Environmental Benefits Of A Plant-Based Diet
Environmental Benefits Of A Plant-Based Diet
The environmental benefits of a plant-based diet offer a myriad of positive aspects that resonate on a global scale.
By choosing fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes over animal products, individuals contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving water resources, and preserving biodiversity.
Plant-based diets require fewer natural resources, as they entail less land, water, and energy for production than meat-intensive diets.
Additionally, cultivating plant-based foods tends to have a lower carbon footprint, mitigating the environmental impacts of agriculture.
Embracing a plant-based lifestyle promotes personal health and fosters sustainability and environmental stewardship.
It is a crucial avenue for combating climate change and fostering a more harmonious relationship with the planet.

Environmental Benefits Of A Plant-Based Diet
A plant-based diet benefits the environment in several ways, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions, enhanced biodiversity, and the preservation of water resources.

1. Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Animal husbandry is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions due to the large quantities of nitrous oxide and methane it produces.
By transitioning to plant-based foods, individuals can substantially reduce their carbon footprint. Plant-based diets typically entail lower emissions associated with livestock farming.
For instance, cultivating crops for human consumption generally requires less land, water, and energy than raising animals for meat, dairy, and eggs.
Additionally, methane emissions from enteric fermentation and manure management are minimized or eliminated in plant-based farming systems.
This shift towards plant-based eating reduces greenhouse gas emissions and aligns with sustainable agricultural practices.
It lessens the environmental impact of food production, conserves natural resources, and promotes a more harmonious relationship with the planet.
2. Conservation Of Water Resources
Animal agriculture demands substantial water resources, including livestock drinking, feed production, and processing.
This high water consumption contributes to water scarcity and strains freshwater ecosystems. In contrast, plant-based foods typically require less water for cultivation, making them a more sustainable choice.
By realizing the environmental benefits of a plant-based diet, individuals can contribute to conserving freshwater resources and alleviating pressure on water supplies and ecosystems.
This is particularly crucial amid rising global water demand and the escalating challenges of agricultural water usage.
Embracing plant-based eating represents a proactive step towards sustainable water management, ensuring the availability of freshwater for future generations and fostering resilience in the face of water-related challenges.
3. Preservation Of Biodiversity
Livestock farming is frequently linked with habitat destruction, deforestation, and land degradation to establish grazing pastures and cultivate animal feed crops.
This habitat loss significantly threatens biodiversity, jeopardizing ecosystems and wildlife populations.
Plant-based diets offer a solution by reducing the demand for animal products, thus lessening the need for expansive agricultural land.
By embracing plant-based eating, individuals can help mitigate habitat destruction and preserve biodiversity by safeguarding natural habitats and ecosystems.
This shift promotes a more sustainable approach to food production that prioritizes environmental conservation and the protection of wildlife habitats.
Ultimately, by choosing plant-based foods, individuals contribute to preserving biodiversity, ensuring ecosystems' health and resilience for future generations.
4. Reduction Of Land Use
Animal agriculture demands extensive land for grazing livestock and cultivating feed crops like soy and corn.
This expansion frequently results in deforestation and the conversion of natural habitats, leading to biodiversity loss and ecosystem disruption.
A plant-based diet's environmental benefits offer a sustainable alternative, requiring less land for cultivation.
People can help preserve natural habitats and ecosystems by adopting plant-based eating habits, enabling reforestation efforts to mitigate climate change.
This shift promotes a more efficient use of land resources, reduces pressure on ecosystems, and contributes to biodiversity conservation.
Ultimately, embracing plant-based diets supports the preservation of natural landscapes and fosters a more sustainable relationship with the environment.
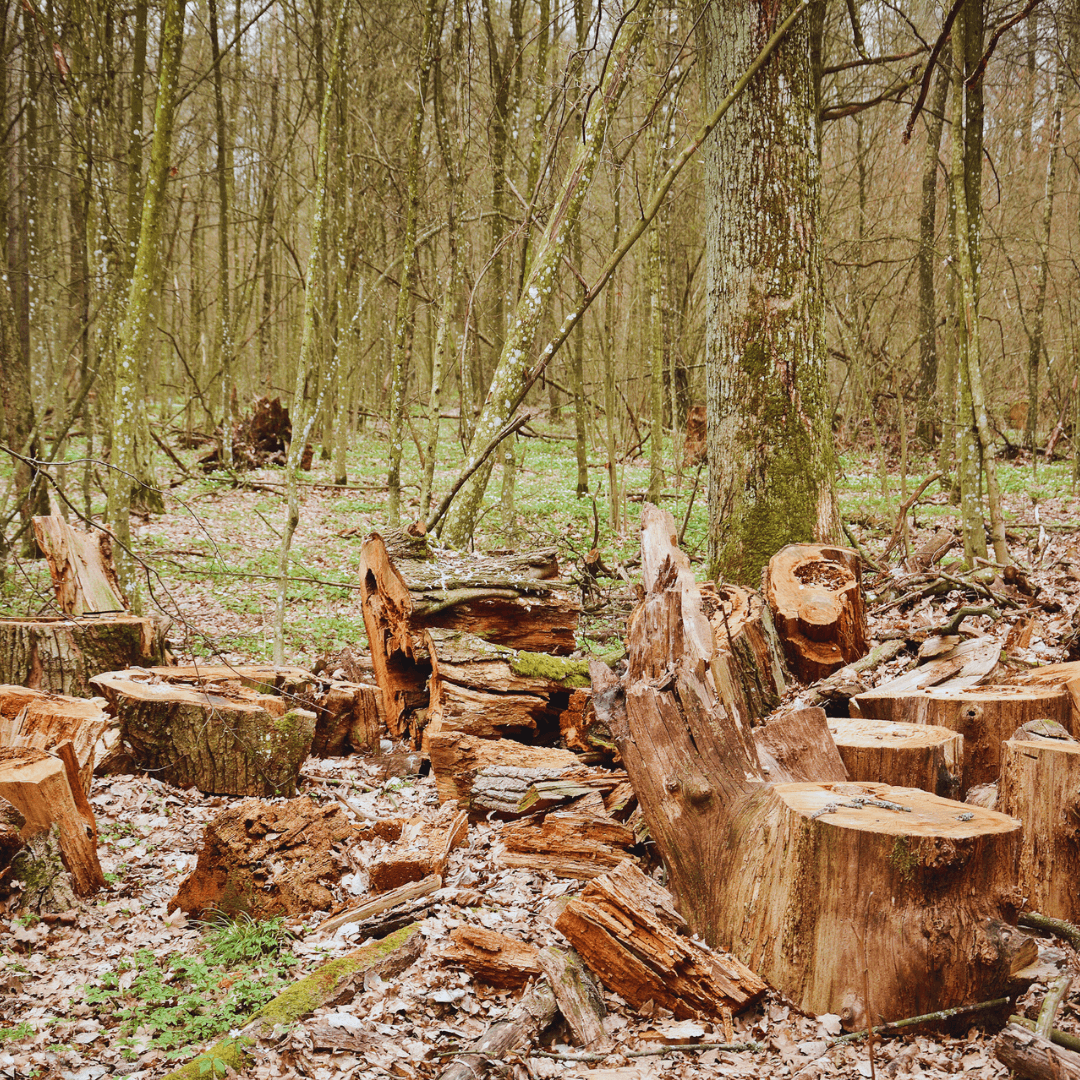

5. Mitigation Of Deforestation
Deforestation is a key result of animal agriculture, especially in areas like the Amazon rainforest, where large land areas are destroyed for cattle pastures and crop production.
Plant-based diets provide a solution by reducing the demand for land conversion for livestock farming.
Opting for plant-based foods over animal products helps mitigate deforestation by alleviating pressure on forests and preserving valuable ecosystems.
This dietary shift not only protects biodiversity but also promotes environmental sustainability on a global scale.
By embracing the ecological advantages of adopting a plant-based diet, individuals actively preserve crucial forest habitats and nurture a healthier planet for both present and future generations.
6. Reduction Of Water Pollution
Livestock farming is a significant source of water pollution, as it often discharges nutrient-rich runoff into waterways.
This runoff can contain excess nutrients from animal waste and fertilizers, contributing to water pollution and eutrophication and harming aquatic ecosystems.
Plant-based diets offer a solution by reducing the need for intensive animal agriculture, thereby mitigating water pollution.
By choosing plant-based foods, individuals can minimize the environmental impact of livestock farming and help protect water quality.
This shift promotes sustainable food production practices that prioritize environmental conservation and safeguard the health of freshwater ecosystems.
Ultimately, embracing plant-based eating reduces water pollution and supports preserving clean water sources for humans and wildlife.
7. Improvement Of Soil Health
Farming methods centred around plants, such as crop rotation and organic agriculture, improve soil health and fertility.
Crop rotation alternates crops in fields to replenish soil nutrients, control pests, and reduce erosion.
Composting and biological pest management are natural techniques used in organic farming instead of synthetic fertilizers and insecticides.
These techniques promote sustainable agriculture and improve soil health, enhancing water retention and microbial diversity.
This boosts crop yields and resilience to environmental stressors. Plant-based farming reduces ecological impacts such as pollution and habitat destruction by minimizing reliance on synthetic inputs.
Improving soil health via plant-based farming ensures sustainable agriculture, offers nutritious crops, and safeguards the environment for future generations.
8. Conservation Of Energy Resources
Plant-based diets represent a substantial preservation of energy resources compared to diets abundant in animal products.
The energy input required for raising livestock and processing animal products far exceeds that needed for growing plant-based foods.
By choosing plant-based diets, individuals reduce the energy demand associated with animal agriculture, including feed production, transportation, and processing.
This transition encourages more effective energy utilization in food production and distribution systems, contributing to energy conservation overall.
Adopting plant-based eating habits ensures the ecological advantages of a plant-based diet while also improving personal health and sustainability by lowering the environmental effect of food production and consuming less energy.
9. Reduction Of Air Pollution
Livestock farming is a significant source of air pollutants, releasing ammonia and methane into the atmosphere.
Ground-level ozone and fine particulate matter are partly formed by ammonia, mostly produced by animal dung and fertilizer used in feed crop production.
These pollutants can worsen respiratory conditions and lower the quality of the air. Methane, a powerful greenhouse gas contributing to climate change and global warming, is released by livestock during digestion and manure breakdown.
A shift to a plant-based diet can help people lessen their influence on the environment by decreasing the need for intensive animal husbandry and, consequently, limiting the amount of pollutants released into the atmosphere.
Livestock emits methane during digestion and manure decomposition, a potent greenhouse gas contributing to global warming.
Adopting a plant-based diet can help humans contribute less to environmental degradation by reducing the need for extensive animal husbandry and, as a result, minimizing the amount of pollutants discharged into the atmosphere.
Changing one's plant-based diet helps fight climate change, preserve public health, and encourage cleaner air.
10. Promotion Of Sustainable Food Systems
Plant-based diets promote sustainable food systems by prioritizing efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and ecosystem preservation.
Unlike animal agriculture, which often involves resource-intensive practices, plant-based diets require fewer resources for food production, such as land, water, and energy.
This efficiency minimizes ecological strain and mitigates greenhouse gas emissions associated with intensive farming.
Additionally, plant-based diets foster biodiversity by curbing habitat destruction and supporting healthier ecosystems.
Individuals contribute to developing a more sustainable food system by embracing plant-based eating.
This shift ensures food security, environmental resilience, and improved well-being for present and future generations, laying the foundation for a more sustainable and harmonious relationship between humanity and the natural world.
Why We Chose To Adopt A Vegan Lifestyle
Adopting a vegan lifestyle can be a conscious decision for various reasons, each deeply rooted in personal values, health considerations, ethical beliefs, and environmental benefits of a plant-based diet. Here's an elaborate discussion outlining some of the primary motivations:

1. Ethical Considerations
Many individuals adopt veganism out of ethical concerns for animals, rejecting their exploitation in industries like factory farming, characterized by confinement and inhumane slaughter practices, while also recognizing the interconnectedness of all living beings and striving to minimize harm in their lifestyle choices.
Central to this motivation is the belief in animal rights, advocating for their freedom from harm and exploitation.
Veganism aligns with the principle of non-violence towards all living beings, promoting compassion and empathy.
By abstaining from animal products, vegans affirm their commitment to this ethical stance, making dietary and lifestyle choices that prioritize animal welfare.
This moral foundation drives individuals to oppose the commodification of sentient beings and seek alternatives that promote respect and kindness towards all creatures.
2. Environmental Sustainability
Veganism is acknowledged as an environmentally sustainable lifestyle choice because it significantly reduces the environmental impact associated with animal agriculture.
Numerous studies have shown that vegan diets are associated with a lower chance of developing chronic illnesses, such as blood pressure, blood sugar regulation, and cholesterol levels.
These benefits also reduce the risk of developing certain malignancies, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes.
The lack of animal products frequently leads to improved weight management and decreased caloric consumption, which lowers the risk of obesity and associated health problems.
Plant-based diets demand fewer natural resources like land, water, and energy than animal-based diets, offering greater efficiency in resource utilization.
Furthermore, they aid in conserving biodiversity by mitigating habitat destruction typically caused by livestock farming.
Adopting a vegan lifestyle promotes personal health and fosters environmental preservation, making it a crucial step toward achieving sustainability.

3. Health And Well-Being
Adopting a vegan diet brings many health benefits rooted in the nutrient density of plant-based foods.
These diets abound in essential nutrients such as fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants (including flavonoids and carotenoids), vital for immune function, digestion, and cellular protection against oxidative stress and inflammation.
Extensive research links vegan diets with reduced risk factors for chronic diseases, like lower blood pressure, improved blood sugar control, and healthier cholesterol levels.
Thus, they lower the likelihood of conditions such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers.
The absence of animal products often results in lower calorie intake and better weight management, reducing the risk of obesity and related health issues.
4. Global Food Security
Veganism enhances global food security by promoting efficient food production and distribution systems.
Plant-based diets demand fewer resources for food production, making them more sustainable and scalable in feeding a burgeoning global population.
By reallocating agricultural resources from animal feed production to the cultivation of crops for direct human consumption, veganism has the potential to mitigate food scarcity and hunger in vulnerable communities worldwide.
This shift optimizes resource utilization and addresses inequities in food distribution, ensuring that nutritious plant-based foods reach those most in need.
Embracing veganism fosters resilience in the face of food insecurity, offering a viable solution to nourish and sustain populations worldwide while safeguarding the planet's health.
5. Cultural And Social Influences
Cultural and social factors significantly shape individuals' vegan lifestyle decisions. Heightened awareness, fueled by documentaries, social media, and educational materials, has sparked conversations about the ethical, environmental, and health ramifications of dietary choices.
This increased dialogue prompts individuals to reconsider their food habits and opt for more sustainable and compassionate alternatives.
Moreover, as veganism gains mainstream acceptance, accessibility to vegan-friendly products, restaurants, and support networks has expanded.
Increasingly, tools, community support, and gastronomic options to suit a wide range of tastes and preferences are helping to make switching to a vegan diet easier.
When social conventions and cultural attitudes change, veganism becomes a feasible and approachable option for people who want to align their eating habits with their principles.
6. Reduction Of Antibiotic Resistance
Veganism emerges as a critical strategy in tackling the escalating threat of antibiotic resistance, a formidable challenge to global health.
In animal agriculture, antibiotics are routinely administered to livestock for disease prevention and growth promotion, fueling the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
This misuse of antibiotics, particularly prophylactic and growth-promoting administration, exerts selective pressure, fostering the proliferation of resistant strains.
By eschewing animal products, vegans notably diminish their exposure to antibiotic residues in meat, dairy, and eggs.
This reduction mitigates the risk of ingesting antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Moreover, veganism advocates a transition from intensive animal farming towards sustainable, humane practices, fostering a more resilient and ecologically sound food system while safeguarding public health.
FAQ
1. Is soy production bad for the environment?
Answer: Cultivating soybeans can have beneficial and detrimental effects on the environment. While soybeans are a relatively efficient source of protein, the environmental impacts of soy cultivation vary depending on factors such as deforestation, monoculture farming practices, and pesticide use.
Sustainable soy production methods, such as agroforestry and organic farming, can help mitigate these impacts and promote environmental conservation.
2. Is palm oil bad for the environment?
Answer: Palm oil production has been associated with significant environmental issues, including deforestation, habitat destruction, biodiversity loss, and greenhouse gas emissions.
The widespread replacement of tropical rainforests with large-scale palm oil plantations threatens the habitats of endangered species like Sumatran tigers and orangutans.
As approved by the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO), sustainable palm oil production methods try to reduce these adverse effects.
Selecting goods made with sustainable palm oil or other oils helps lessen their negative environmental impact.
3. Why are exotic fruits bad for the environment?
Answer: Exotic fruits often incur environmental costs due to long-distance transportation, water-intensive cultivation, and habitat disruption.
Shipping them globally generates greenhouse gas emissions, while cultivation demands water and energy resources.
Monoculture farming for exotic fruits can lead to habitat destruction and biodiversity loss.
Choosing locally grown and seasonal fruits reduces the environmental footprint associated with transportation and cultivation, promoting sustainability and minimizing ecological harm.
4. Why are eggs bad for the environment?
Answer: Eggs can have environmental drawbacks primarily due to the intensive resource requirements of poultry farming.
Large-scale egg production contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, as poultry require feed production, transportation, and manure management.
Furthermore, the concentration of poultry in confined spaces can lead to pollution issues like nutrient runoff.
However, sustainable practices such as free-range or pasture-raised methods can mitigate some of these environmental impacts by promoting animal welfare and reducing resource intensity.
5. Why are shrimp bad for the environment?
Answer: Shrimp farming and harvesting can pose significant environmental concerns. Intensive shrimp farming often involves clearing mangrove forests and vital ecosystems that support biodiversity and protect coastlines.
Additionally, shrimp farms can contaminate water from excess feed, antibiotics, and waste.
Furthermore, shrimp production has a high carbon footprint due to energy-intensive processes such as aeration and water treatment.
Overfishing of wild shrimp stocks also disrupts marine ecosystems. Sustainable shrimp aquaculture and responsible seafood sourcing can help mitigate these environmental impacts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there is no denying the advantages of a plant-based diet for the environment. Our dietary decisions significantly impact our world's health, from lowering greenhouse gas emissions to protecting biodiversity and conserving water.
By embracing plant-based foods, individuals can contribute to mitigating climate change and promoting sustainability in agriculture.
Moreover, the shift towards plant-based eating aligns with an ethos of environmental stewardship, encouraging a more harmonious relationship with the natural world.
As we strive to create a more sustainable future, incorporating more plant-based foods into our diets emerges as a powerful and accessible solution.
Let us continue to explore and embrace the myriad benefits of plant-based living for the well-being of both ourselves and our planet.
I trust you enjoyed this article about the Environmental Benefits Of A Plant-Based Diet. Please stay tuned for more blog posts soon. Take care!
JeannetteZ
>>>Please click here to read my Vegan Travel Guides To World Destinations<<<
>>>Want To Learn How To Create Delicious, Cruelty-Free, Healthy AND 100% Vegan Meals? Try These Awesome Vegan Cooking Courses With A Free 7-DAY MEMBERSHIP<<<
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I would love to hear from you. Please leave me your questions, experiences, and remarks about the Environmental Benefits Of A Plant-Based Diet article in the comments section below. You can also email me at Jeannette@LivingTheVeganLifestyle.org.
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. I earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate and other affiliate programs. Please read my full disclosure.
Here are links to some of my favourite articles:
Vegan Recipes Gluten And Dairy-Free – Culinary Magic
Vegan Diet B12 Deficiency – What You Need To Know
What Is A Lacto Ovo Vegetarian Diet