduced by the bees and the evaporation process are critical to honey's unique composition and characteristics.
Honey is composed primarily of fructose and glucose, simple sugars that provide its sweet taste and energy content.
The enzymes also give honey its natural acidity and contribute to its antimicrobial properties.
The colour, flavour, and aroma of honey vary depending on the types of flowers from which the bees collect nectar.
Different flowers impart distinct pollen and nectar profiles to the honey, resulting in a wide range of honey varieties, from light and mild to dark and robust.
Humans have valued honey for centuries for its culinary uses, natural sweetness, and potential health benefits.
It's commonly used as a sweetener in beverages, baked goods, and cooking. Additionally, honey has been a part of traditional medicine in various cultures, claiming antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and wound-healing properties.
However, it's important to note that honey production involves the exploitation of bees, and ethical concerns arise from practices such as hive management and the potential disruption of bee colonies.
This has led to debates about the ethics of consuming honey, particularly in the context of veganism.
As such, individuals seeking honey alternatives often turn to plant-based sweeteners like maple syrup, agave nectar, or date syrup.
Do Vegans Eat Honey?
Whether vegans consume honey is a topic of debate within the vegan community. Generally, many vegans avoid honey for ethical and environmental reasons.
Honey production involves the exploitation of bees, which can include practices such as clipping the wings of queen bees to prevent swarming, replacing honey with sugar water, and even killing entire colonies during harvesting.
These practices are seen as harmful to bee populations and disrupt the natural behaviours of these important pollinators.
Furthermore, vegans often consider the commercial beekeeping industry exploitative of bees and their labour, as it involves manipulating and profiting from their work without properly caring for their well-being.
Advocates for ethical veganism argue that respecting the autonomy and welfare of all sentient beings, including insects, aligns with the core principles of veganism.
However, some vegans may choose to consume honey under specific circumstances. Certain individuals follow a “bee-friendly” approach, where they seek out honey from local, small-scale beekeepers who prioritize the well-being of their bees and follow more natural and sustainable practices.
These beekeepers may refrain from using harmful treatments, such as pesticides, and prioritize the health and vitality of their colonies.
Ultimately, choosing to consume honey as a vegan is personal, and opinions vary within the vegan community.
While some vegans strictly avoid honey due to the ethical concerns surrounding beekeeping practices, others may make exceptions based on their beliefs, values, and individual assessments of beekeeping operations.
Individuals must educate themselves about the beekeeping industry and make informed choices that align with their vegan principles and ethical considerations.
For those who prefer to avoid honey altogether, there are a variety of plant-based alternatives available, such as maple syrup, agave nectar, date syrup, and various other sweeteners that do not involve the exploitation of animals.
Nutritional Value Of Honey
The nutritional value of honey has long been appreciated for its richness in natural sugars, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Honey contains various sugars, primarily fructose and glucose, which provide a quick and natural energy source.
It also boasts an array of essential vitamins and minerals, including B vitamins, calcium, iron, magnesium, and potassium.
Also, honey is a source of antioxidants, such as phenolic compounds, which can help combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
Some studies have suggested that honey may have antibacterial and wound-healing properties, making it a traditional remedy for minor ailments.
However, while honey does offer potential health benefits, its consumption poses ethical concerns for vegans due to the methods of honey production and their impact on bee colonies.
The honey extraction process from hives involves removing the bees' hard-earned food source, which raises questions about these vital pollinators' well-being and natural behaviour.
Vegans who choose to forgo honey opt for other plant-based sweeteners and food sources to meet their nutritional needs while aligning with their ethical principles of avoiding animal exploitation.
Vegan Sweeteners To Use Instead Of Honey
Several vegan-friendly sweeteners serve as excellent alternatives to honey, offering a wide range of flavours and nutritional benefits. Here are some details about these plant-based sweeteners:
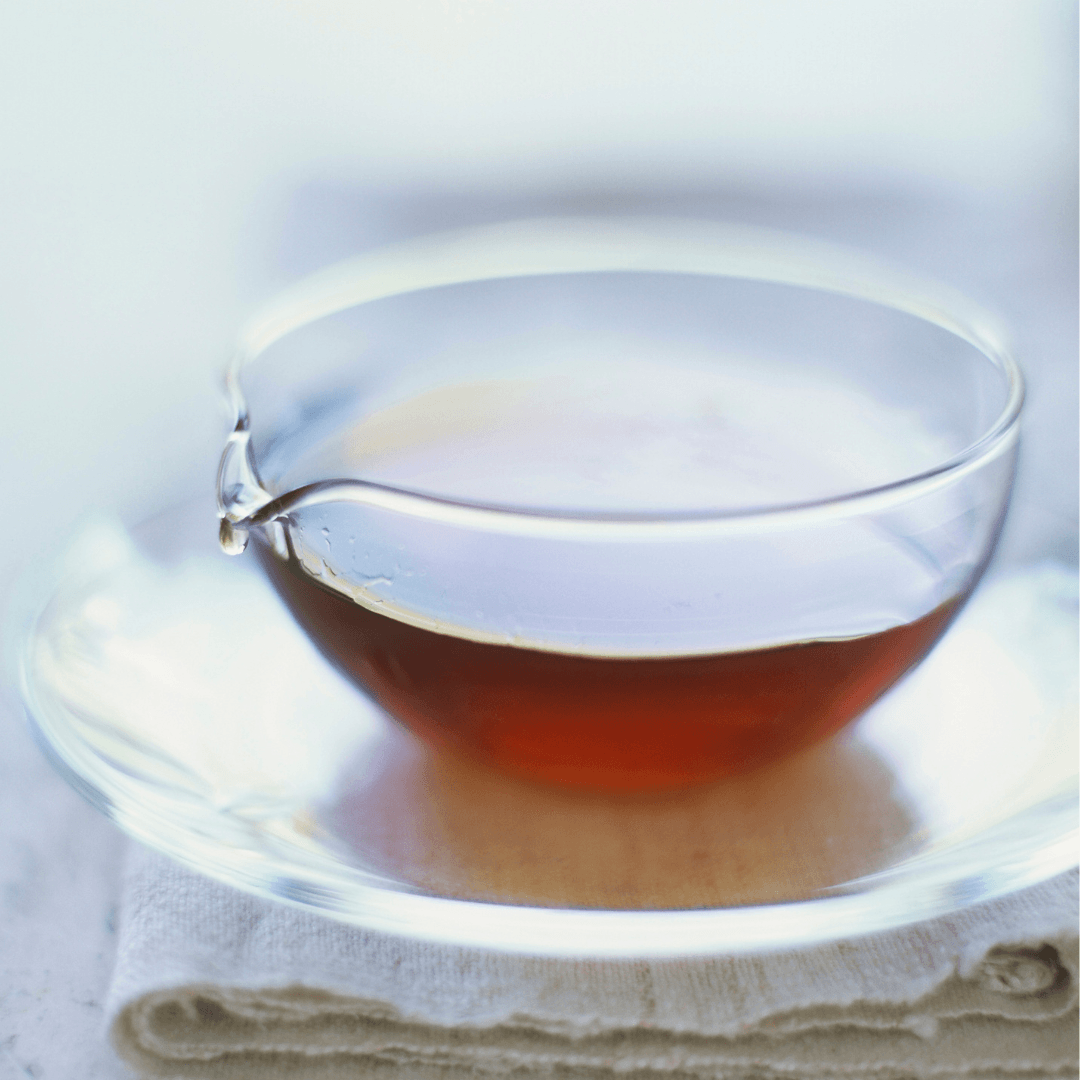

1. Agave Nectar
Agave nectar, derived from the agave plant, is a versatile and widely recognized vegan sweetener that has gained popularity for its mild flavour and low glycemic index.
This natural syrup offers a sweetness comparable to honey but with a unique taste profile. It is often used as a one-to-one replacement for traditional sweeteners in various culinary applications.
Because agave nectar is sweeter than honey, a smaller quantity is usually sufficient to achieve the desired level of sweetness in recipes, making it a calorie-efficient option.
Its ability to dissolve quickly in cold and hot liquids and its smooth consistency makes it a convenient choice for sweetening beverages, such as teas and smoothies.
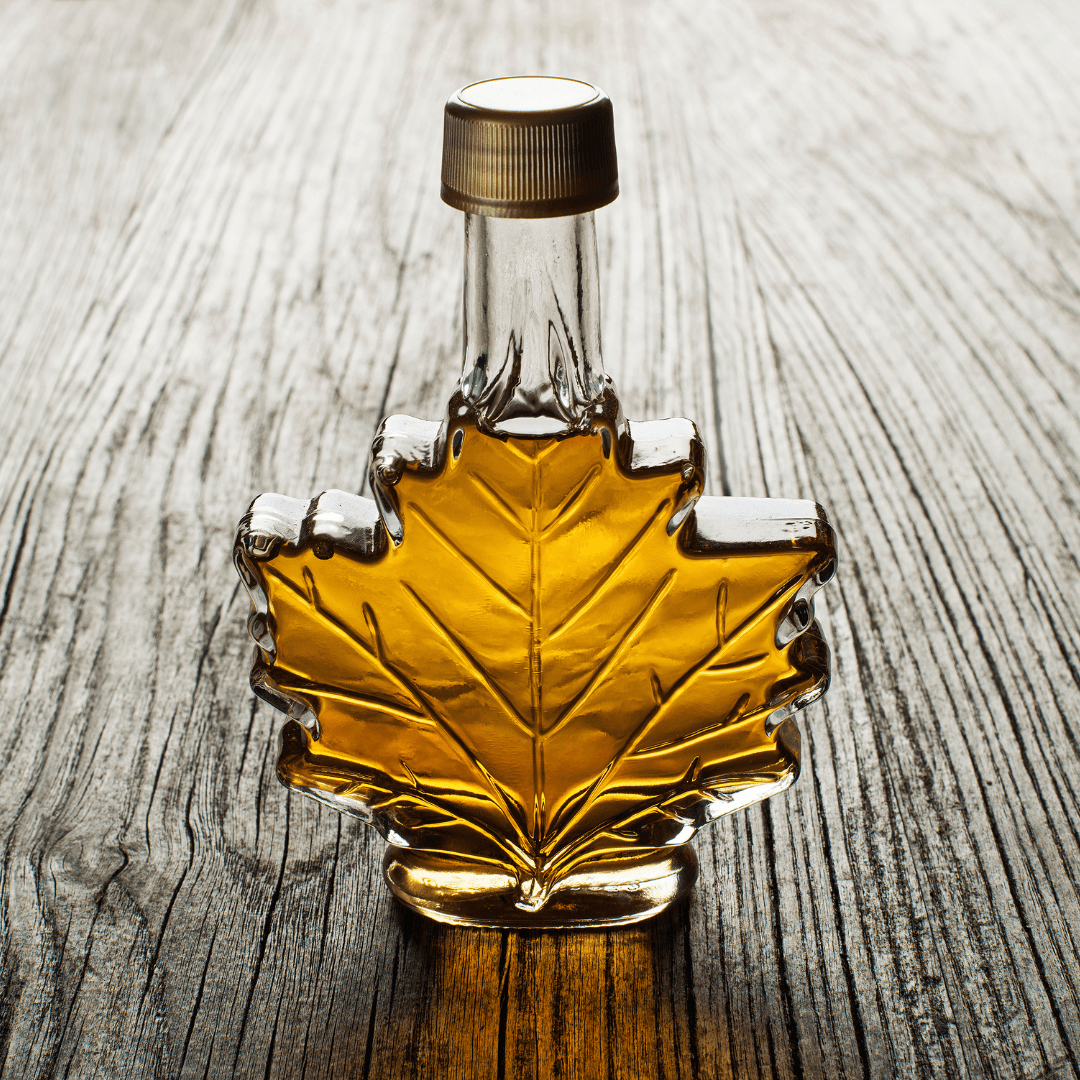

2. Maple Syrup
Maple syrup, derived from the sap of maple trees, is a beloved vegan sweetener renowned for its distinctive and indulgent flavour profile.
This natural syrup offers a rich and complex taste that adds depth to various dishes. Maple syrup has become synonymous with breakfast classics like pancakes and waffles, making it a popular choice to drizzle over these morning staples.
It's also commonly used to enhance the sweetness of desserts, such as ice creams, cakes, and pastries, and to create flavorful glazes for savoury dishes.
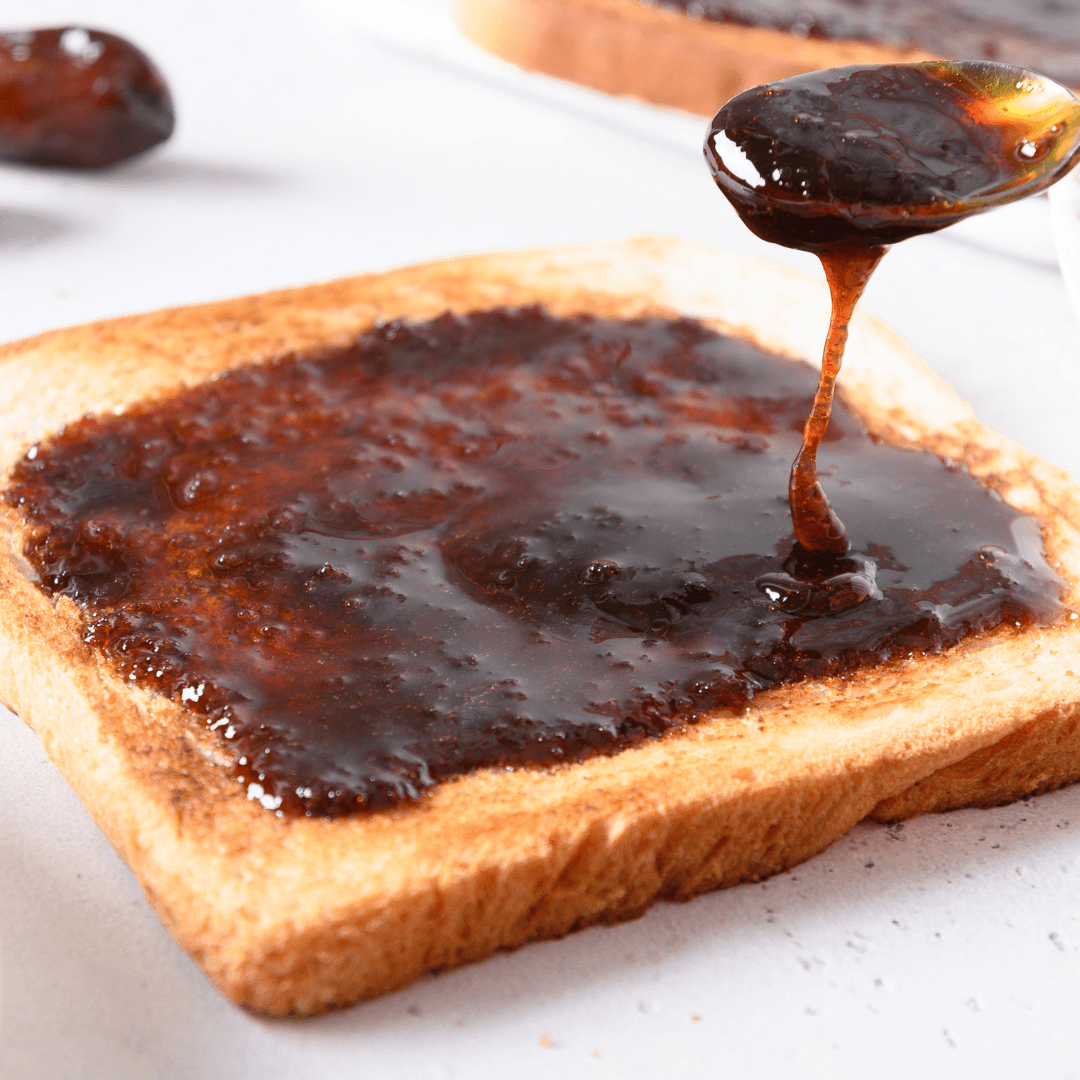

3. Date Syrup
Date syrup, concocted by blending dates with water, produces a luscious and naturally sweet liquid with a distinct caramel-like flavour.
Not only does date syrup offer a delightful taste, but it also brings nutritional value. Laden with natural sugars, it is an energy source, boasting essential nutrients such as dietary fiber, iron, and potassium.
This combination of sweetness and nutrients makes it an appealing vegan sweetener option. Date syrup's velvety texture and rich taste make it an exceptional addition to various culinary creations.
It effortlessly lends itself to beverages like smoothies, providing a natural sweetening element, and it can be employed in baking to impart its unique caramel essence to cookies, cakes, and muffins.
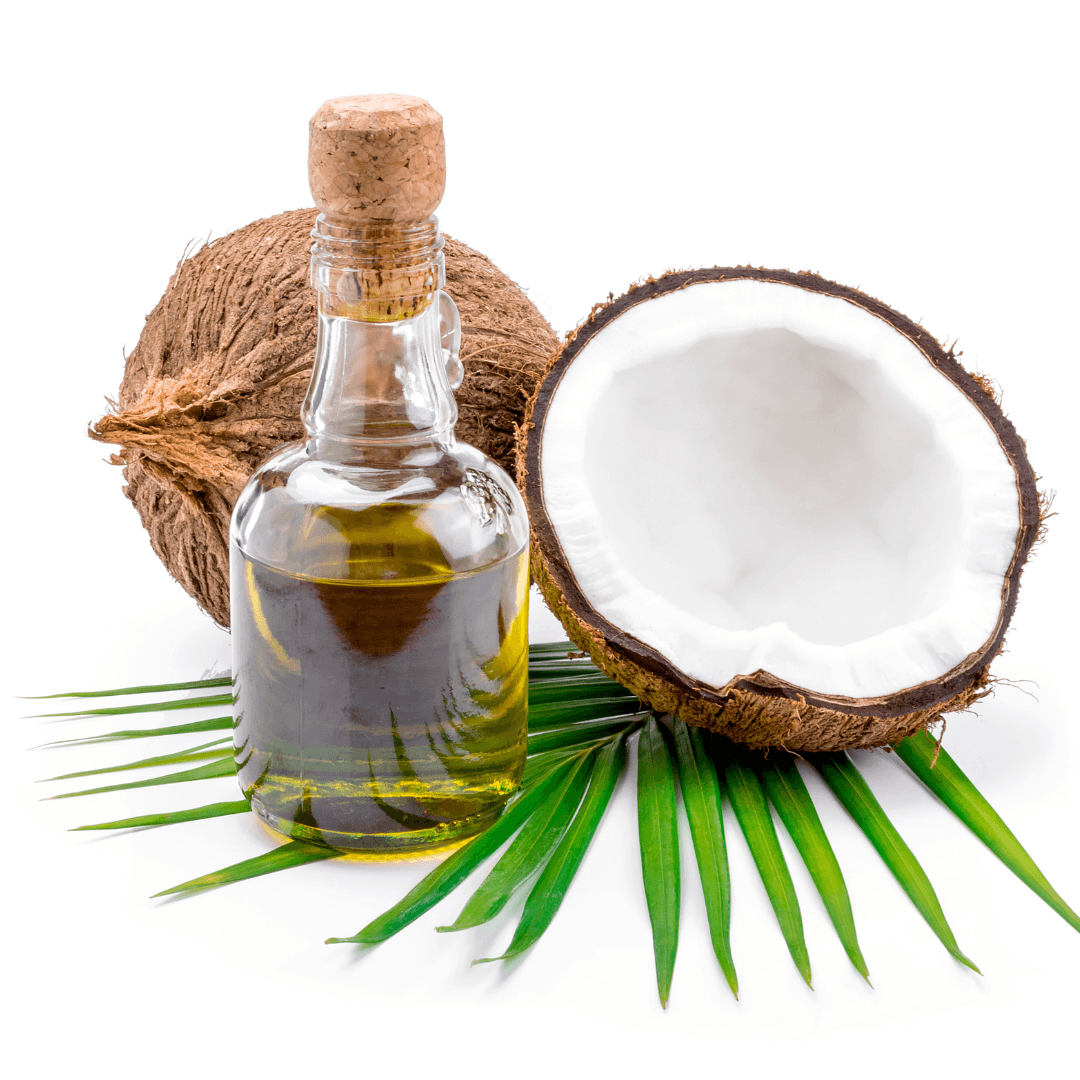

4. Coconut Nectar
Coconut nectar, obtained from the blossoms of coconut trees, offers a uniquely delicate caramel flavour that sets it apart as a vegan sweetener.
Notably, its low glycemic index makes it a favourable choice for those seeking to manage blood sugar levels.
Besides its pleasant taste, coconut nectar brings a wealth of vitamins and minerals, including B vitamins and zinc, contributing to its appeal as a health-conscious alternative.
This all-natural nectar finds its place in various culinary applications, stretching from desserts like cakes, cookies, and puddings, where it imparts its mild sweetness and subtle caramel undertones, to the world of savoury creations.
It can be seamlessly integrated into dressings, marinades, and sauces to balance flavours and add a hint of sweetness.
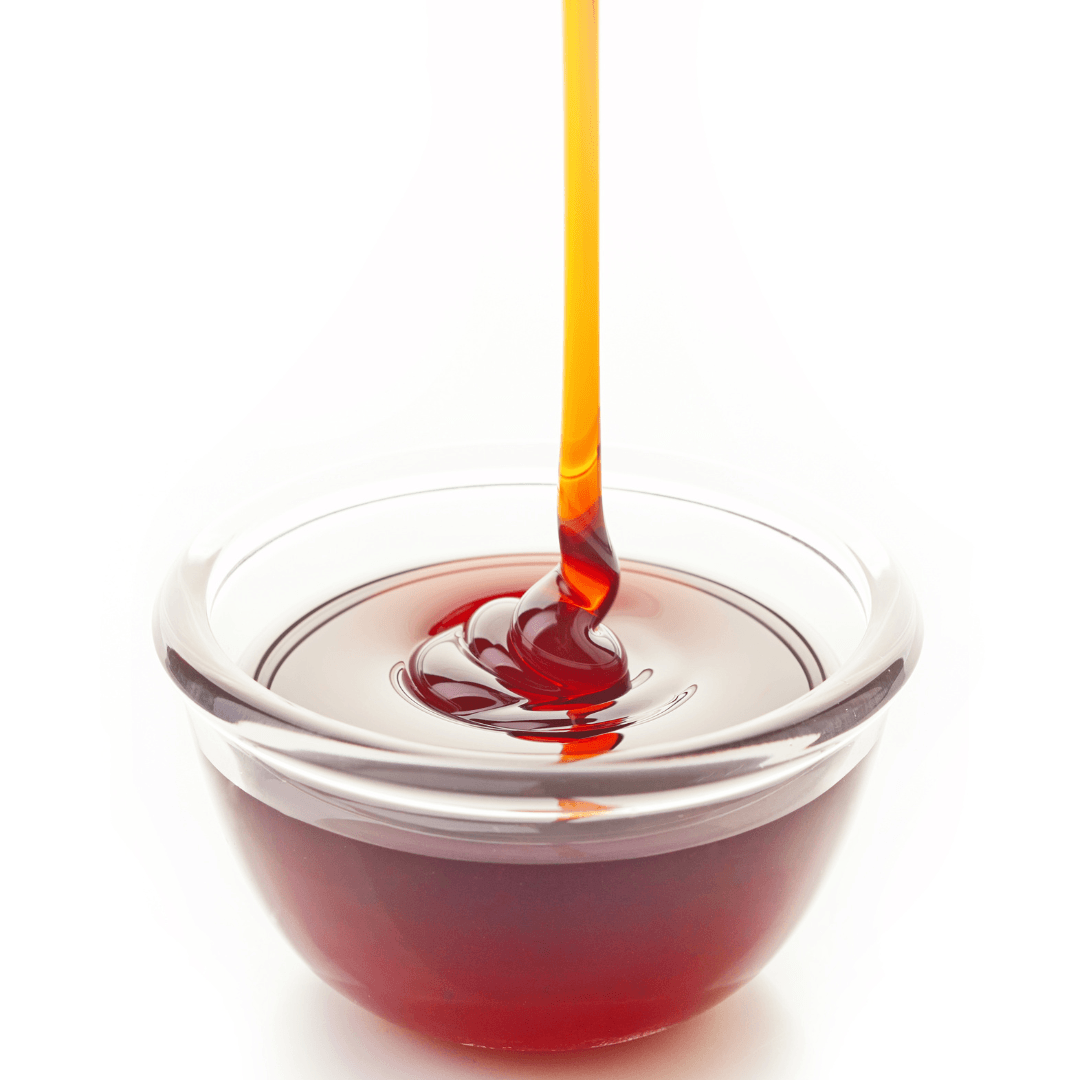

5. Brown Rice Syrup
Brown rice syrup, a product of fermented cooked brown rice, offers a subtle and mild sweetness that distinguishes it as a suitable vegan substitute for honey.
Its flavour profile is less intense than other sweeteners, making it an adaptable choice for various culinary applications.
This syrup finds its place in baking, contributing a gentle sweetness without overwhelming the overall taste.
Its versatility also extends to beverages, functioning as a mindful and health-conscious sweetener option for drinks like teas, coffees, or smoothies.
Homemade energy and granola bars can also benefit from their natural sweetness, enhancing taste and nutritional value.
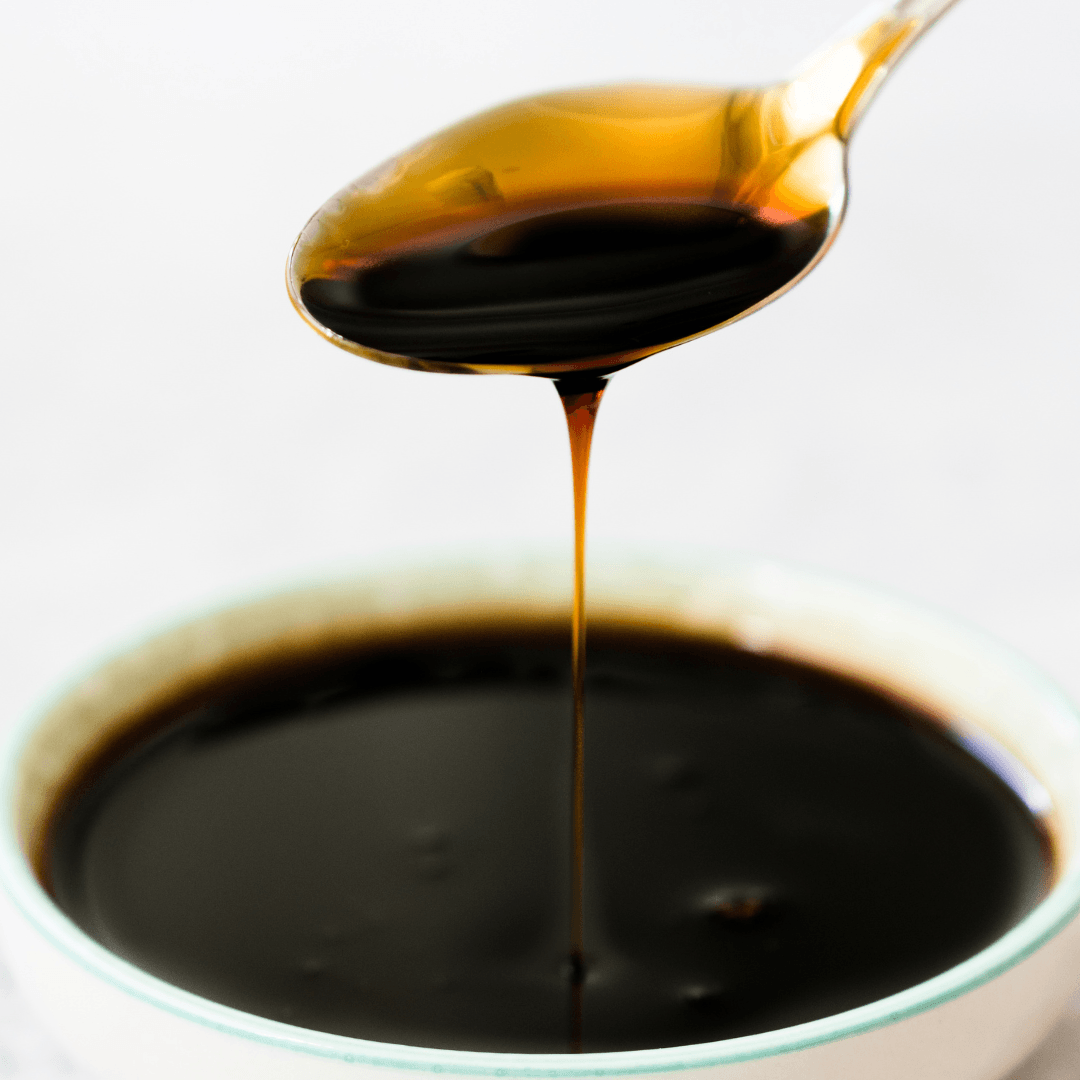

6. Molasses
A rich and distinctive sweetener is a byproduct derived from sugar cane or sugar beet processing.
With its robust and bittersweet flavour, molasses adds depth and complexity to various dishes and recipes. Its dark and dense nature makes it an ideal candidate for baking, contributing a unique taste to cookies, cakes, and bread.
Additionally, molasses is found in culinary creations like barbecue sauces, whose intense flavour can lend a smoky and tangy profile.
Apart from its delightful taste, molasses is a valuable source of essential minerals, including iron, calcium, and magnesium, enhancing its nutritional profile.
Due to its distinct attributes and versatility, molasses is a favoured vegan alternative to honey, offering a depth of flavour that can elevate sweet and savoury dishes.
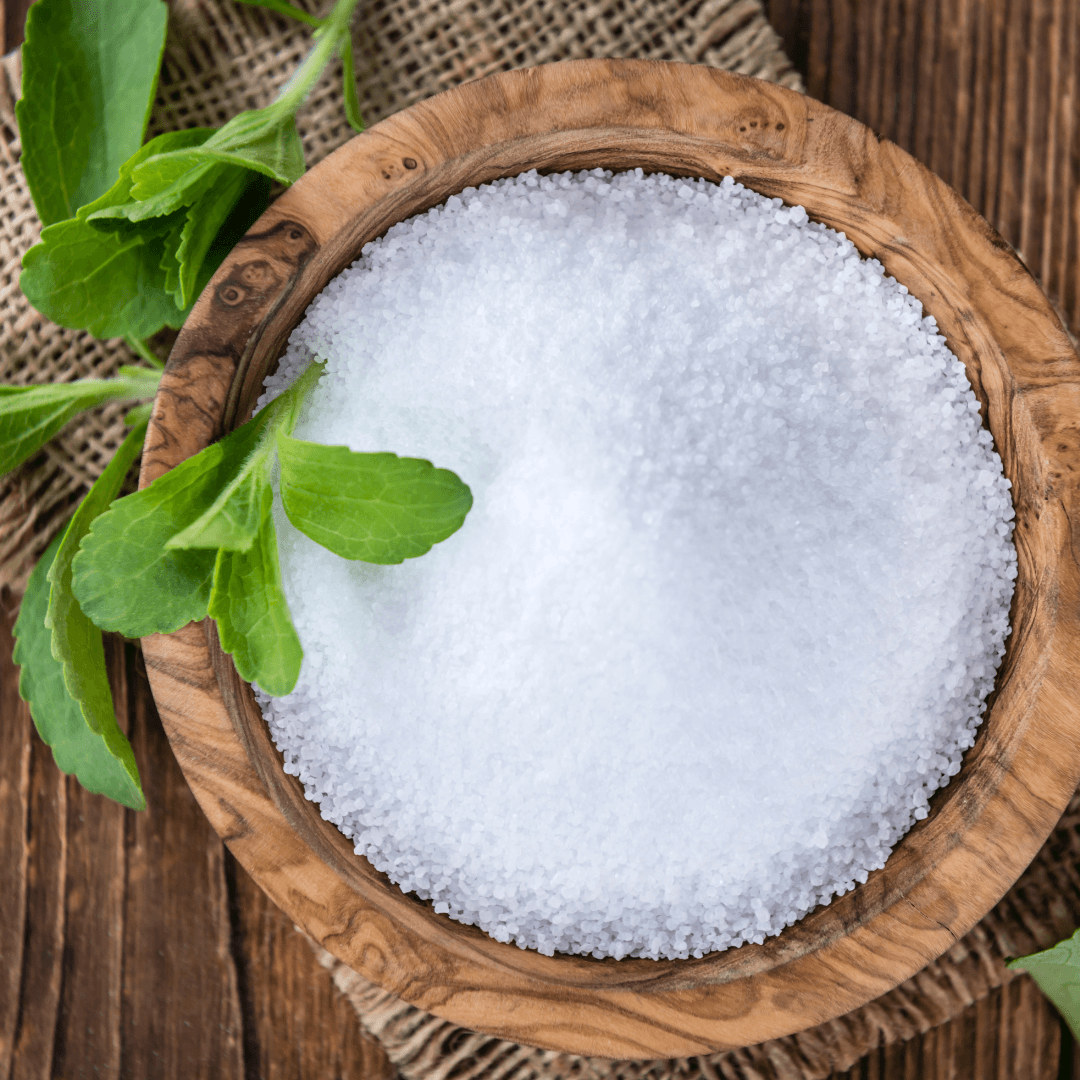

7. Stevia
Stevia, a natural sweetener derived from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant, is a calorie-free alternative that boasts exceptional sweetness without the caloric impact of sugar.
Stevia's sweetness originates from its natural compounds, steviol glycosides, which are often sweeter than traditional sugar.
This potency allows only small quantities to achieve desired sweetness levels in various culinary applications, from hot beverages to baked goods.
Stevia is available in various forms, including liquid, powder, and granulated, making it versatile and adaptable to different cooking and baking needs.
With its negligible impact on blood sugar levels, stevia appeals to individuals seeking to manage their sugar intake or maintain a low-carb lifestyle.
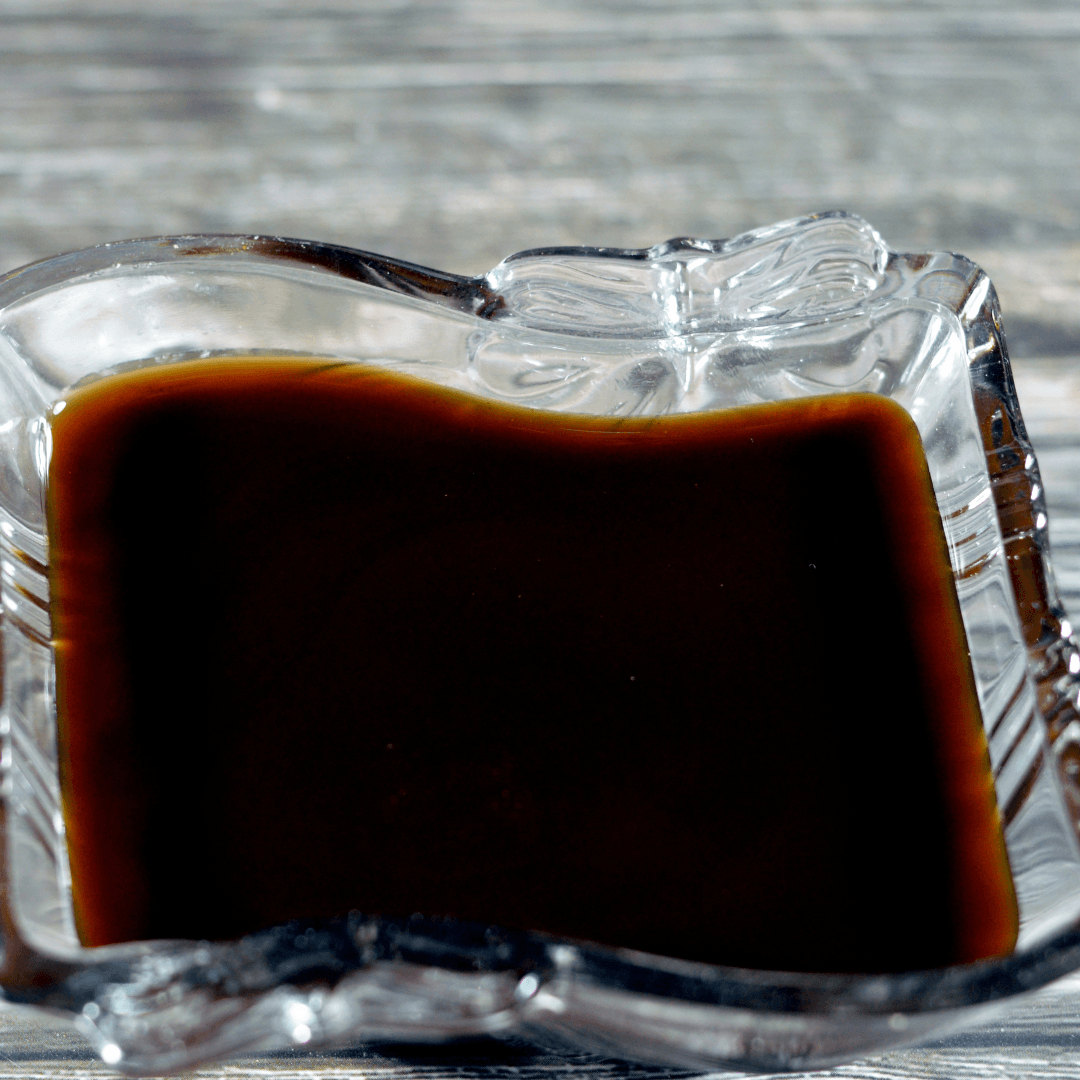

8. Blackstrap Molasses
Blackstrap molasses is a concentrated form that offers a wealth of nutrients, including notable amounts of iron, calcium, and magnesium.
Derived from the third boiling of sugar cane or sugar beet syrup, blackstrap molasses carries a robust and distinct flavour profile, making it a popular choice for adding depth and complexity to various dishes.
Beyond its unique taste, this type of molasses stands out for its impressive nutritional content, making it a sought-after ingredient in recipes where both flavour and health benefits are desired.
Due to its iron content, blackstrap molasses is often recommended as a natural dietary source of this essential mineral, particularly beneficial for individuals seeking to address or prevent iron deficiency.
Blackstrap molasses finds its place in sweet and savoury dishes, adding a rich and earthy undertone while supplying a range of essential minerals that enhance its value as a versatile and healthful ingredient.
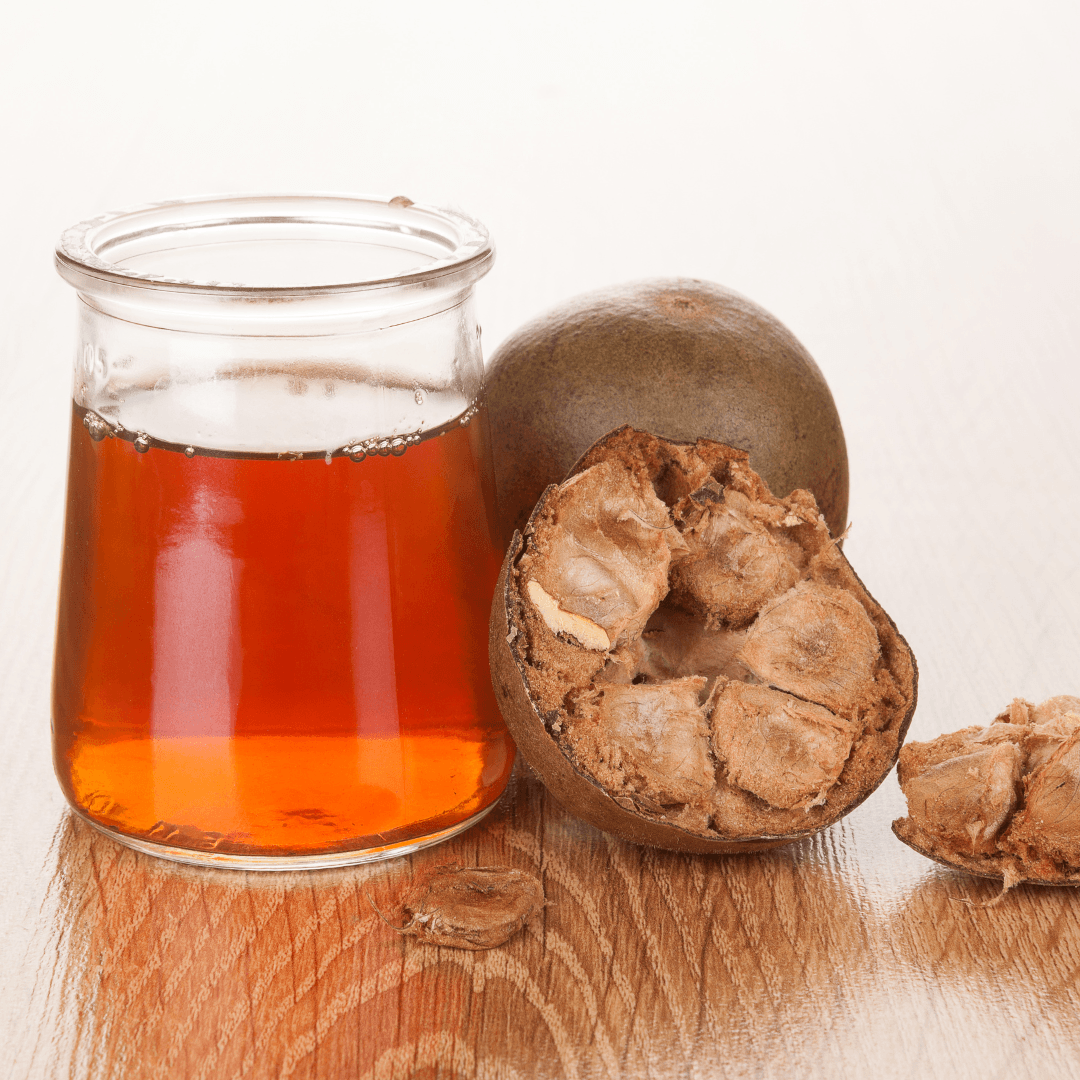

9. Monk Fruit Sweetener
Monk fruit sweetener, derived from monk fruit extract, is a natural sugar alternative that offers sweetness without the caloric content or significant impact on blood sugar levels.
With its impressive ability to provide a sweet taste without the metabolic consequences of traditional sugar, monk fruit sweetener has gained popularity as a diabetic-friendly and low-calorie option.
The unique compounds found in monk fruit, called mogrosides, are responsible for its intense sweetness while containing negligible calories.
This characteristic makes monk fruit sweetener appealing to those seeking to manage their weight or blood sugar levels.
Monk fruit sweetener can be incorporated seamlessly into various recipes as a substitute for traditional sugar in baked goods, beverages, and other culinary creations.
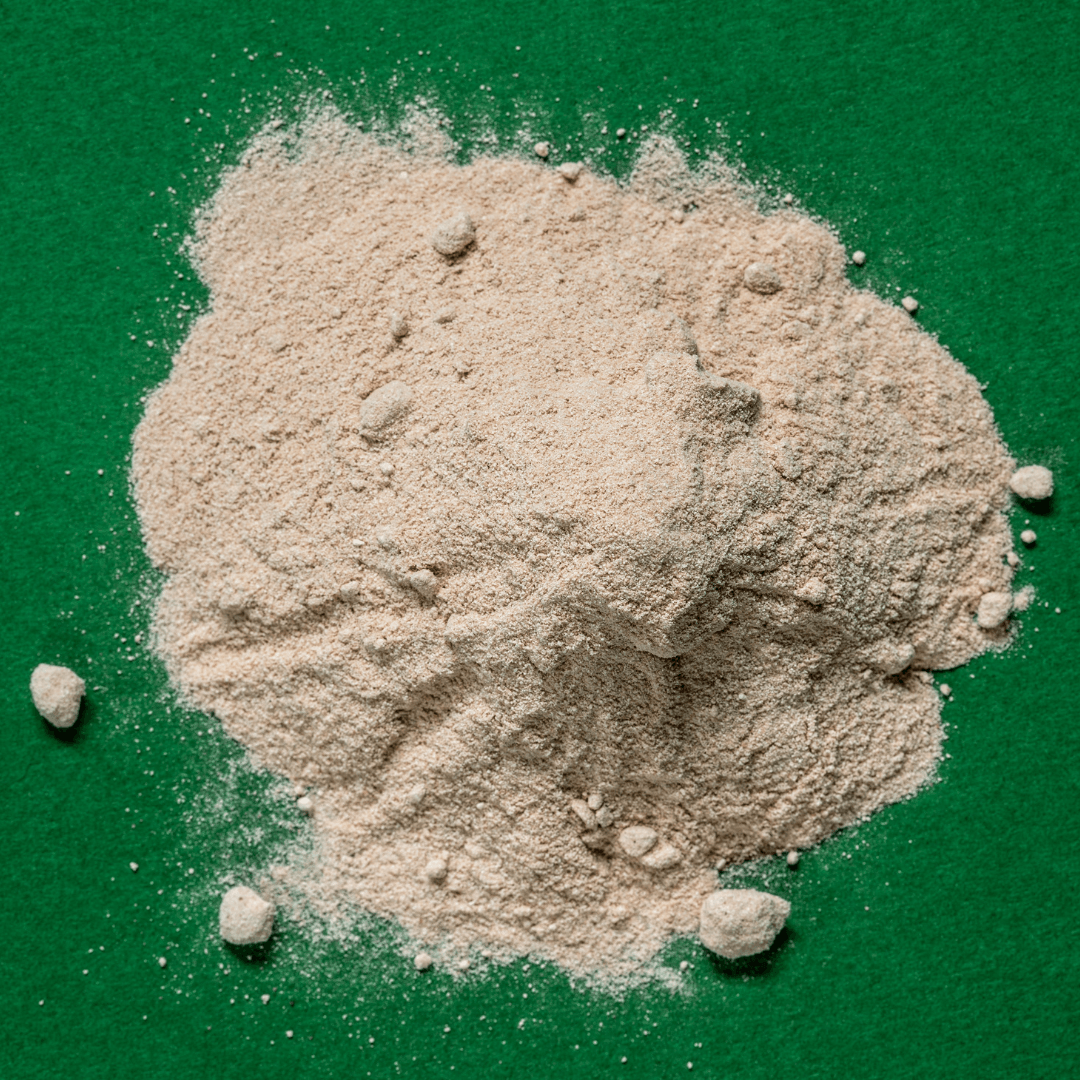

10. Lucuma Powder
Lucuma powder, derived from the tropical fruit native to South America, offers a distinctive and enticing natural sweetness to various culinary creations.
With flavour notes that evoke the delightful combination of maple and caramel, lucuma powder has found its place as a unique and flavorful sweetener in the world of plant-based alternatives.
Its versatility is showcased in various dishes, including smoothies, desserts, and baked goods, where it imparts a rich and indulgent taste.
Beyond its delectable flavour, lucuma powder also brings a nutritional punch, containing essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that contribute to overall well-being.
This exotic and naturally sweet powder has become a cherished ingredient for those seeking to infuse their creations with an enticing taste that pays homage to the flavours of South America while offering a wholesome and health-conscious choice.

11. Barley Malt Syrup
Barley malt syrup, crafted from sprouted barley grains, boasts a distinct malted flavour that adds a touch of complexity to culinary endeavours.
Frequently utilized in bread-making, this syrup enhances the depth of flavour and aids in achieving that coveted golden crust.
Beyond the world of baking, barley malt syrup serves as a versatile sweetener, seamlessly integrating into a range of recipes.
Its unique profile brings a nuanced sweetness, making it a valuable addition to sauces, dressings, and marinades.
With its natural sweetness and rich taste, barley malt syrup provides a healthier alternative to refined sugars in various dishes.
Its use aligns with those who appreciate its distinctive flavour and are committed to incorporating wholesome and natural ingredients into their gastronomic creations.
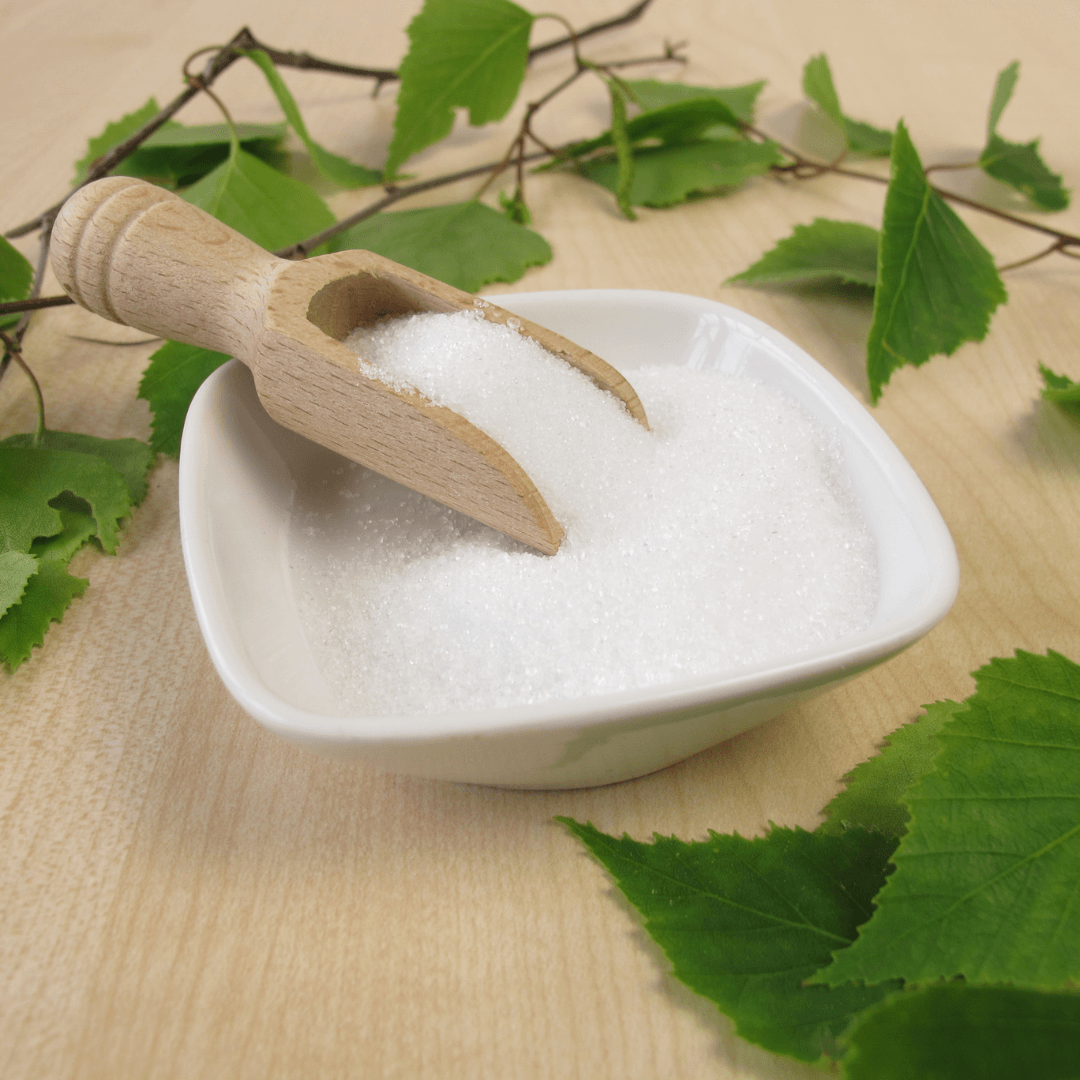

12. Birch Xylitol
Birch xylitol, a sugar alcohol sourced from birch trees, offers a sweetening solution that closely mimics the taste of sugar.
With its comparable sweetness, it seamlessly substitutes sugar in various recipes, enabling a simple one-to-one replacement.
Beyond its sweetening prowess, birch xylitol boasts a lower caloric content than traditional sugar, making it a preferred choice for those mindful of their calorie intake.
This natural alternative offers an appealing option for individuals seeking to reduce their sugar consumption while still enjoying the delightful sweetness in their favourite dishes.
Its versatility and ease of use render birch xylitol a desirable addition to the pantry of health-conscious and culinary-savvy individuals alike.
These vegan-friendly sweeteners offer a variety of tastes and nutritional profiles, providing excellent options for those who choose to avoid honey while still enjoying the pleasures of natural sweetness in their culinary creations.
Conclusion
Whether vegans eat honey remains a nuanced and debated topic within the vegan community.
While most vegans choose to avoid honey due to concerns about bee welfare and the potential exploitation of bees in honey production, diverse perspectives influence individual choices.
Some vegans may consume honey if they find ethical and sustainable sources, such as bee-friendly certified products or support for bee conservation efforts.
Others may opt for bee-free honey alternatives made from plant-based ingredients as a cruelty-free substitute.
Moreover, veganism's dynamic and evolving nature allows for constantly reevaluating ethical choices as individuals continually seek to align their values with their actions.
Ultimately, whether vegans choose to include or exclude honey from their diet, the ongoing discussion about honey highlights the importance of thoughtful consideration, compassion, and dedication to a lifestyle that strives to minimize harm to animals and promote a sustainable and ethical relationship with the environment.
I trust you enjoyed reading the article Do Vegans Eat Honey? Please stay tuned. There are more blog posts to come very shortly.
JeannetteZ
>>>Please click here to read my Vegan Travel Guides To World Destinations<<<
>>>Want To Learn How To Create Delicious, Cruelty-Free, Healthy AND 100% Vegan Meals? Try These Awesome Vegan Cooking Courses With A Free 7-DAY MEMBERSHIP<<<
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Ideas? Thoughts? Questions? I would love to hear from you. Please leave me your questions, experience, and remarks about Do Vegans Eat Honey in the comments section below. You can also reach me by email at Jeannette@LivingTheVeganLifestyle.org.
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. I earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate and other affiliate programs. Please read my full disclosure.
Here are some links to some of my favourite articles:
Best Vegan Chicken Nuggets In Canada