Vitamin E For Vegans: The Ultimate Guide To This Essential Nutrient
Strong antioxidant vitamin E is essential for cell defence, immune system stimulation, and healthy skin and eyes. Vitamin E is easily accessible in various plant-based foods for vegans, ensuring you can meet your needs without relying on animal products.
Numerous plant-based foods are rich in this vital nutrient, making it easy to meet your needs with the proper knowledge.
This guide will explore the importance of Vitamin E for vegans.
It highlights vegan-friendly sources and tips for incorporating them into your diet to support a healthy, plant-based lifestyle.
How Much Vitamin E Do We Need?
For most individuals, the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for vitamin E is approximately 15 milligrams (22.4 IU) per day, though this varies by age and gender.
This quantity supports immune function, protects cells from oxidative stress, and promotes healthy skin and eyes. Pregnant and breastfeeding women have similar requirements, though infants and children need less.
Since vitamin E is fat-soluble, the body stores it in its fatty tissues. Hence, getting enough regularly is essential, but excessive supplementation is unnecessary and can even be harmful.
Vegans may typically get enough vitamin E each day from a balanced diet because plant-based sources such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils are high in the vitamin.
Almonds, sunflower seeds, spinach, and avocado are particularly potent sources, making them excellent choices for a daily boost.
For vegans who may worry about deficiencies, incorporating various foods can provide sufficient Vitamin E without needing supplements.
However, those with health conditions affecting fat absorption, such as cystic fibrosis or Crohn’s disease, might require additional guidance from a healthcare provider.
A mindful diet approach is needed to ensure that one gets the right amount of Vitamin E to support a vibrant, healthy vegan lifestyle.
Sources Of Vitamin E In A Vegan Diet
Vegans can enjoy a variety of plant-based foods rich in Vitamin E. Here are some of the best sources:
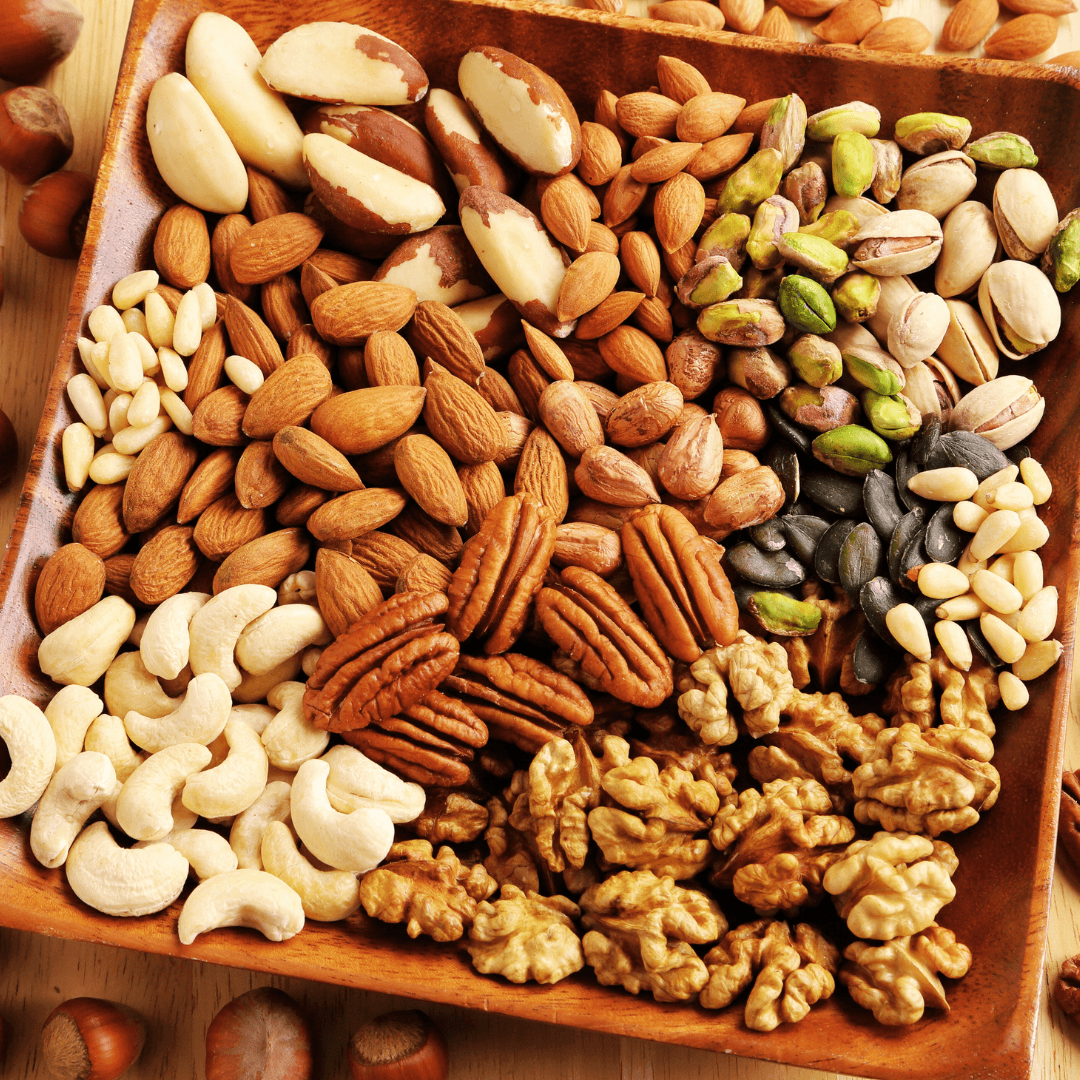
1. Nuts
Almonds are among the best sources of Vitamin E, providing 7.3 mg per ounce. Hazelnuts and peanuts are also reasonably priced, making them convenient and tasty options for a nutrient-packed snack.
They’re versatile and easy to add to meals, whether in smoothies, granola, or alone. Their healthy fats and Vitamin E support skin health and boost your immune system simply and satisfyingly.

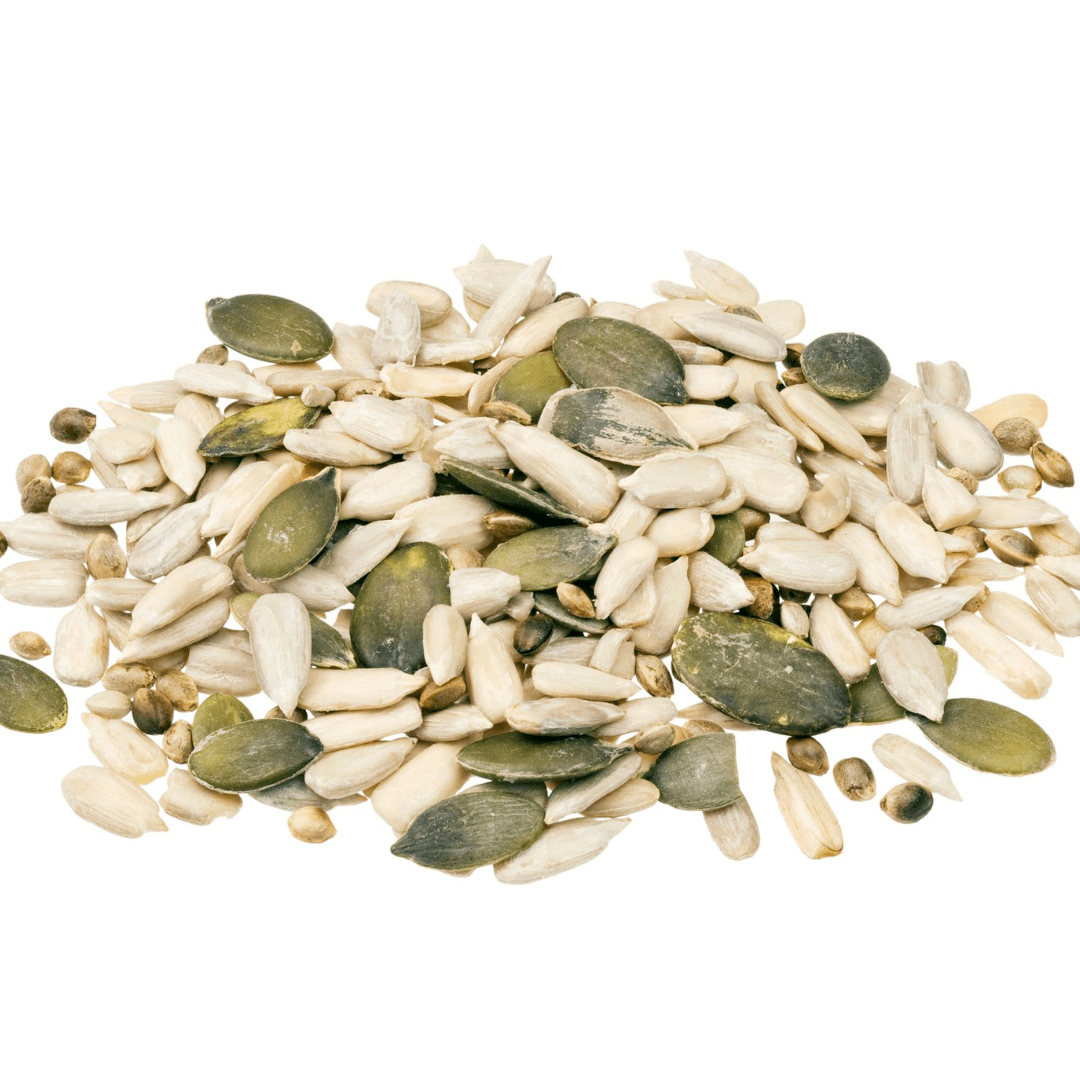
2. Seeds
Vitamin E is abundant in sunflower seeds, which provide 7.4 mg per ounce, about half the daily requirement! Pumpkin seeds are also a solid choice, adding a nutrient boost to salads, smoothies, or as a snack.
These seeds are rich in minerals, antioxidants, and good fats. They promote skin vibrancy, heart health, and general wellness in a tiny, crunchy package.

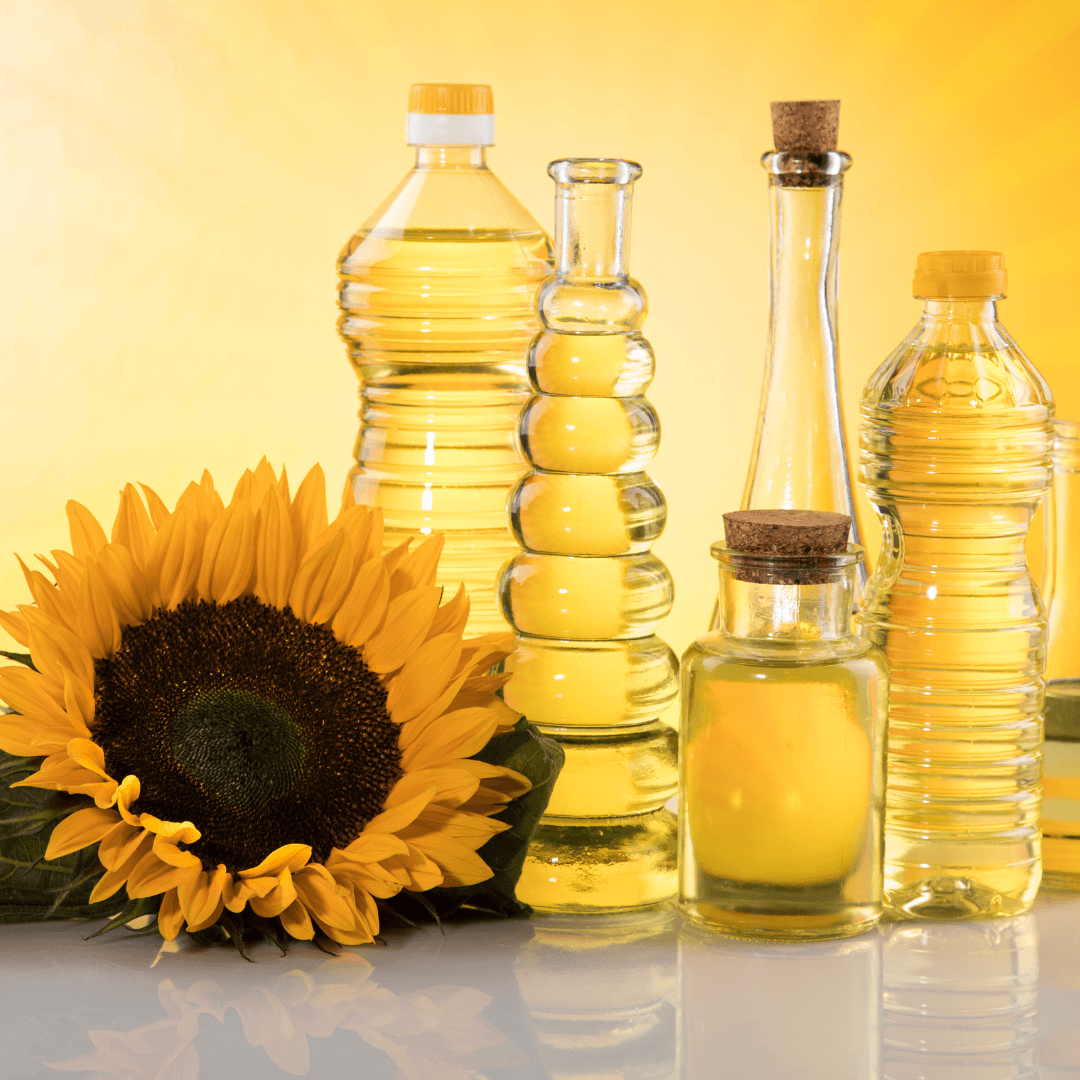
3. Vegetable Oils
Wheat germ oil is the highest in Vitamin E, with around 20 mg per tablespoon, making it a standout source. Sunflower, safflower, and olive oils are also excellent choices.
These oils are perfect for pouring over food, dressing salads, and sautéing because they are high in antioxidants and good fats.
By adding these oils to your meals, you can significantly increase your intake of Vitamin E, which supports cell protection, immunity, and healthy skin.

4. Green Leafy Vegetables
Leafy greens such as spinach, Swiss chard, and collard greens are excellent sources of Vitamin E, with one cup of spinach providing approximately 0.6 mg. A healthy diet must include these veggies, high in vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients.
Incorporating foods rich in Vitamin E for vegans into salads, smoothies, or stir-fries can help boost your intake of this essential nutrient, along with fiber and antioxidants, for improved overall wellness.

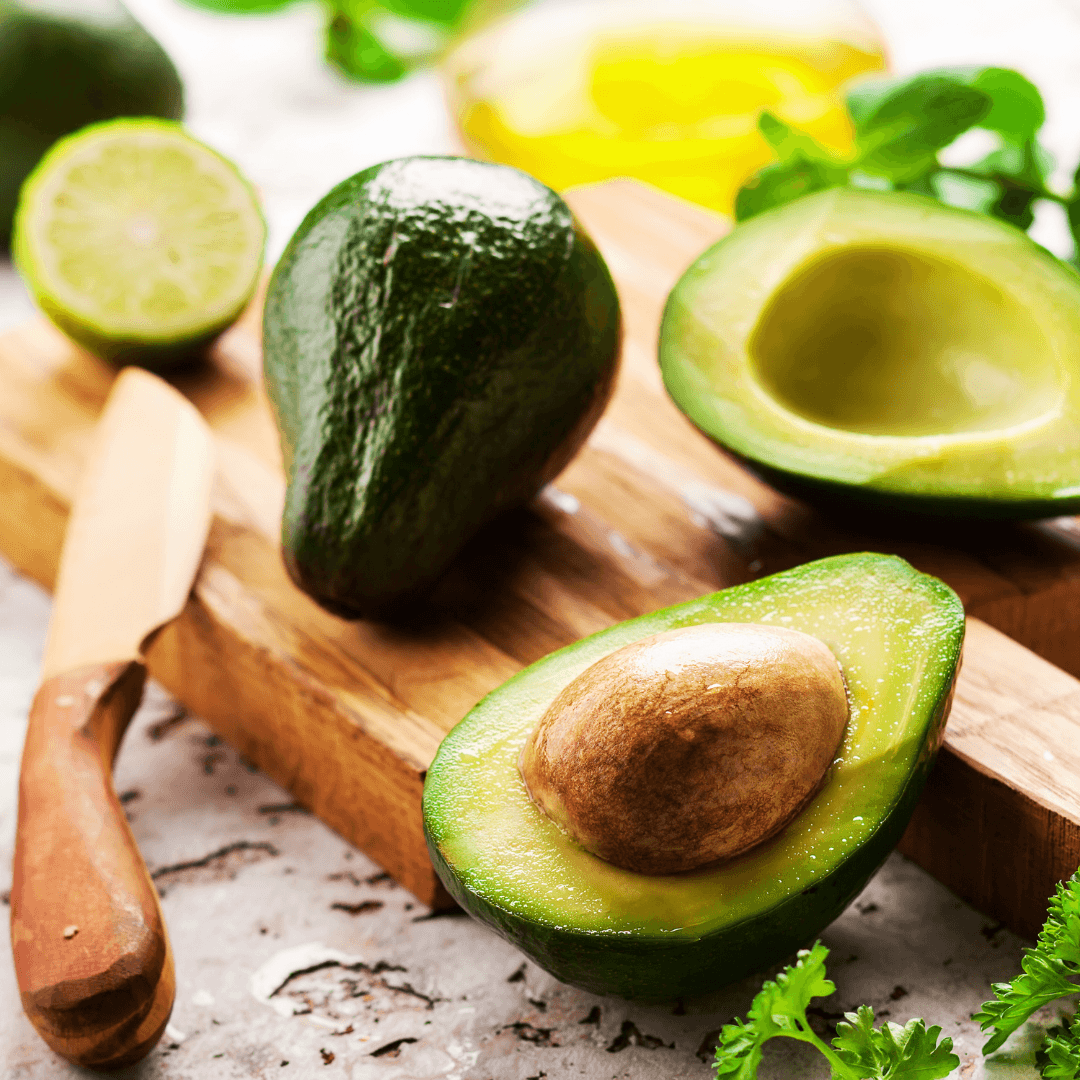
5. Avocado
A single avocado offers up to 4 mg of Vitamin E, making it an ideal source of this essential nutrient. Avocados are also a great source of fiber, antioxidants, and good fats. They are versatile and can be added to salads or sandwiches, or spread on toast.
They help maintain healthy skin, reduce inflammation, and support overall heart health, making them a nutritious and delicious addition to a vegan diet.

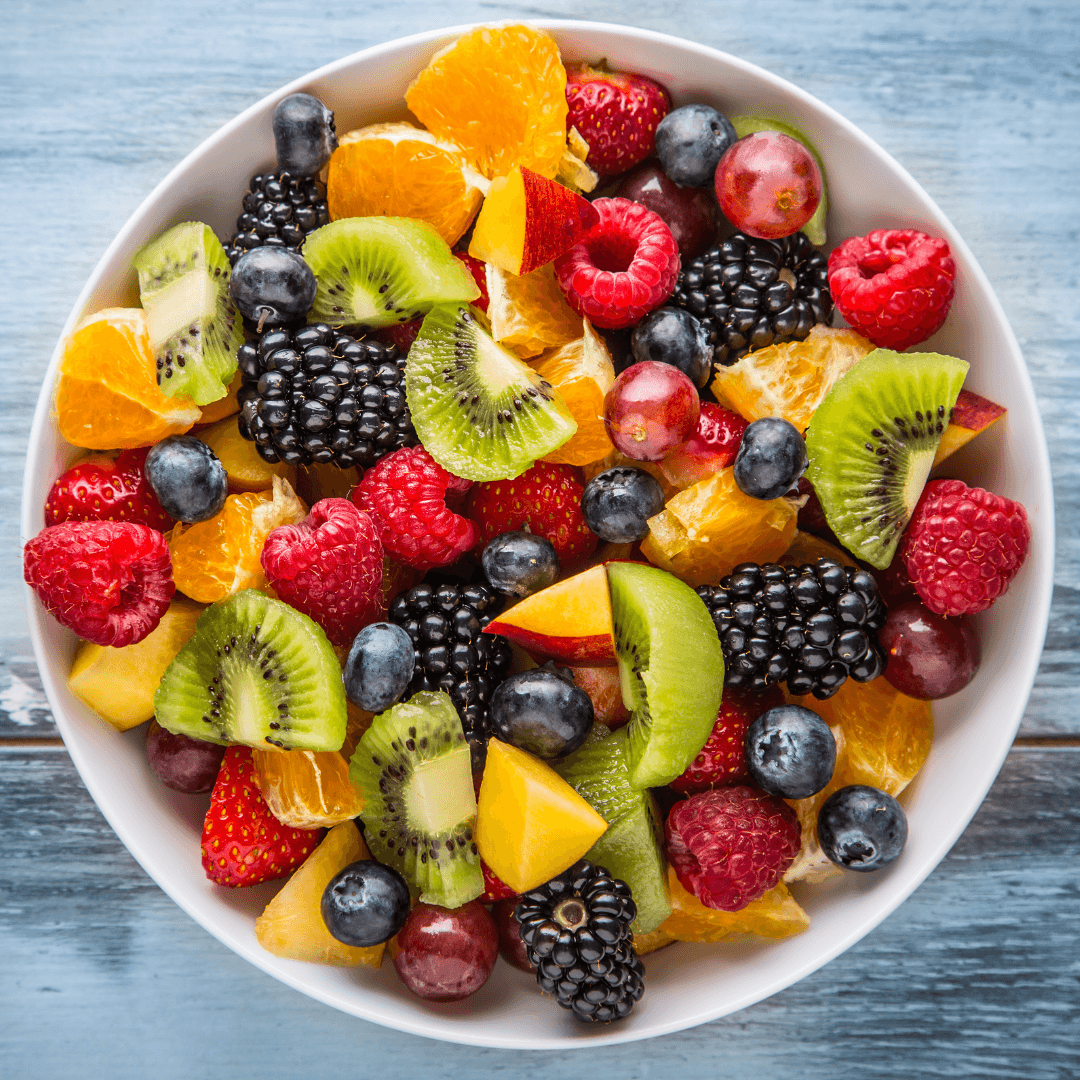
6. Fruits
Fruits like kiwis, blackberries, and mangoes provide moderate amounts of Vitamin E and other vitamins and antioxidants. Eating a portion of these fruits is a tasty way to increase your Vitamin E intake while savouring their incredible flavours.
They’re perfect in smoothies, fruit salads, or as snacks. They support immune health, skin vitality, and overall well-being while adding variety and natural sweetness to your diet.

7. Whole Grains
Whole grains like oats, quinoa, and brown rice provide moderate amounts of Vitamin E, fibre, iron, and other essential minerals. These grains are great for energy, digestive health, and overall wellness.
Adding them to salads, breakfasts, or side dishes is a simple way to boost your intake of Vitamin E while still enjoying a nutritious, fulfilling, and complete meal.
8. Tomatoes
Tomatoes are a mild source of Vitamin E for vegans, and cooking them can enhance nutrient absorption, making them a tasty addition to various meals. Adding them to sauces, soups, or fresh salads provides a colourful, delicious way to enhance your meals.
Tomatoes are also rich in antioxidants, which support cell health and protect against damage. Their versatility and natural sweetness make them a perfect addition to various vegan dishes, providing taste and nutrition.
9. Bell Peppers
Vitamin E is especially abundant in red and yellow bell peppers, which provide good antioxidants. Because of their sweet, crunchy texture, bell peppers are perfect for salads, stir-fries, and snacking.
In addition to vitamin E, bell peppers contain vitamin C and other elements promoting collagen synthesis, skin vibrancy, and immunological function.
Their vibrant colour and flavour bring a delightful twist to any meal, making them both nutritious and flavourful.

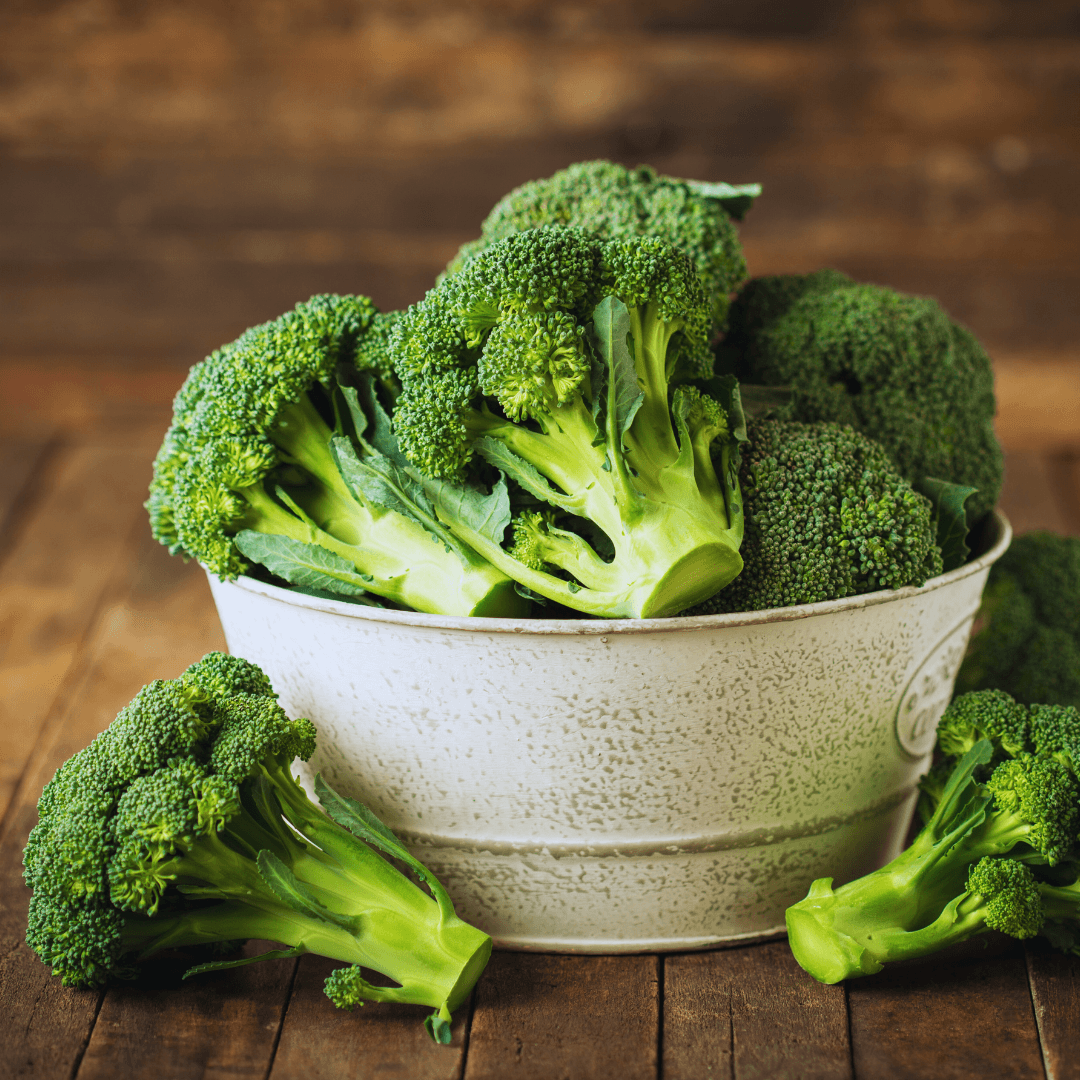
10. Broccoli
Broccoli is a great source of vitamin E, especially when you roast or steam it to retain its benefits. This green vegetable pairs well with various dishes and offers multiple health benefits, including immune support and skin health.
Packed with vitamins A, C, and K, as well as antioxidants, broccoli is a nutrient-dense option that can be easily added to any meal, supporting overall wellness.

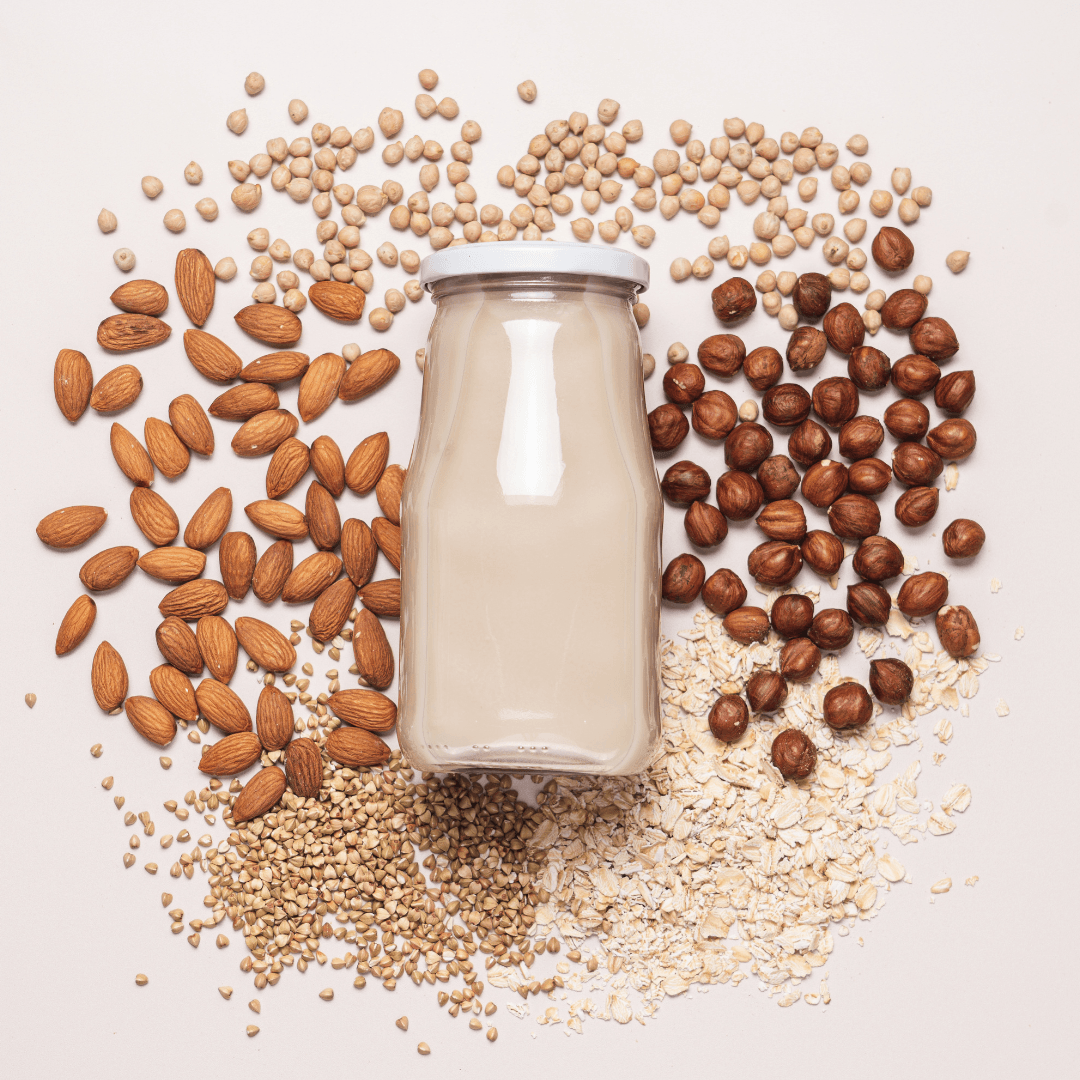
11. Fortified Plant Milk
Fortified plant milk, such as almond, soy, and oat milk, is enriched with Vitamin E, making it a convenient and versatile addition to a vegan diet. It can be added to smoothies, coffee, or poured over cereal, offering an easy way to boost your Vitamin E intake.
Along with the essential nutrients, they provide calcium and other vitamins, supporting bone health, skin vitality, and overall nutrition in a delicious form.

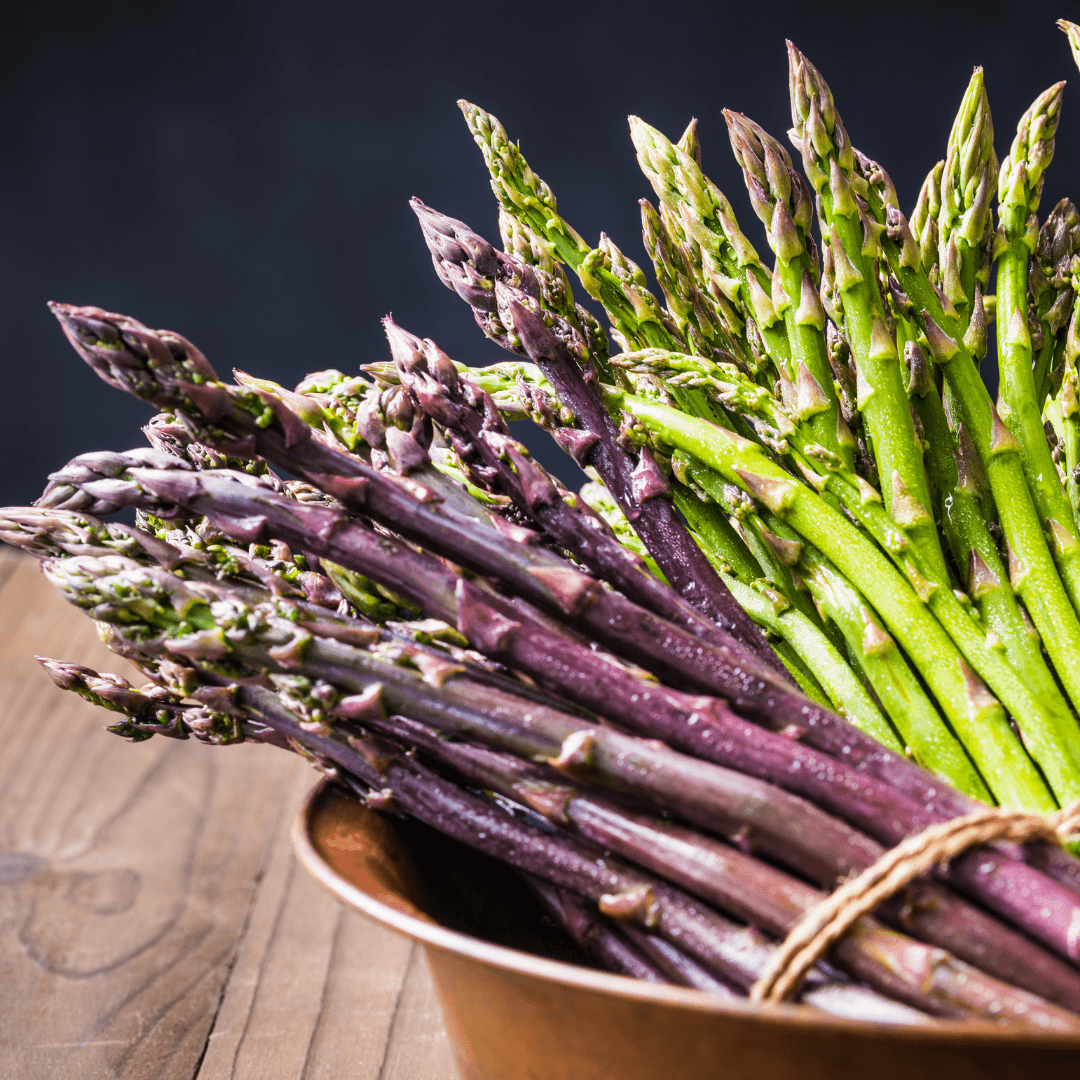
12. Asparagus
Asparagus provides a modest amount of Vitamin E and a rich blend of vitamins A, C, and K. Whether grilled, steamed, or roasted, asparagus is a flavourful and nutrient-packed side dish that complements a balanced vegan meal.
The antioxidants and vitamins found in asparagus support skin health, immune function, and overall wellness. Its unique flavour and versatility make it an excellent choice to enhance your meals' taste and nutritional profile.

The Benefits Of Vitamin E For Vegans
This antioxidant-rich vitamin is crucial for vegans for the following reasons:
1. Powerful Antioxidant Properties
A potent antioxidant, vitamin E aids the body's defence against free radicals. Unstable substances called free radicals can cause oxidative stress, which damages cells and contributes to the development of chronic diseases.
By combating oxidative stress, Vitamin E helps protect the body from conditions like heart disease, cancer, and premature aging.
Vegans can obtain these protective benefits by consuming plant-based sources of Vitamin E, such as nuts, seeds, and green leafy vegetables.
2. Supports Skin Health
Vitamin E is widely known for its role in promoting healthy skin. By keeping the skin flexible, it reduces the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. Because of its antioxidant properties, it shields the skin from pollution and UV rays.
For vegans, sources like avocados, nuts, and seeds naturally nourish and protect the skin. Regular consumption of Vitamin E-rich foods can also aid in healing scars, burns, and other skin conditions.
3. Improves Immune Function
Vitamin E is essential for vegans to boost immune system health, enhance immune cell function, and help the body fight infections despite potential nutrient gaps in a plant-based diet.
It improves immune cell function, helping the body fight infections and illnesses. A healthy immune system is essential for vegans, as plant-based diets can sometimes be low in certain nutrients that support immune function.
Vegans can ensure their immune systems remain strong and resilient by including Vitamin E-rich foods like spinach, broccoli, and sunflower seeds.
4. Promotes Heart Health
Vitamin E helps support cardiovascular health by preventing the oxidation of LDL cholesterol, which can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries.
This reduction in oxidative damage lowers the risk of atherosclerosis, arterial constriction, and other cardiovascular disorders.
Due to plant-based diets, vegans tend to have lower cholesterol levels and healthier hearts. They can further benefit from Vitamin E's heart-healthy properties by incorporating more nuts, seeds, and plant oils, such as olive oil, into their meals.
Want to Share Your Passion for Vegan Living?
Discover how easy and fulfilling vegan living can be —
from recipes and travel to lifestyle and sustainability tips.
Read this blog post next:
How to Start a Vegan Blog (and Turn Your Passion into Purpose).
5. Enhances Cognitive Function
Research suggests that Vitamin E may offer protection against neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer's and cognitive decline. It is believed to reduce oxidative stress in the brain, thereby protecting neurons and maintaining mental function.
Almonds, sunflower seeds, spinach, and other foods high in vitamin E provide vegans with a natural means of promoting brain health and lowering their risk of cognitive decline as they age.
6. Vitamin E Helps Manage Hormonal Balance
Maintaining hormonal equilibrium, especially in women, requires vitamin E. It is thought to stimulate the production of estrogen, which helps control menstrual cycles and lessen symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
This is particularly beneficial for vegans, as plant-based diets can sometimes be lower in certain nutrients like iron, which is crucial for hormone health. Foods like avocado, sunflower seeds, and green leafy vegetables can support hormone regulation and well-being.
7. Supports Eye Health
Vitamin E is essential for preserving eye health because it shields the cells in the eyes from oxidative damage, which can cause cataracts and age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Incorporating sources of Vitamin E, such as spinach, sweet potatoes, and bell peppers, into vegan diets can support good vision and reduce the risk of age-related eye conditions.
8. Improves Circulation and Reduces Inflammation
It is well known that vitamin E helps increase blood circulation by preventing platelets from clotting and facilitating the blood's flow throughout the body.
Several conditions, such as autoimmune disorders and arthritis, are associated with chronic inflammation, and anti-inflammatory compounds can help alleviate it.
Vegans incorporating Vitamin E-rich foods such as almonds, sunflower seeds, and spinach can help reduce inflammation and naturally improve circulation.

Challenges Vegans Face With Vitamin E Intake
Meeting the recommended daily Vitamin E intake for vegans can be challenging, despite Vitamin E's abundance in various plant-based foods. Here are some of the primary difficulties:
1. Limited Sources In The Vegan Diet
Many plant-based foods contain Vitamin E, but are often less concentrated than animal-derived sources. For example, many of the richest sources of Vitamin E, such as eggs and dairy products, are not part of a vegan diet.
While many plant-based foods provide Vitamin E for vegans, they are often less concentrated than animal-derived sources, so vegans may need to incorporate options like nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils to meet daily needs.
2. Inadequate Daily Intake
The recommended daily vitamin E intake for adults is 15 mg daily. While foods like sunflower seeds, almonds, and avocado are excellent sources, they may not always be part of a person’s everyday meals.
Inadequate intake of these foods, whether due to dietary preferences, lack of availability, or simply not consuming them in sufficient quantities, can lead to deficiencies.
For instance, many vegans may opt for low-fat diets or avoid certain foods, such as nuts, due to concerns about calorie intake, thereby inadvertently reducing their Vitamin E intake.
3. Vitamin E Absorption
Vitamin E, a fat-soluble vitamin, is better absorbed when consumed in fat form. However, many vegan diets emphasize low-fat foods, which can hinder the absorption of this essential nutrient.
It may be more challenging for vegans who avoid high-fat foods like avocados, nuts, and seeds to absorb Vitamin E from plant-based sources.
Pairing Vitamin E-rich foods with healthy fats, such as olive oil, flaxseeds, and avocados, is crucial to ensure proper absorption.
4. Different Forms Of Vitamin E
Vitamin E has several forms, with alpha-tocopherol being the most active in the human body. Many plant-based sources contain tocopherols and tocotrienols, which the body may need to utilize more efficiently.
While Vitamin E from plant-based sources is still beneficial, vegans may have difficulty obtaining the most bioavailable form. This is particularly relevant when relying on fortified foods, where the form of Vitamin E may vary.
5. Fortified Foods May Not Provide Enough
While many vegan-friendly products are fortified with Vitamin E for vegans, they may only sometimes provide enough to meet the daily recommended intake.
The amount of Vitamin E added to these foods can vary, and some fortified options may contain low levels that do not make a notable difference.
As such, vegans relying solely on fortified foods may still need to pay close attention to their overall Vitamin E consumption to avoid deficiencies.
Common Myths About Vitamin E And Veganism
Myth #1: Vegans Can’t Get Enough Vitamin E
This myth is easily debunked by highlighting the many plant-based sources rich in Vitamin E. Vegans can access sufficient Vitamin E from nuts, seeds (like sunflower seeds), avocados, leafy greens, and vegetable oils. A well-planned diet that includes these foods ensures optimal Vitamin E intake without the need for animal products.
Myth #2: Only Supplements Provide Sufficient Vitamin E
Whole food sources of Vitamin E, like nuts, seeds, and green vegetables, offer a more bioavailable and balanced intake than supplements.
These foods provide additional nutrients, antioxidants, and fiber, supporting overall health in ways supplements cannot. Whole foods are the best way to naturally meet daily Vitamin E needs while enjoying a variety of flavours.
FAQs
Q1: Can I Get Enough Vitamin E On A Vegan Diet?
Yes! Plenty of plant-based foods are rich in vitamin E, including nuts (like almonds), seeds (such as sunflower seeds), plant oils, and green leafy vegetables. A well-balanced vegan diet can meet your daily vitamin E requirements.
Q2: Do I Need To Take A Vitamin E Supplement As A Vegan?
Most vegans can get enough vitamin E from food sources. However, specific individuals may benefit from a supplement, especially if they have limited access to vitamin E-rich foods or specific health conditions that affect nutrient absorption.
Q3: Can I Cook With Vitamin E-Rich Oils, Or Will Cooking Destroy Vitamin E?
Cooking with vitamin E-rich oils like olive or sunflower oil is okay, but high heat can reduce their vitamin E content. To preserve vitamin E, consider using these oils in salads or adding them after cooking.
Q4: Are There Any Side Effects Of Taking Too Much Vitamin E?
Yes, taking excessive amounts of vitamin E, mainly through supplements, can have adverse effects like exhaustion, nausea, and even bleeding problems. Stick to the recommended daily intake and only use supplements if necessary.
Conclusion
Vitamin E is crucial for general health for vegans, and you can naturally achieve your nutritional needs by including a range of plant-based foods in your meals.
By incorporating various foods into your meals, you can ensure you meet your Vitamin E needs without relying on supplements. As a vegan, you can maintain your health and vigour by carefully managing your diet.
I trust you enjoyed this article on Vitamin E For Vegans: The Ultimate Guide To This Essential Nutrient. Please stay tuned for more plant-based recipes, vegan travel tips, and lifestyle inspiration.
Take care!
— JeannetteZ 🌿
💬 Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I’d love to hear from you. Please leave your comments below, or email me directly at Jeannette@LivingTheVeganLifestyle.org.
📚 More Vegan Lifestyle Reads
🌱 My #1 Recommendation for Online Success
Sharing my passion for vegan living — from food to fashion — has been such a rewarding journey.
If you’ve ever dreamed of building your own ethical lifestyle brand or blog, this is the best place to start.
🌟 See How Vegan Bloggers Build Online Income — Try WA Free (No Credit Card Needed)
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate and participant in other affiliate programs, I earn from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you. Please read my full affiliate disclosure.