Best Vegetarian Diet Guide
Vegetarian Diet Guide – Embracing A Plant-Powered Lifestyle
Starting a vegetarian diet provides a route to ethical living and healthy health.
A vegetarian diet excludes meat, poultry, and fish in favour of plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
This dietary decision lowers carbon emissions while supporting heart health, weight control, and general well-being.
When adopting a vegetarian lifestyle, it's essential to ensure a balanced intake of important nutrients like protein, iron, calcium, and vitamin B12 through various plant sources and fortified foods.
With mindful planning and culinary exploration, a vegetarian diet can be delicious, nourishing, and sustainable for individuals and the planet.

What Is A Vegetarian Diet?
Veganism, a stricter form of vegetarianism, excludes all animal products, including dairy, eggs, and sometimes honey, as outlined in a vegetarian diet.
This ethical lifestyle choice extends beyond diet to avoid exploiting animals for any purpose. Vegans prioritize plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, ensuring a compassionate and sustainable approach to eating.
Vegans advocate for animal rights, environmental conservation, and personal health within a holistic dietary framework by abstaining entirely from animal-derived products.
A vegetarian diet guide outlines a dietary approach emphasizing plant-based foods while excluding meat, poultry, and seafood. Here's a breakdown of a vegetarian diet:
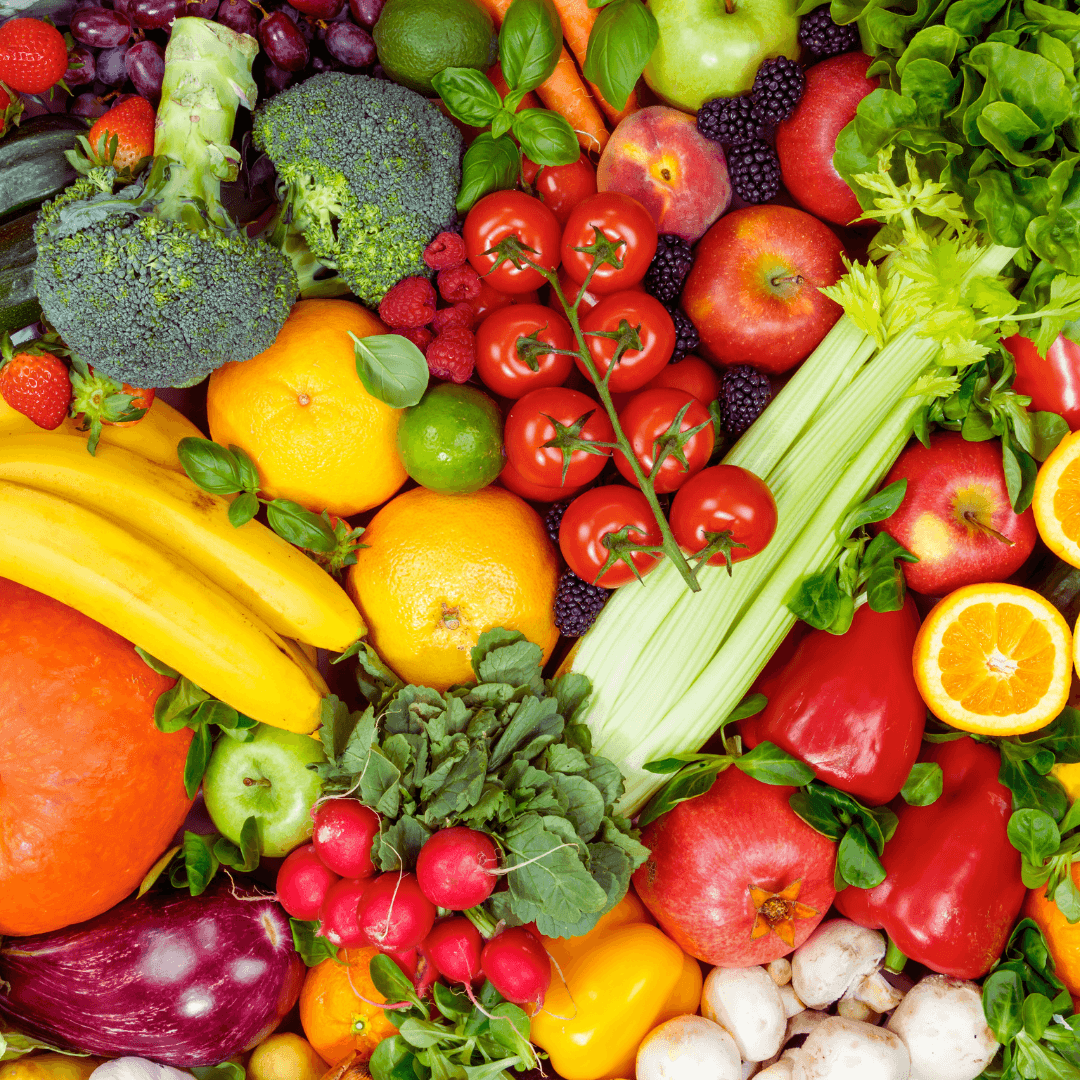

1. Fruits And Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are foundational in a vegetarian diet, offering vital vitamins, minerals, fibre, and antioxidants essential for health.
Rich in nutrients and low in calories, fruits and vegetables promote overall well-being and support various bodily functions.
Incorporating a colourful array of fruits and vegetables ensures a diverse nutrient intake, aiding digestion, immunity, and disease prevention.
They are the cornerstone of a balanced vegetarian diet, contributing to its nutritional richness and health benefits.
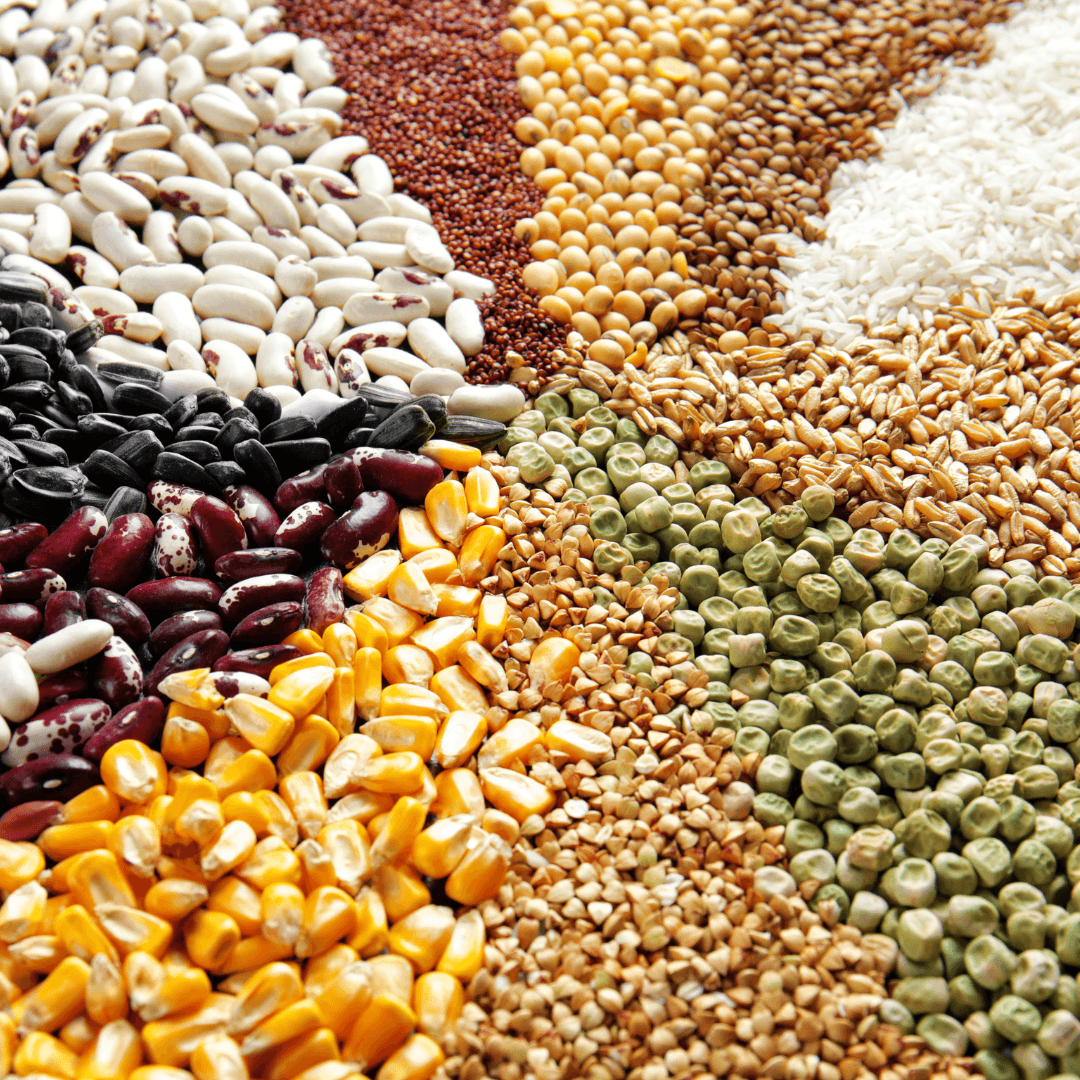

2. Grains For A Vegetarian Diet
Grains like brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat pasta are key in vegetarian diets. They offer carbohydrates for energy and fiber for digestion.
Whole grains, richer in nutrients than refined counterparts, supply vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Their diversity ensures a balanced nutrient intake, bolstering overall health. Incorporating them adds texture and flavour to vegetarian meals, enhancing satiety and nutritional value.
With whole grains as a foundation, vegetarian diets thrive, supporting a healthy lifestyle and sustainable eating habits.
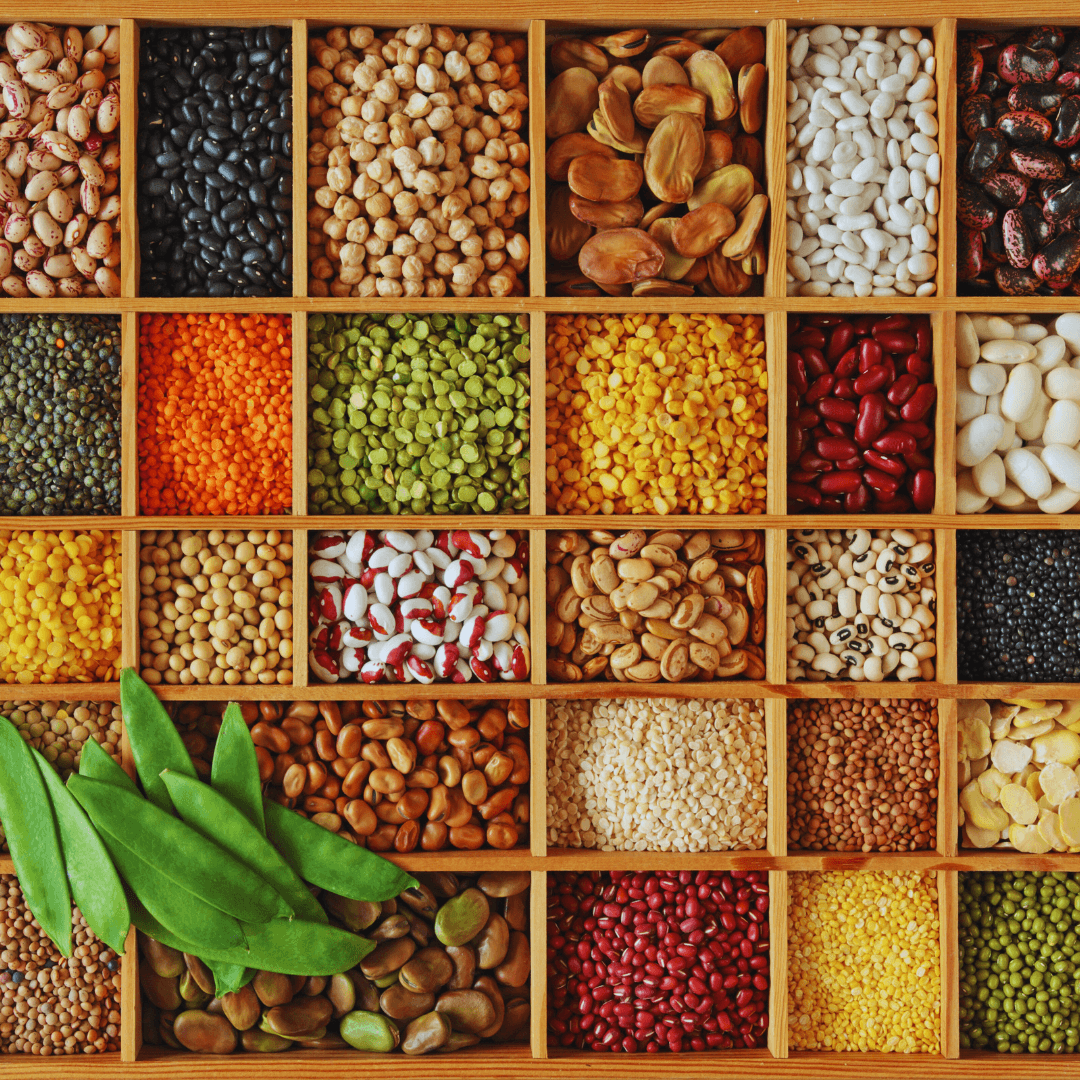

3. Legumes
Legumes, including beans, lentils, chickpeas, and others, are vital in a vegetarian diet, providing protein, fiber, iron, and essential nutrients highlighted in a vegetarian diet.
Rich in plant-based protein, they support muscle health and provide sustained energy.
Additionally, legumes offer dietary fiber for digestive wellness and iron for blood health, meeting crucial nutritional needs.
Incorporating a variety of legumes into a vegetarian diet enhances their nutrient profile and adds delicious texture and flavour, making them a cornerstone of balanced vegetarian eating.
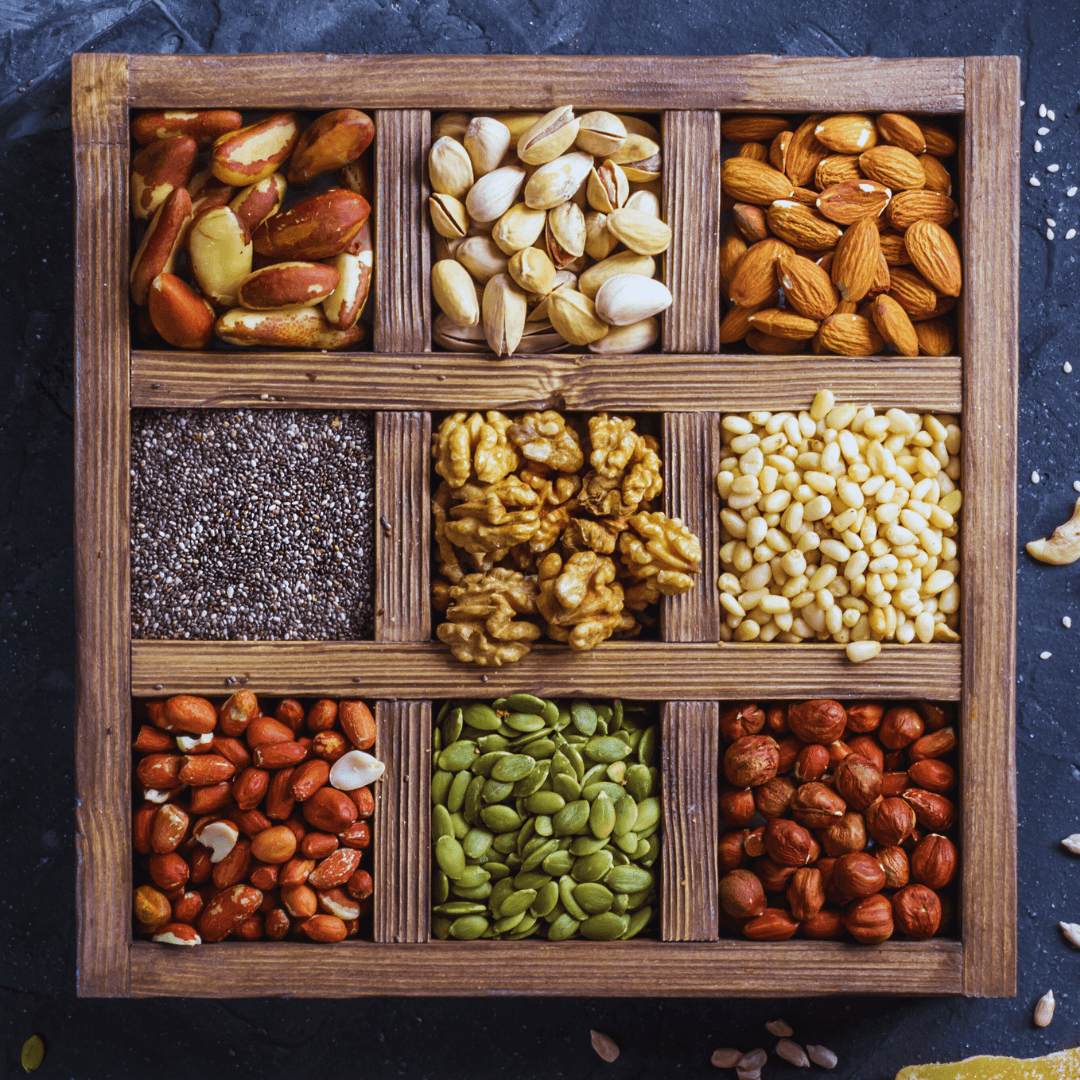

4. Nuts And Seeds For A Vegetarian Diet
Nuts and seeds, such as almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and pumpkin seeds, are necessary for a vegetarian diet.
They are high in protein, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals, promoting overall health. Incorporating nuts and seeds into meals and snacks provides long-lasting energy, boosts brain function, and supports cardiovascular health.
These nutrient-dense ingredients bring wonderful flavour and texture to vegetarian dishes, improving their nutritional profile and encouraging a healthy and full diet.

5. Dairy
Some vegetarians may consume dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt as an option. As a vegetarian diet suggests, they provide additional protein, calcium, and vitamin D.
While dairy is not required, it can easily meet some nutrient requirements for a vegetarian diet.
However, low-fat choices should be chosen and consumed in moderation to maintain a balanced diet. Dairy can help with overall nutritional adequacy and culinary diversity in vegetarian diets.

6. Eggs
According to a vegetarian diet guide, vegans incorporate eggs, which provide an additional source of protein, vitamins, and minerals.
While not mandatory, eggs are nutrient-rich for those who include them in their diet. They offer essential nutrients like vitamin B12, choline, and selenium, supporting overall health and well-being.
Including eggs adds versatility to vegetarian meals and ensures a well-rounded intake of essential nutrients within the dietary framework.
What Are The Health Benefits Of A Vegetarian Diet?
A vegetarian diet guide offers several health benefits. Let’s explore what are the health benefits of a vegetarian diet:
1. Reduced Risk Of Chronic Diseases
Vegetarians often experience a reduced risk of chronic diseases compared to meat-eaters.
Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and pumpkin seeds are all crucial components of a vegetarian diet.
They are high in protein, good fats, vitamins, and minerals, all contributing to general wellness. Incorporating nuts and seeds into meals and snacks gives long-lasting energy, improves brain function, and promotes cardiovascular health.
Additionally, the absence of red and processed meats in vegetarian diets is associated with a lower risk of colorectal and other cancers.
These health benefits underscore the importance of plant-centric eating patterns in disease prevention and overall well-being.
2. Improved Weight Management
In a vegetarian diet guide, improved weight management is a notable benefit. Vegetarian diets are typically lower in calories and saturated fats yet higher in fiber and complex carbohydrates than omnivorous diets.
This nutrient profile aids with weight reduction and maintenance by increasing feelings of fullness, regulating blood sugar levels, and boosting metabolism.
Furthermore, plant-based foods have a lower energy density, allowing people to eat greater portions while maintaining their weight properly.
A vegetarian diet promotes good eating habits that help with long-term weight management and overall well-being by focusing on complete, unadulterated foods.

3. Better Digestive Health
A vegetarian diet promotes better digestive health through its high fiber derived from plant-based foods.
Fibre improves regular bowel movements, prevents constipation, and reduces the risk of digestive diseases such as diverticulosis.
Plant-based foods rich in dietary fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, which promote optimal digestive function and gut health.
By incorporating these fibre-rich foods into meals, individuals following a vegetarian diet can maintain a healthy digestive system, experience improved gastrointestinal comfort, and reduce the risk of digestive complications.
4. Lower Cholesterol Level
A vegetarian diet often results in lower LDL cholesterol (the “bad” cholesterol) than omnivorous diets.
This is primarily attributed to the absence of dietary cholesterol in animal products like meat, poultry, and dairy.
By avoiding these sources of cholesterol, vegetarians may experience reduced LDL cholesterol levels, lowering their risk of heart disease and stroke.
Additionally, plant-based foods' high fiber content and healthier fat profiles contribute to favourable cholesterol levels.
A vegetarian diet emphasizing whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds can help maintain optimal cholesterol levels and support cardiovascular health.
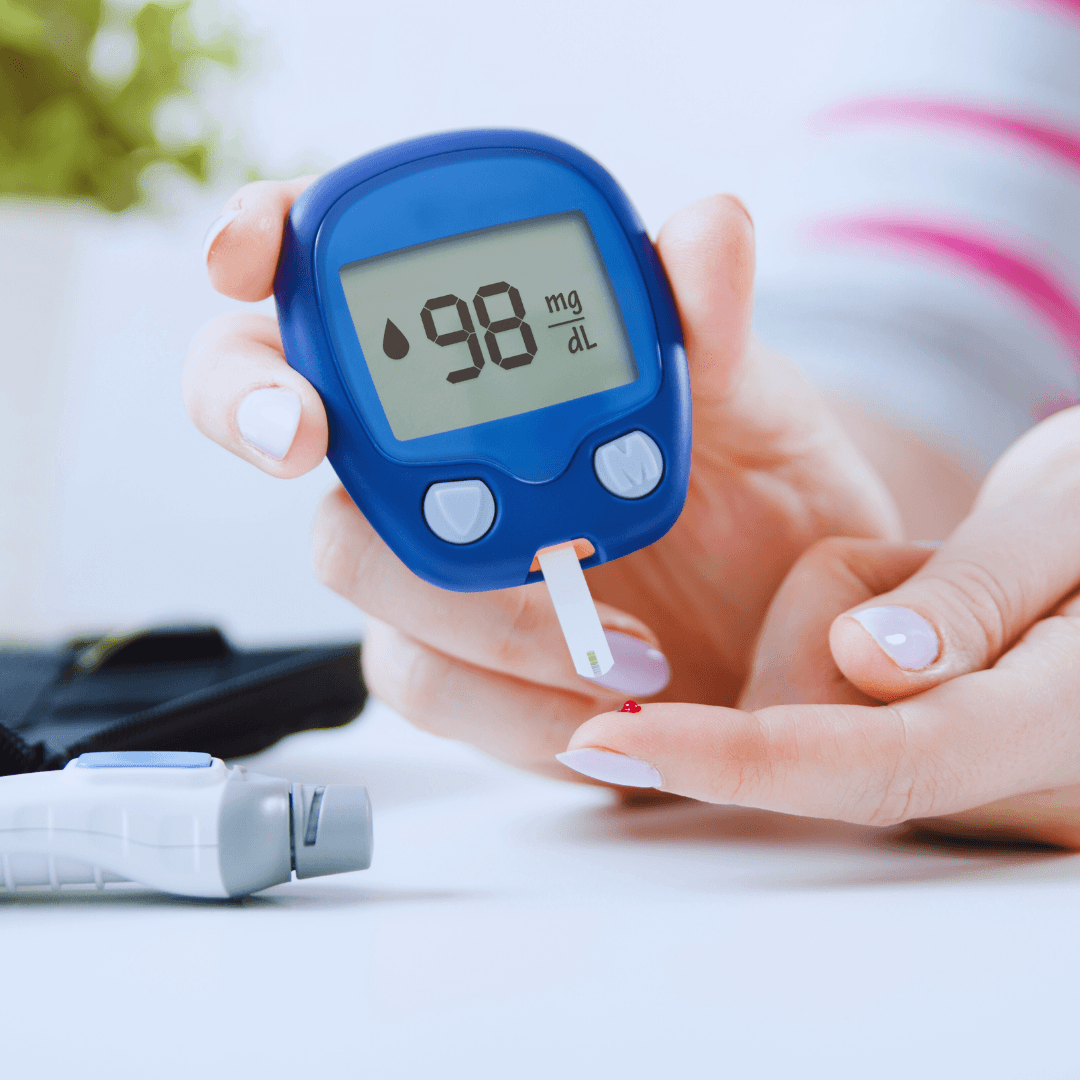

5. Improved Blood Sugar Control
Vegetarian diets are linked to improved blood sugar control, particularly advantageous for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
Focusing on plant-based foods rich in fibre, complex carbohydrates, and nutrients can help vegetarians better regulate blood sugar levels.
This dietary approach helps prevent blood sugar spikes and promotes stable insulin response, reducing the risk of diabetes complications.
Incorporating whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts into meals forms the foundation of a vegetarian diet, offering sustained energy and supporting optimal blood sugar management for overall health and well-being.
6. Reduced Risk Of Hypertension
Plant-based diets, characterized by their abundance of potassium and low sodium content, reduce hypertension risk.
Potassium regulates blood pressure by counteracting sodium's actions and promoting vasodilation, which decreases blood pressure levels.
Excess salt intake, however, has been linked to raised blood pressure. Plant-based diets prioritize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
This helps maintain a favourable potassium and sodium balance, which supports cardiovascular health and reduces the risk of hypertension-related problems.

7. Improved Bone Health
While calcium intake might be lower in certain vegetarian diets, incorporating fruits, vegetables, and plant-based sources of calcium remains crucial for maintaining bone health.
These foods contain vital nutrients such as calcium, magnesium, vitamin K, and potassium, which promote bone density and strength.
Dark leafy greens, tofu, almonds, fortified plant milk, and orange juice are calcium-rich plant-based options.
Vegetarians can ensure adequate calcium intake by including various foods to support optimal bone health and reduce the risk of osteoporosis-related issues.

8. Lower Risk Of Stroke
A vegetarian diet that is abundant in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and nuts may decrease the risk of stroke.
This dietary pattern benefits blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and inflammation, all risk factors for stroke.
By prioritizing nutrient-dense, plant-based foods, vegetarians support cardiovascular health and reduce the likelihood of stroke-related complications.
The combination of fiber, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals in these foods contributes to overall well-being and helps maintain optimal vascular function.
Adopting a vegetarian diet can be a proactive measure in stroke prevention, promoting long-term health and vitality.
How Do You Have A Healthy Vegetarian Diet?
To maintain a healthy vegetarian diet, we must know how to have a healthy vegetarian diet. Consider these tips as a vegetarian diet guide:

1. Include A Variety Of Food
To maintain a healthy vegetarian diet, ensure dietary diversity by including various foods.
Incorporate multiple fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds to guarantee a comprehensive intake of essential nutrients crucial for overall well-being.
By embracing this variety, you can harness the diverse nutritional profiles of different foods, optimizing your nutrient intake and supporting your body’s functions.
Aim to incorporate other colours, textures, and flavours into your meals to make them nutritious and enjoyable. This will ensure you meet your body’s requirements for sustained health and vitality.
2. Get Enough Protein
Ensure sufficient protein intake in your vegetarian diet by incorporating various protein-rich foods.
Eat plant-based foods such as beans, lentils, tofu, nuts, and seeds to meet your protein requirements.
These meals are protein-rich and contain critical elements such as fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
Diversifying your protein sources allows you to maintain a well-rounded and balanced diet that promotes muscular health, satiety, and general well-being.
Experiment with different recipes and cooking ways to creatively incorporate these protein-rich items into your meals, improving nutrition and flavour in your vegetarian diet plan.
3. Prioritize Nutrient Options
Focus on nutrient-dense foods to optimize your vegetarian diet. Prioritize selections that contain iron, calcium, vitamin B12, and other critical minerals for overall health.
Eat iron-rich foods such as leafy greens, lentils, fortified cereals, and nuts to promote blood health.
Choose calcium-rich foods like fortified plant-based milk, tofu, almonds, and leafy greens to promote bone health.
Additionally, ensure adequate vitamin B12 intake through fortified foods or supplements. By prioritizing these nutrient-rich options, you can support your body's needs and thrive on a vegetarian diet.

4. Limit Processed Food For A Healthy Vegetarian Diet
To maintain a healthy vegetarian diet, you must know how to limit your consumption of processed foods and instead prioritize whole, unprocessed options.
Minimize intake of processed vegetarian alternatives, such as veggie burgers or mock meats, which may contain added sodium, unhealthy fats, and preservatives.
Choose entire foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, which are high in nutrients and free of additives.
Focusing on whole, unprocessed foods on a vegetarian diet maximizes nutrient intake, improves overall health, and maintains adequate nutrition. Choose natural, whole foods for maximum vitality.
5. Stay Hydrated
Maintain hydration by prioritizing water consumption and incorporating water-rich foods into your diet.
Drink enough water throughout the day to maintain bodily functions and avoid dehydration.
Additionally, to supplement your fluid intake, consume fruits and vegetables with high water content, such as cucumbers, watermelon, strawberries, and lettuce.
These hydrating foods contribute to water intake and provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Staying hydrated with fluids and water-rich foods can support optimal hydration, aid digestion, promote clear skin, and enhance overall well-being on your vegetarian diet.
6. Opt For Healthy Fats
Include sources of healthy fats in your vegetarian diet to improve heart health. Choose foods high in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, such as avocados, almonds, seeds, and olive oil, which have been shown to improve cardiovascular health.
When ingested in moderation, these good fats help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and the risk of heart disease.
Including these nutrient-dense foods in your meals provides essential fatty acids, vitamins, and antioxidants, supporting overall well-being.
By prioritizing healthy fats, you can maintain heart health and enhance the nutritional quality of your vegetarian diet.
7. Listen To Your Body
Listen to your body’s signals and tailor your vegetarian diet guide accordingly. Pay close attention to how different foods make you feel, noting any changes in energy levels, digestion, mood, or overall well-being.
If certain foods cause discomfort or negatively impact your health, consider adjusting your diet to accommodate your needs.
Experiment with food choices, meal timing, and portion sizes to find what works best. By prioritizing self-awareness and making informed dietary choices, you can optimize your vegetarian diet to support your unique health and wellness goals.
8. Plan Balanced Meals
Plan well-rounded meals that encompass a variety of nutrients for balanced nutrition. Ensure each meal includes a combination of carbohydrates, protein, healthy fats, fiber, vitamins, and minerals to support overall health and well-being.
Incorporate whole grains, legumes, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds into your meals to provide diverse nutrients.
Balancing these food groups can optimize your nutrient intake, promote sustained energy levels, and support various bodily functions.
Aim for colourful, flavorful meals that nourish your body and satisfy your taste buds, ensuring a satisfying and nutritious vegetarian diet.
FAQ
1. What is not a beneficial characteristic of a vegetarian diet?
Answer: Nutrient inadequacies are one possible disadvantage of a vegetarian diet, especially regarding elements like vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids frequently present in animal products.
With careful planning, vegetarians may be able to obtain adequate levels of these nutrients, which can lead to health issues like anemia, bone health concerns, and impaired cognitive function.
However, if necessary, these deficiencies can often be mitigated with mindful food choices and supplementation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, eating a vegetarian diet has numerous health benefits, including a lower risk of acquiring chronic illnesses such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes.
People can eat a nutrient-dense diet that supports general health by focusing on plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
While careful planning is crucial to ensure sufficient nutrients like protein, iron, calcium, and vitamin B12, a well-balanced vegetarian diet can provide all essential nutrients for optimal health.
Moreover, by prioritizing sustainability and ethical concerns, vegetarians contribute to environmental conservation and animal welfare, fostering long-term health and vitality.
I trust you enjoyed this article about the Best Vegetarian Diet Guide. Please stay tuned for more blog posts soon. Take care!
JeannetteZ
>>>Please click here to read my Vegan Travel Guides To World Destinations<<<
>>>Want To Learn How To Create Delicious, Cruelty-Free, Healthy AND 100% Vegan Meals? Try These Awesome Vegan Cooking Courses With A Free 7-DAY MEMBERSHIP<<<
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I would love to hear from you. Please leave me your questions, experiences, and remarks about the Best Vegetarian Diet Guide article in the comments section below. You can also email me at Jeannette@LivingTheVeganLifestyle.org.
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. I earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate and other affiliate programs. Please read my full disclosure.
Here are links to some of my favourite articles:
Vegan Recipes Gluten And Dairy-Free – Culinary Magic
Vegan Diet B12 Deficiency – What You Need To Know
What Is A Lacto Ovo Vegetarian Diet
Vegetarians And Vitamin B12 Deficiency






