Pros And Cons Of Plant-Based Meat

Pros And Cons Of Plant-Based Meat
The global shift towards more sustainable and compassionate food choices has sparked a significant rise in the popularity of plant-based diets.
As part of this movement, vegan meat alternatives have emerged as a prominent option for individuals seeking to reduce their reliance on animal products.
These innovative alternatives aim to replicate traditional meat's taste, texture, and nutritional profile, offering a range of benefits that align with ethical, environmental, and health considerations.
However, like any dietary choice, there are pros and cons to incorporating vegan meats into one's diet.
This article will explore the advantages and potential drawbacks of vegan meat consumption, providing a comprehensive overview for individuals looking to make informed food choices.
Whether you're a committed vegan, a curious omnivore, or anywhere in between, understanding the pros and cons of vegan meat can help you navigate the evolving landscape of sustainable and ethical eating.

What Is Plant-Based Meat
The term “plant-based meat,” sometimes known as “vegan meat” or “vegetarian meat,” describes culinary items created to resemble the flavour, appearance, and texture of conventional animal-based meat while being wholly made of plant-derived materials.
These innovative alternatives are crafted using a combination of plant proteins, such as soy, peas, lentils, wheat, and even fungi like mushrooms.
These proteins are often processed and combined with other plant-based ingredients like oils, starches, and flavourings to create products that closely resemble the mouthfeel and culinary versatility of meats like beef, poultry, pork, and seafood.
Plant-based meat aims to provide consumers with a cruelty-free and environmentally sustainable alternative to conventional animal-derived meat products.
This is particularly important as concerns about animal welfare, climate change, and health have prompted many to seek more ethical and sustainable dietary choices.
Plant-based meat can be found in various forms, including burger patties, sausages, meatballs, nuggets, deli slices, and ground “meat.”
These products are often designed to be cooked, seasoned, and enjoyed in the same ways as their animal counterparts.
The development of plant-based meat involves intricate food science and culinary innovation.
Manufacturers aim to replicate the taste and texture of meat and recreate the experience of cooking and consuming meat-based dishes.
As a result, plant-based meats have evolved to be remarkably similar to animal-based meats in terms of flavour, texture, and even “juiciness,” achieved through techniques like beet juice infusion to simulate the appearance of cooked meat.
Plant-based meat has gained significant popularity due to its potential benefits for consumers and the planet.
It offers a way to enjoy familiar flavours and meals while reducing the environmental impact of conventional livestock farming and addressing ethical concerns related to animal agriculture.
However, like any processed food, plant-based meats may have nutritional considerations, and individuals should be mindful of their overall diet to ensure a well-rounded and balanced approach to plant-based eating.
Pros Of Plant-Based Meat
Plant-based meat has gained popularity for several compelling reasons, offering a range of benefits for individuals, animals, and the environment. Here are some key pros of plant-based meat:
1. Healthier Choice
Plant-based meats offer a compelling advantage in promoting a healthier diet. They often have lower cholesterol and saturated fat levels than their animal-based equivalents.
When saturated fat and cholesterol are taken in excess, the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular issues is dramatically increased.
Plant-based meats derive their fats from nuts, seeds, and plant oils, rich in heart-healthy unsaturated fats.
These healthier fats contribute to improved lipid profiles by increasing “good” HDL cholesterol levels and reducing “bad” LDL cholesterol levels in the bloodstream.
Moreover, the lower saturated fat content of plant-based meats supports weight management efforts.
High saturated fat intake can contribute to obesity, a risk factor for numerous chronic conditions, including diabetes and certain cancers.
By opting for plant-based meats, individuals can reduce their caloric intake from saturated fats and choose a more balanced source of protein. This shift can aid in weight control and improve overall metabolic health.

2. Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations play a significant role in the appeal of plant-based meats. By opting for these alternatives, individuals make a conscious choice to promote improved animal welfare and contribute to the reduction of animal suffering.
Traditional meat production involves practices that often lead to the confinement, mistreatment, and slaughter of animals on a massive scale within factory farming systems.
Plant-based meats offer a way to shift away from this model, as they are crafted entirely from plant-derived ingredients without the need for animal exploitation.
One of the key benefits of plant-based meats is the elimination of animal slaughter. This aspect resonates with individuals who seek to align their dietary choices with compassionate values, as well as those who advocate for animal rights.
Additionally, the reduced demand for factory farming associated with plant-based meats can lead to decreased environmental stress caused by the livestock industry.
By reducing the need for large-scale animal agriculture, the release of greenhouse gases, deforestation, and depletion of natural resources can be mitigated.
Furthermore, the ethical considerations extend beyond the direct impact on animals and encompass broader societal and cultural aspects.
As more people opt for plant-based meats, there is a potential to foster a shift in societal attitudes toward more humane and sustainable food practices.
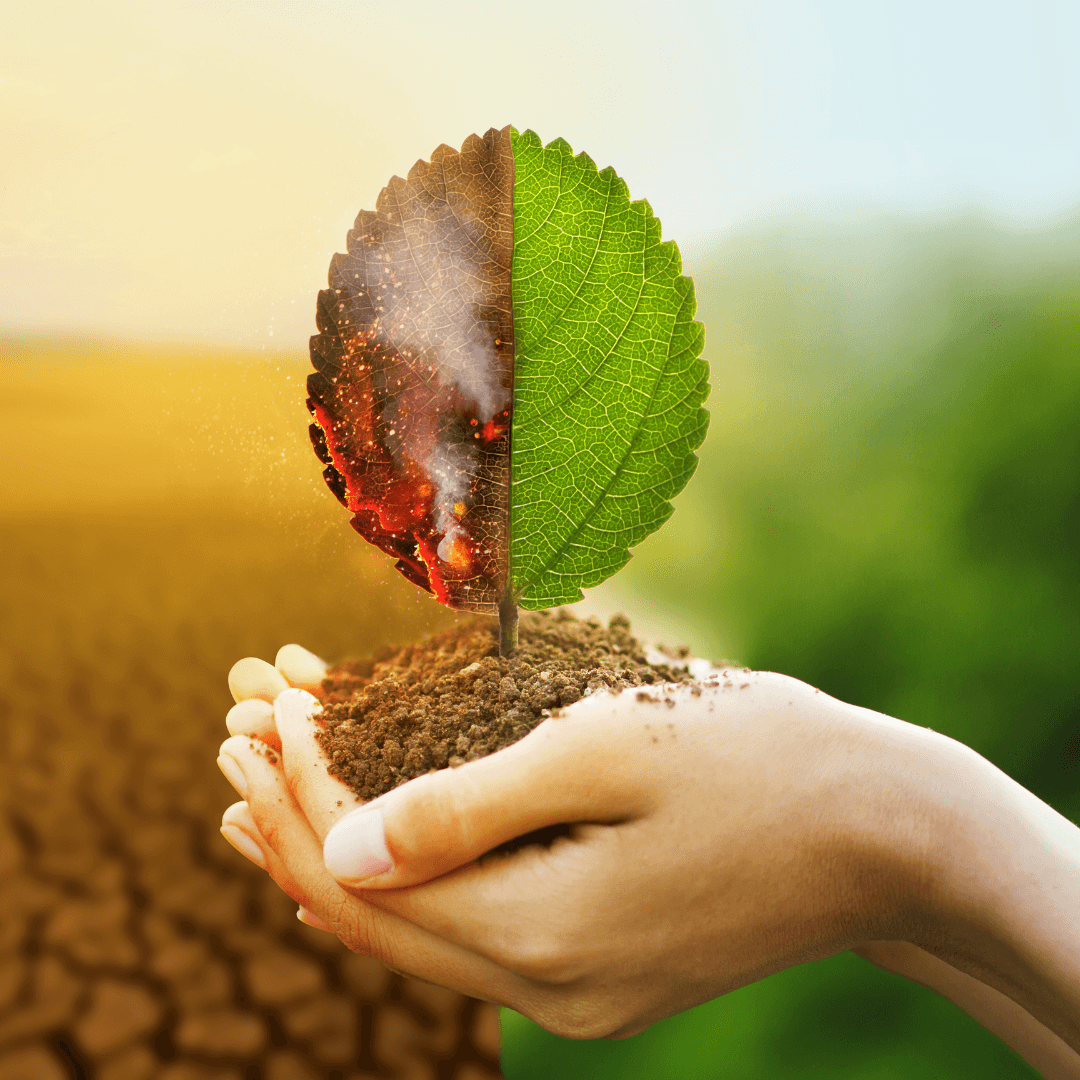

3. Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of plant-based meats is a compelling proponent of their adoption.
Unlike conventional meat production, which is resource-intensive and contributes to various environmental issues, plant-based meats offer a more sustainable alternative.
One of the most significant advantages lies in their reduced demand for land. Plant-based meats rely on crops directly consumed by humans rather than using vast land areas for animal farming and feed production.
This helps mitigate deforestation, preserve natural habitats, and conserve biodiversity.
Water usage is another critical factor. Producing traditional meat requires substantial water for animal hydration and feed crops.
In contrast, plant-based meats generally have a lower water footprint, as they bypass the intermediary step of raising animals for consumption.
This can alleviate water scarcity concerns and reduce strain on local ecosystems and water sources.

4. Allergen-Free
One notable advantage of plant-based meats is their allergen-free nature, making them an inclusive and safe option for individuals with food allergies or dietary restrictions.
Traditional animal-based meats often contain common allergens like dairy and eggs, which can pose a significant health risk for those with sensitivities.
In contrast, plant-based meats are crafted from non-allergenic sources, such as legumes, grains, and vegetables, minimizing the risk of allergic reactions.
This allergen-free characteristic of plant-based meats is particularly significant for individuals with lactose intolerance or egg allergies.
These individuals can enjoy the flavours and textures of meat alternatives without compromising their health or comfort.
Additionally, plant-based meats can allow families with mixed dietary preferences to share meals without worrying about allergen cross-contamination.
Furthermore, the absence of allergens in plant-based meats can simplify meal planning and preparation for individuals who need to avoid certain foods strictly.
They offer a versatile foundation for crafting various dishes, from sandwiches to stir-fries, that cater to diverse dietary needs without sacrificing taste or nutrition.

5. Diverse Nutrient Profile
Plant-based meats offer a diverse nutrient profile beyond the protein content typically associated with meat substitutes.
Many of these products are intentionally fortified with essential nutrients such as vitamin B12, iron, and zinc, commonly found in animal-derived foods.
This fortification is a strategic approach to address potential nutritional gaps in a vegan diet.
Vitamin B12, for instance, is primarily available in animal products, and its deficiency can lead to anemia and nervous system complications.
By fortifying plant-based meats with vitamin B12, manufacturers help vegans and vegetarians meet their daily requirements without relying solely on supplements.
Similarly, iron and zinc, crucial for blood health and immune function, are often found in higher amounts in animal foods.
Fortified plant-based meats provide these essential minerals, ensuring that individuals can maintain optimal health without compromising their dietary choices.
By offering a convenient and familiar source of essential nutrients, fortified plant-based meats support individuals in achieving a well-rounded and nourishing diet.

6. Global Food Security
Global food security is a pressing concern as the world's population expands. Plant-based meats offer a promising solution to this challenge by presenting a more efficient and sustainable protein source.
Conventional meat production is resource-intensive, requiring vast amounts of land, water, and feed to raise animals for slaughter. In contrast, plant-based meats can be produced with significantly lower environmental impacts.
They require fewer natural resources, emit fewer greenhouse gases, and have a reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional meat production.
We can alleviate the strain on agricultural systems and ecosystems by adopting plant-based meats as a protein source.
The land and water saved by shifting towards plant-based alternatives can be repurposed for more sustainable agricultural practices, such as growing crops directly for human consumption rather than animal feed.
This reallocation of resources can lead to increased food production efficiency and better utilization of arable land, contributing to improved global food security.
Traditional meat production is constrained by land availability and the time required for animal growth and reproduction.
In contrast, plant-based meats can be produced more rapidly and consistently, allowing for increased protein output to keep up with rising population trends.

Cons Of Plant-Based Meat
While plant-based meats have become increasingly well-liked and well-recognized for their many advantages, it's crucial to be aware of any potential drawbacks or difficulties their usage poses.
People should be aware of various issues when adopting plant-based meat substitutes into their meals, and these downsides cover them all.
Although plant-based meats have many advantages, there are also some possible risks and difficulties that come with eating them:
1. Nutritional Profile Variability
One of the potential drawbacks of plant-based meats is the variability in their nutritional profiles, which can stem from differences in manufacturing processes, ingredients, and formulations across various brands and products.
While some plant-based meat options are crafted to provide healthful alternatives, others may undergo significant processing, resulting in elevated sodium, saturated fats, and additives levels.
This nutritional variability highlights the importance of diligent label reading and product selection.
Consumers who prioritize health should opt for plant-based meats that are minimally processed, contain whole-food ingredients, and are relatively low in sodium and unhealthy fats.
By carefully examining nutritional information, individuals can make informed choices that align with their dietary goals and overall well-being.
It's also worth noting that as the popularity of plant-based meats continues to rise, the market is evolving, and newer, healthier options are continually being introduced, providing consumers with a broader array of choices to suit their nutritional preferences.

2. Allergies And Sensitivities
While plant-based meats offer an allergen-friendly alternative for individuals avoiding dairy and eggs, it's important to recognize that they may still contain other allergenic ingredients like soy or gluten.
This consideration is particularly crucial for individuals with specific allergies or sensitivities.
Soy is a prevalent protein source in many plant-based meats, and gluten-containing ingredients might be used for texture or binding.
Therefore, individuals allergic to soy or gluten should meticulously review ingredient labels before consuming these products.
Fortunately, the growing demand for allergen-free options has prompted some plant-based meat brands to develop products that cater to these dietary needs.
For those with allergies, exploring allergen-free plant-based meats or alternatives made from less common protein sources can be a way to enjoy the benefits of plant-based eating without compromising health or safety.
Overall, while plant-based meats can offer many versatile and ethical food choices, it's important to be aware of potential allergenic ingredients and choose products that align with individual dietary requirements.

3. Cost
One significant drawback of plant-based meats is their potentially higher cost than traditional meat products.
The production and processing of plant-based ingredients and the research and development required to create realistic meat alternatives can contribute to elevated prices.
While prices may vary among different brands and types of plant-based meats, the novelty and innovative nature of these products often result in them being priced higher than conventional meats.
This cost disparity can challenge budget-conscious consumers, particularly those with lower incomes or larger families.
Additionally, the accessibility of plant-based meats may be limited in some regions, where availability is scarce or the cost is prohibitive.
However, as the demand for plant-based options continues to rise and technology advances, economies of scale could potentially lead to reduced production costs and more affordable prices over time.
In the meantime, consumers interested in incorporating plant-based meats into their diets should consider budgeting accordingly and exploring cost-effective ways to enjoy the benefits of plant-based eating, such as cooking from scratch using affordable plant-based ingredients.
4. Processing And Additives
An important consideration for plant-based meats is the level of processing and the use of additives.
Achieving a meat-like texture and flavour often requires extensive processing involving various additives, preservatives, and enhancers.
Even though regulatory bodies typically view these substances as safe, some people might be wary of consuming foods that have undergone extensive processing.
The use of additives and preservatives, even if safe, can raise questions about the overall nutritional quality of plant-based meats.
For individuals who prioritize a minimally processed diet, the reliance on these additives may be a potential drawback.
Moreover, some consumers prefer a simpler and more natural approach to their food choices.
It's worth noting that the degree of processing can vary among different brands and types of plant-based meats.
As the market for these products continues to evolve, there is potential for innovations that prioritize using fewer additives and more whole, recognizable ingredients.
For those who have concerns about additives, reading ingredient labels and opting for plant-based meats with a shorter and more straightforward list of ingredients could be a strategy to mitigate this concern while still enjoying the benefits of plant-based eating.

5. Availability And Accessibility
One potential drawback of plant-based meats is their availability and accessibility, which vary widely depending on geographic location and local market dynamics.
While the popularity of plant-based eating is on the rise, plant-based meat products may not yet be as ubiquitous as their traditional meat counterparts.
In larger urban areas or regions with a strong focus on health and sustainability, plant-based meats are more likely to be readily available in grocery stores, restaurants, and fast-food chains.
However, the options for finding these products might be more limited in smaller towns or less densely populated areas.
This limited accessibility can pose challenges for individuals interested in incorporating more plant-based options into their diets but have limited access to these products.
Moreover, the availability of certain plant-based meats, such as more specialized or niche products, can also be constrained by local market demand and distribution networks.
As the demand for plant-based foods continues to grow, the availability of plant-based meats will also expand over time.
In the meantime, individuals in areas with limited access to plant-based meats can explore online retailers, specialty stores, or farmers' markets as potential sources.
Additionally, the accessibility issue highlights the importance of advocating for more widespread availability of plant-based options and encouraging local businesses to include these products in their offerings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the pros and cons of plant-based meat highlight the multifaceted nature of this innovative food trend.
Plant-based meats offer numerous benefits, including their potential to be a healthier choice, their positive impact on animal welfare and the environment, and their contribution to global food security.
These products can provide essential nutrients, reduce saturated fat intake, and cater to diverse dietary preferences.
Moreover, the rise of plant-based meats has sparked innovation in the food industry, promoting sustainability and ethical considerations.
Ultimately, the decision to incorporate plant-based meats into one's diet depends on individual values, health considerations, and culinary preferences.
The growing popularity of these products signifies an exciting shift towards more sustainable and compassionate food choices.
As the field of plant-based meat continues to evolve, balancing the pros and cons will be pivotal in maximizing the benefits and minimizing potential drawbacks.
I trust you enjoyed reading the article about the Pros And Cons Of Plant-Based Meat. Please stay tuned. There are more blog posts to come very shortly.
JeannetteZ
>>>Please click here to read my Vegan Travel Guides To World Destinations<<<
>>>Do You Want To Surprise Your Family And Guests With Delicious Vegan Lunches And Dinners Regularly? Become A Member At Veecoco – My #1 Recommendation – And Have Access To Over 700 Delicious, Healthy AND 100% Vegan Recipes<<<
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Ideas? Thoughts? Questions? I would love to hear from you. Please leave me your questions, experiences and remarks about the Pros And Cons Of Plant-Based Meat in the comments section below. You can also reach me by email at Jeannette@LivingTheVeganLifestyle.org.
>>>Click here to read more about Vegan Meat on Wikipedia<<<
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. I earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate and other affiliate programs. Please read my full disclosure.