Plant-Based Meat vs Real Meat
Plant-Based Meat vs Real Meat
In recent years, the growing popularity of plant-based diets and the increasing awareness of environmental and ethical concerns have sparked significant interest in vegan meat as an alternative to real meat.
As more individuals explore the possibilities of incorporating plant-based options into their diets, it becomes essential to understand the key differences between vegan meat and real meat.
In contrast, both options may serve as protein sources, but their composition, sourcing, nutritional profiles, and environmental impact differ significantly.
This article aims to provide an insightful comparison between vegan and real meat, shedding light on various aspects such as ingredients, health implications, taste and texture, environmental considerations, and cultural perspectives.
By examining these distinctions, readers can understand the benefits and challenges associated with each type of meat, ultimately empowering them to make informed and conscious dietary choices that align with their values and preferences.
Understanding Plant-Based Meat vs Real Meat
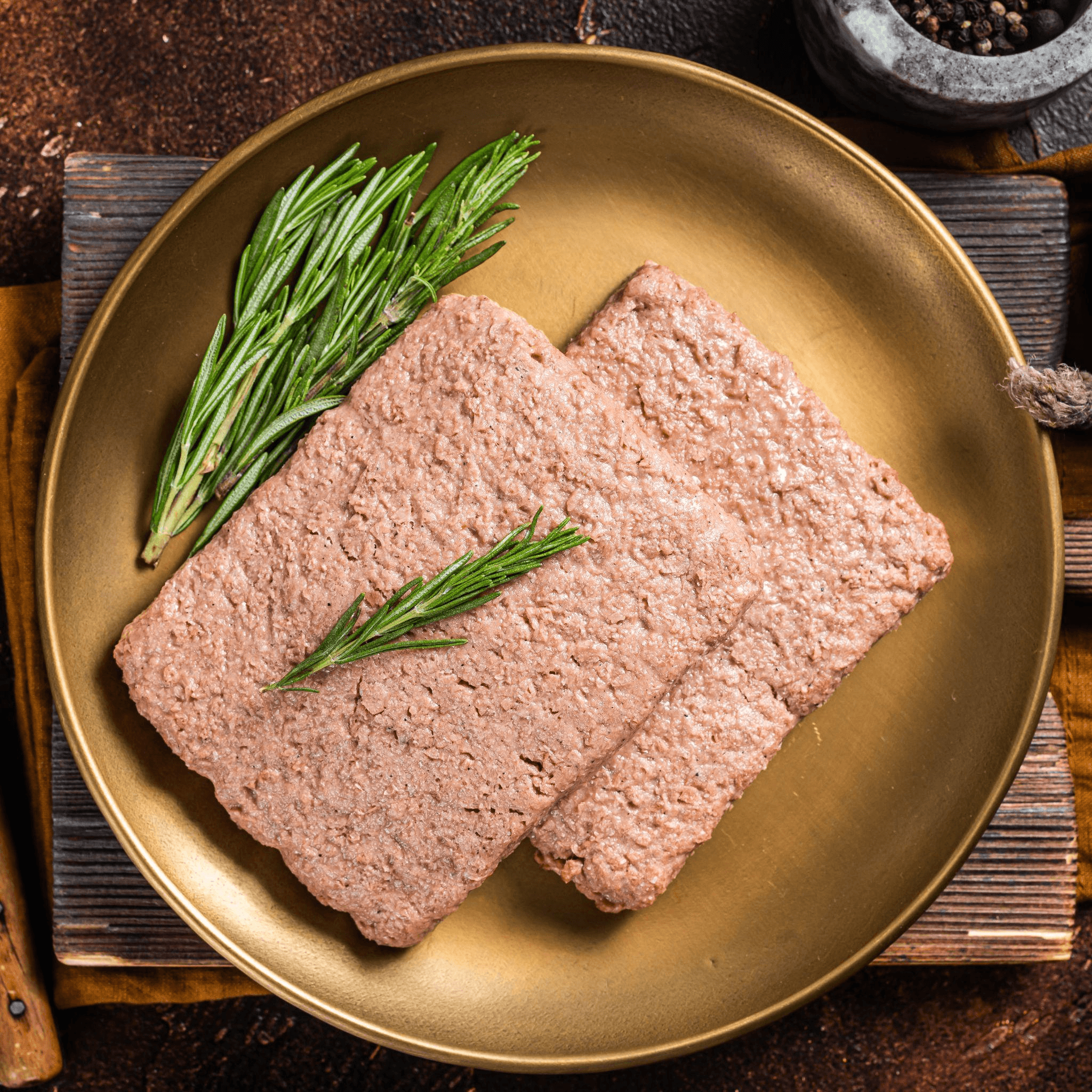

What Is Plant-Based Meat?
Vegan or plant-based meat or meat alternatives are made entirely from plant-based ingredients. It is designed to mimic real meat's taste, texture, and appearance while completely free from animal products.
The primary protein sources in vegan meat are typically derived from plants such as soy, peas, lentils, chickpeas, mushrooms, and wheat gluten (seitan).
These ingredients are processed and combined with various seasonings, binders, and flavourings to create products that resemble familiar meat-based dishes like burgers, sausages, chicken nuggets, and more.
Vegan meat is a popular choice among those following plant-based diets, vegetarians, and vegans, as it allows them to enjoy familiar meat-like dishes without contributing to animal suffering or environmental concerns associated with conventional meat production.
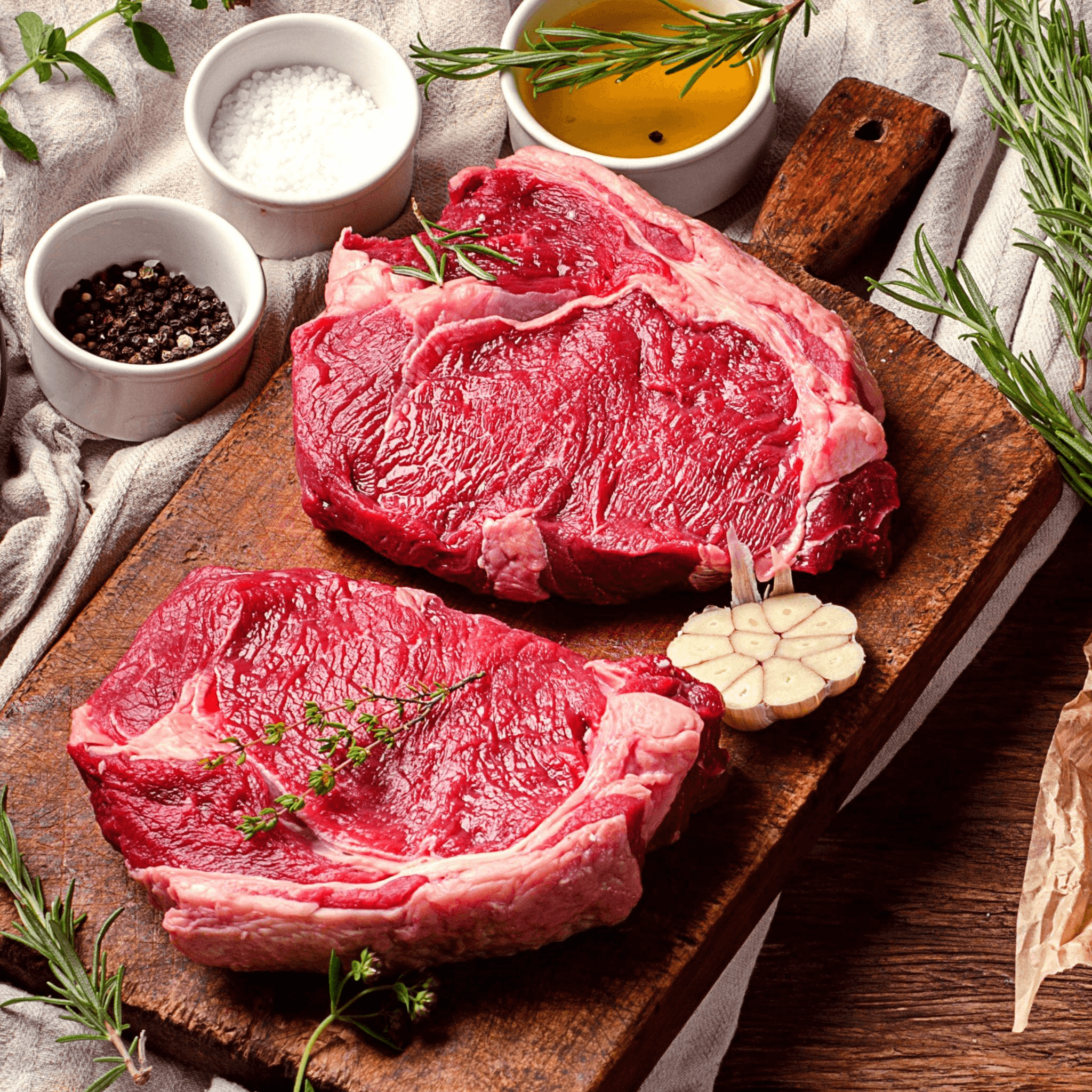

What Is Real Meat?
Real meat, also called animal or conventional meat, is derived from the flesh of animals such as cows, pigs, chickens, and fish. It is a significant part of traditional diets worldwide and is a primary source of protein for many people.
Real meat is rich in essential nutrients like protein, iron, zinc, and vitamin B12, which are important for overall health and well-being.
However, its production involves raising and slaughtering animals, which raises ethical concerns about animal welfare and the environmental impact of the livestock industry.
The consumption of real meat has been linked to various health risks, including heart disease, certain types of cancer, and environmental issues like deforestation, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions.
In summary, vegan meat is a plant-based alternative designed to replicate the taste and texture of real meat without any animal-derived ingredients.
On the other hand, real meat is sourced from animals and has been a staple in human diets for centuries.
Understanding the differences between these two types of meat can help individuals make informed choices based on their dietary preferences, ethical considerations, and environmental impact.
Plant-Based Meat vs Real Meat
Two distinct paths have emerged in food choices, each offering a compelling culinary journey: plant-based meat and real meat.
As dietary preferences and ethical considerations continue to shape our eating habits, it is essential to understand the fundamental differences between these two meat categories.
Let’s differentiate plant-based meat from real meat:

1. Ingredients And Sources
Vegan or plant-based meat derives its ingredients solely from plants, avoiding animal-derived components.
Common ingredients used in vegan meat production include soy, wheat gluten, pea protein, jackfruit, and various legumes.
These plant-based proteins are carefully processed and combined with other plant-derived ingredients to mimic the texture and taste of real meat.
Additionally, vegan meat often incorporates various seasonings, herbs, and spices to enhance flavour and create a palatable, realistic meat-like experience.
In contrast, real meat originates from animal sources, typically cattle, poultry, pork, or fish. The meat is harvested from the muscle tissues of animals, offering a rich source of animal-based protein, essential amino acids, and vitamins like vitamin B12 and iron.
The animal breed, food, species and the particular cut of meat influence real meat's flavour, texture, and nutritional composition.
The distinction between vegan meat and real meat lies fundamentally in their ingredient origins.
Vegan meat relies on a combination of plant proteins and seasonings to create a meat-like experience, while real meat directly results from animal tissue.
Understanding these ingredient differences is vital for considering dietary choices based on ethics, health, and environmental factors.

2. Nutritional Profile
Several notable differences arise when comparing vegan and real meat dietary profiles.
Vegan meat, crafted from plant-based proteins like soy, wheat, or pea protein, tends to have a lower fat content than real meat.
It is frequently lower in saturated fat and cholesterol, making it a popular alternative for people looking for heart-healthy foods.
Additionally, some vegan meats are fortified with essential vitamins and minerals like vitamin B12, which is naturally abundant in real meat.
However, real meat is an excellent source of complete protein, containing all the essential amino acids the human body needs.
On the other hand, vegan meat might require a combination of various plant-based sources to achieve a complete protein profile.
Vegan meats may contain non-heme iron from plant sources, which the body cannot readily absorb.
Real beef is high in heme iron, which is more easily absorbed by the body. While heme iron from actual meat does not need to be consumed with meals high in vitamin C to improve absorption, non-heme iron must.
The vitamin B12 found in real meat is also a natural supply of this compound, which is necessary to create red blood cells and healthy nerves.
Although certain vegan meat products have vitamin B12 added, it's vital to remember that not all kinds may contain enough of the vitamin.
In conclusion, both vegan meat and real meat have distinct nutritional strengths. Vegan meat often offers a lower-fat option with no cholesterol, suitable for those seeking plant-based alternatives.
On the other hand, real meat is a natural source of complete protein, heme iron, and vitamin B12.
Understanding the nutritional differences between the two can help individuals make informed dietary choices that align with their health and ethical preferences.

3. Environmental Impact
Vegan meat and actual meat differ significantly from each other in terms of their effects on the environment.
The ecological impact of vegan meat from plant-based sources is typically far smaller than that of genuine meat from raising livestock.
To graze animals and grow feed crops, meat production necessitates a sizable quantity of land, resulting in habitat loss and deforestation.
In addition, raising cattle contributes significantly to the emissions of greenhouse gases, mainly methane, which hurts the climate.
On the other hand, vegan meat production involves less land use and has a reduced water footprint, as plant-based sources require less water than raising livestock.
Furthermore, vegan meat production emits fewer greenhouse gases, making it a more environmentally sustainable choice.
Choosing vegan meat over real meat can contribute to conserving natural resources, reducing deforestation, and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
By opting for plant-based alternatives, individuals can play a part in promoting a more sustainable and eco-friendly food system for the future.

4. Ethical Considerations
The ethical considerations surrounding vegan meat and real meat consumption are at the heart of the debate on animal welfare.
Vegan meat offers a cruelty-free alternative as it is produced without exploiting or harming animals.
This aligns with the growing consciousness of consumers who are increasingly concerned about the treatment of animals in the meat industry.
Real meat, on the other hand, raises significant ethical concerns due to the practices involved in livestock farming.
Animals are often subjected to confined and crowded living conditions, and practices like factory farming can lead to stress, pain, and suffering.
The slaughtering process itself is a contentious issue, as it involves killing animals for meat consumption.
Choosing vegan meat allows consumers to opt for a compassionate approach by reducing the demand for the real meat and promoting the welfare of animals.
By embracing plant-based alternatives, individuals can make a conscious ethical choice to support practices prioritizing animal welfare and compassion, thus contributing to a more humane and compassionate food system.

5. Health Benefits And Risks
The health benefits and risks of consuming vegan meat and real meat offer interesting insights into the impact of dietary choices on overall well-being.
Vegan meat is generally considered a healthier option due to its lower saturated fat and cholesterol content than real meat.
Plant-based alternatives often contain more beneficial fats, like unsaturated fats, which can benefit heart health and cholesterol levels.
Moreover, plant-based meat is typically free from harmful substances found in real meat, such as antibiotics and hormones, associated with certain human health risks.
On the other hand, real meat provides essential nutrients like complete proteins, iron, and vitamin B12, which are important for overall health.
However, excessive meat eating has been associated with a higher risk of developing some conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, and a few types of cancer.
The secret to a balanced diet is moderation and picking nutrient-rich sources, whether from plants or animals.
Incorporating various whole foods, including legumes, grains, fruits, vegetables, and vegan and real meat in balanced proportions, can support optimal health while minimizing potential risks associated with either type of meat.
When making dietary choices, individuals need to consider their health needs and preferences, consulting with healthcare professionals to create a diet that promotes their well-being.

6. Food Safety
Food safety is crucial when comparing vegan and real meat. Vegan meat, being plant-based, generally carries a lower risk of bacterial contamination commonly associated with real meat, such as E. coli, salmonella, and listeria.
Alternatives made of plants do not contain the same infections found in raw or undercooked animal-derived foods.
However, properly handling and preparing vegan meat is essential to prevent cross-contamination with other foods that may contain harmful bacteria.
On the other hand, real meat poses a higher risk of foodborne illnesses due to the potential presence of bacteria from the animal's digestive tract or external environment.
Proper cooking and storage are crucial to reducing these risks. In both cases, consumers should pay attention to product labelling, storage instructions, and expiration dates to ensure food safety.
Additionally, purchasing plant-based meat products from reputable brands and retailers can provide a layer of confidence in their safety.
Ultimately, practicing good food hygiene, proper cooking techniques, and following recommended guidelines for handling and preparing both plant-based meat and real meat are essential to safeguarding against foodborne illnesses and ensuring a safe and enjoyable dining experience.

7. Cooking And Culinary Applications
Vegan and real meat offer distinct culinary experiences and versatile applications in various recipes.
Vegan meat, often made from plant-based proteins like soy, wheat, or pea protein, has come a long way in replicating the taste and texture of real meat.
Its ability to be seasoned and flavoured like real beef makes it a popular choice for vegan burgers, tacos, stir-fries, and plant-based meatballs.
Furthermore, it goes well with various cuisines, enabling people with a plant-based diet to partake in their favourite and most well-known foods.
On the other hand, real meat, derived from animals, offers a rich and varied flavour profile, from beef's juiciness to the chicken's tenderness and lamb's gaminess.
Real meat excels in traditional meat-based recipes, such as grilled steaks, roasted poultry, and slow-cooked stews, whose unique taste and texture play a central role.
The versatility of vegan and real meat caters to different dietary preferences and cooking styles, providing ample opportunities for culinary exploration.
Whether one prefers the plant-based options of vegan meat or the time-honoured tradition of real meat, each has its place in the kitchen, allowing individuals to craft diverse and delicious meals to suit their tastes and lifestyles.

8. Accessibility And Availability
Depending on the geography and market demand, the accessibility and availability of vegan and genuine meat items can vary greatly.
Demand for vegan meat substitutes has increased dramatically in many urban areas and progressive regions due to the popularity of plant-based diets.
As a result, a wide range of vegan meat products, including meatless ground beef vegan sausages and chicken nuggets, are frequently offered in grocery shops, supermarkets, and specialist health food stores.
Additionally, restaurants and fast-food chains are increasingly incorporating plant-based meat substitutes into their menus to cater to the growing number of flexitarians and vegans.
In contrast, in more rural or conservative regions, the availability of vegan meat products may be limited due to lower demand or cultural preferences for traditional meat-based diets.
Real meat, sourced from livestock, remains a dominant dietary staple in such areas, with a wide selection of meat cuts available at local butcher shops and supermarkets.
The local agricultural industry and farming practices often influence real meat accessibility in these regions.
Furthermore, the distribution of vegan meat products can be influenced by transportation and logistical challenges, especially when the demand for these products is concentrated in specific urban centers. This can result in uneven availability in more remote areas.
Overall, the accessibility of vegan and real meat is closely tied to consumer preferences, cultural norms, and evolving market trends.
While plant-based meat has seen significant growth and increased availability in recent years, its accessibility may continue to grow alongside changing dietary habits and consumer demands.
Conversely, the accessibility of real meat remains robust in many regions, reflecting its long-standing role as a dietary staple for millions worldwide.

9. Price Comparison
The cost comparison between vegan and real meat can vary depending on several factors, including product type, brand, location, and local market trends.
Real meat tends to be more expensive than many vegan alternatives, especially premium cuts of beef or specialty products.
The production of real meat involves expenses related to animal rearing, feed, veterinary care, and processing, contributing to its higher price point.
On the other hand, the cost of vegan meat is influenced by the ingredients used in its production and the manufacturing processes involved.
Some plant-based ingredients, like soy and pea protein, can be cost-effective, while others, such as nuts and seeds, may have higher price tags.
However, as the demand for vegan meat rises, economies of scale and technological advancements gradually reduce production costs, making plant-based options more affordable for consumers.
Additionally, considering the environmental impact and health benefits associated with plant-based diets, consumers may view vegan meat's slightly higher upfront cost as an investment in their health and the planet.
It's essential to note that while vegan meat may be cheaper in some cases, the cost comparison can vary depending on location and availability.
In regions where real meat is heavily subsidized or has a long-standing presence in the culinary culture, it may still maintain a competitive edge over vegan meat.
Ultimately, consumers' economic considerations and dietary preferences are crucial in determining which option, vegan or real meat, best aligns with their budget and values.
Conclusion
In conclusion, vegan and real meat differ beyond their ingredients and nutritional profiles. Vegan meat offers a cruelty-free and sustainable alternative to real meat, addressing ethical concerns surrounding animal welfare and environmental sustainability.
It provides a diverse range of plant-based options that cater to various dietary preferences, including those with allergies or intolerances.
Moreover, vegan meat's lower carbon footprint and reduced environmental impact contribute to a more sustainable food system.
Ultimately, both vegan and real meat have their merits, and the choice between them depends on individual preferences, dietary requirements, and ethical considerations.
The rising popularity of vegan meat reflects a growing awareness of environmental and animal welfare issues, prompting more people to embrace plant-based alternatives.
As technology and innovation advance, the distinction between plant-based meat and real meat may evolve, offering consumers even more diverse and sustainable choices for their dietary needs.
I trust you enjoyed this article about Plant-Based Meat vs Real Meat. Please stay tuned for more blog posts soon.
Take care!
JeannetteZ
>>>Please click here to read my Vegan Travel Guides To World Destinations<<<
>>>Want To Learn How To Create Delicious, Cruelty-Free, Healthy AND 100% Vegan Meals? Try These Awesome Vegan Cooking Courses With A Free 7-DAY MEMBERSHIP<<<
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I would love to hear from you. Please leave me your questions, experience, and remarks about the Plant-Based Meat vs Real Meat article in the comments section below. You can also email me at Jeannette@LivingTheVeganLifestyle.org.
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. I earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate and through other affiliate programs. Please read my full disclosure.
Here are links to some of my favourite articles:
Nourishing Your Body With Vitamin D-Rich Vegan Foods
Best Vegan Beauty Personal Care Products
Best Vegan Pet Food For Health And Happiness
How To Find Leather-Free Interiors