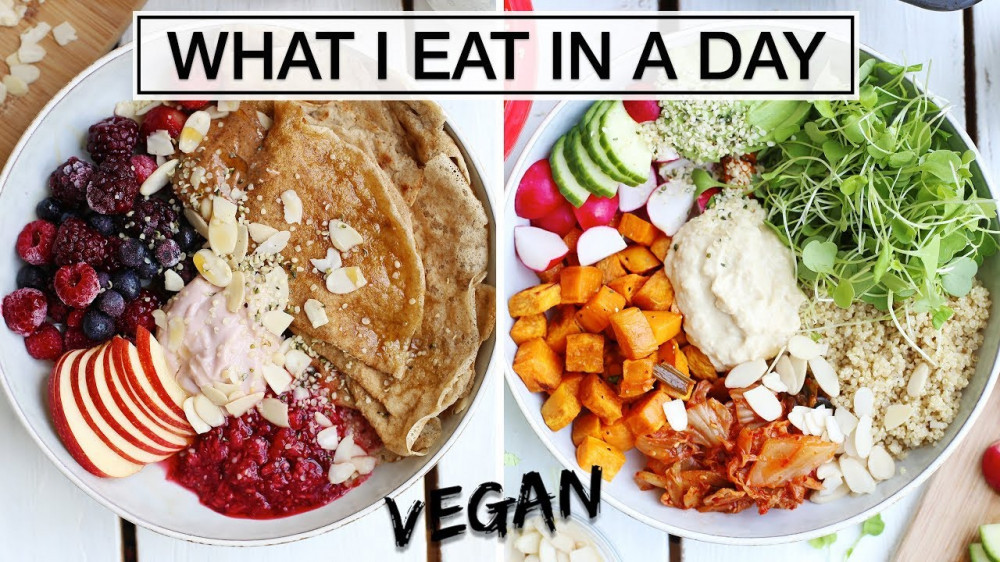
What Do Vegans Eat In A Day
What Do Vegans Eat In A Day
Everybody loves to talk about the latest and greatest disease-preventing superfood — but have you actually made it a part of your daily diet? As a cardiovascular nurse and nutrition consultant, I spend much of my time wading in the muck of preventable chronic diseases, and I’ve dedicated my life to understanding nutrition science and lifestyle medicine.
And more importantly for you, how those two disciplines can be used to prevent and treat disease. What I’ve found is that certain healthy foods — normal foods, not hard-to-find superfoods — have a remarkable capacity to protect you from disease, increase athletic performance, and give you a fighting chance of living a long, healthy life.
Vegetarian diets continue to increase in popularity. Reasons for following a vegetarian diet are varied but include health benefits, such as reducing your risk of heart disease, diabetes and some cancers. Yet some vegetarians rely too heavily on processed foods, which can be high in calories, sugar, fat and sodium.
And they may not eat enough fruits, vegetables, whole grains and calcium-rich foods, thus missing out on the nutrients they provide. However, with little planning, a vegetarian diet can meet the needs of people of all ages, including children, teenagers, and pregnant or breastfeeding women. The key is to be aware of your nutritional needs so that you plan a diet that meets them.
The vegan movement is very strong right now, with many people choosing to make the often-dramatic diet and lifestyle change. There are now countless blogs, Instagram accounts, websites and restaurants dedicated to the diet/ lifestyle that have made veganism more accessible, easy and acceptable than ever.
Where a vegetarian may eat some animal products like dairy and eggs, a vegan eats absolutely no animal products, including any foods that have come from an animal – including things like honey. The reasons for going vegan range from the known health benefits of including more plant foods and reducing animal foods from the diet, environmental reasons and the treatment and harm that may come to the animals in processing.
These are all incredibly valid reasons for making such a drastic change to a diet. However, much care needs to go into creating a perfectly balanced vegan diet because so very many essential nutrients can be missing, which can cause serious health implications in the long term. More often than not, some of those nutrients simply can’t be met in the diet alone, and often dietary supplements will be needed to fill in those nutritional gaps.
There are many different interpretations of the so-called plant-based diet. For example, vegan, vegetarian, the Mediterranean diet, the flexitarian diet, and simply limiting meat intake in favour of plant-based foods all qualify as plant-based diets.
No matter which plans you opt for, one thing’s for sure: Prioritizing plant-based foods has never been more popular. According to a Washington Post article, the research firm Mintel found that the number of food and drinks that included the phrase “plant-based” increased 268 percent between 2012 and 2018. (The Mintel report is available only through purchase.) (1)
Krista Linares, RDN, MPH, a registered dietitian and the founder of Nutrition con Sabor, based in Raleigh, North Carolina, says there are two main reasons for the surge in popularity of plant-based diets. “First, concerns over global warming have led to people looking for more environmentally sustainable options, and animal proteins are generally thought of as less environmentally sustainable than plant-based proteins,” she says. “Second, there has been an influx of popular documentaries promoting plant-based or vegan and vegetarian diets.”
The Importance Of A Healthy Diet
Studies have shown that it takes only six minutes for your brain to register the damage that a diet has on your health. When you eat junk food, it slows your body’s ability to absorb certain nutrients, impairs your immune system, and disrupts your hormonal and digestive systems.
The truth is, everything that you put in your mouth has an impact on your health. Eat all the good stuff. Virtually all our medical research is supporting the fact that vegetables, fruits, and whole grains are the foundation of a healthy diet.
Vegetarian diets are rich in healthful fats. Most popular types of vegetarian foods, such as beans, soy, nuts and seeds, are high in good unsaturated fats such as omega-3 fatty acids, which lower cholesterol levels and may help prevent heart disease. Not all fats are created equal, however. For example, animal fat may provide the body with important healthful compounds like vitamin A and protein, while plant fat may not be as good for health.
Plant-based diets also provide many important nutrients. Vegetables are the richest source of protein, and highly nutritious dark green vegetables such as broccoli, spinach, and kale are high in fiber. Eating plenty of vegetables helps keep you full for longer, helps you keep a healthy weight and protects you against many diseases.
Why Are Vegan Diets Good For You?
First, it’s true that in most cases, meat-eating is associated with an increased risk of developing chronic diseases, such as obesity, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. But the association is only one of the many unknowns that make it hard to disentangle cause and effect.
Vegan diets are a convenient way to save your digestive system. If you’re getting the same amount of protein, fat, and carbohydrates as if you were eating meat, then these micronutrients are being digested at the same rate, but the fiber, minerals, and other components that cause gas, bloating, and gas are coming into your gut at a lower rate.
Because they exclude foods that may contain a lot of fat, sugar or calories, a vegan diet generally tends to be lower in calories, especially from saturated fats. In fact, following a vegan diet can reduce your risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes and some cancers. So, if you're following a vegan diet for health reasons, you can lower your risk of some common health problems.
Vegan diets don't depend only on what you eat but on how much you eat, too. So, with careful planning, you can have a healthy, balanced diet. You can lose weight by going vegan, but you'll likely experience a rapid drop in your weight. For some people, this can happen in only one week.
What Are The Drawbacks Of Being Vegan?
Let’s be clear: there are no drawbacks to being vegan. It has been scientifically proven to be an incredibly healthy lifestyle for your heart, brain, and gut. What I’d suggest is to adopt veganism as a lifestyle, not a diet. This means eating only whole foods (vegetables, fruits, and grains) that you grow or raise yourself, as well as eating other healthful foods like legumes, nuts, seeds, beans, and nuts.
Is a vegan diet best for everyone? Oh, yes. There are countless people whose health has improved drastically and who have significantly reduced their inflammation and their suffering, simply by switching their diet from a highly processed, highly saturated-fat, and highly-processed-sugar one to a plant-based, unprocessed one.
On one hand, it may be easier to live a vegan lifestyle, but not all meat substitutes are suitable for pregnant or nursing mothers or children. Many people who have tried vegetarianism have chosen to return to a meat diet. While meat does have nutritional benefits, it does not have the benefits of plant foods such as fiber, vitamins and minerals, and it's possible for a person to have too many of certain nutrients.
Some adults may also find vegetarian diets too restrictive and prefer to eat meat. Excluding meat from your diet can cause digestive issues, and may not allow you to meet your vitamin and mineral needs. The health benefits of vegan and vegetarian diets are only in the long term.
How To Get Started With Veganism
Before you start following a vegan diet, you will need to stock your fridge and pantry with vegan-friendly foods. For starters, you may want to try replacing meat with plant-based foods, such as tofu, tempeh, seitan, lentils and quinoa, as well as vegetables such as broccoli, cauliflower, carrots, spinach, tomatoes, potatoes and sweet potatoes.
Then it’s time to move on to fruits and vegetables, which provide many of the vitamins and minerals that we need every day. Avoid sugars, such as table sugar, brown sugar and fructose. Chewing your food slowly helps to reduce cravings for sweet foods. Also, avoid excess caffeine, and be careful of eating too many processed foods. Lastly, and most importantly, eat a wide variety of foods.
What Do Vegans Eat In A Day?
On a typical day, a vegetarian will eat a little less than half as much animal protein as a carnivore eats, and a little more than one-quarter as much saturated fat. An omnivore eats three times as much of those items and five times as much processed carbs. By going vegan, you can reduce the calories in your diet by a third, nearly eliminate cholesterol and high blood pressure, and get the huge amount of beneficial nutrients that your body needs in a balanced diet.
Losing weight — A vegetarian diet does not have the same calories as a meat-eating diet, which means that you can lose a lot of weight very quickly. Plus, the high-quality plant protein in plant-based foods makes it easy to lose weight and keep it off.
Veganism originated in Denmark, and the Vegan Society’s official position is that a vegan diet is ethical, environmentally friendly, and healthful. Vegetarians live on approximately 1.5-2 cups of vegetables per day, and to meet this need they usually eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, along with beans, whole grains and nuts, as well as beans and other legumes.
Veganism is also high in protein. As much as 200 grams of protein are required daily for health and energy. Vegan diets tend to be very healthy, especially for women. They include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and beans and lentils as staples, along with nuts, seeds, soy and legumes, fish and eggs, which are often all used in a variety of ways.
Fruits And Vegetables
The plain truth is that you can’t live without fruits and vegetables, and the more of them you eat, the better off you are. Look at how many people suffer from chronic disease in this country, especially from heart disease and diabetes. Remember, it’s not about excluding certain foods from your diet, but about eating a variety of foods that are as close to being in their natural state as possible. Just because they’re in a packaged form, it doesn’t mean they’re always safe or the best for you.
Fruits and vegetables offer a host of benefits to vegans, including high-fibre and vitamin C, which can protect against heart disease, bone health, cancer, diabetes and certain types of arthritis. Furthermore, plant foods, like fruits and vegetables, contain a variety of beneficial phytochemicals, such as beta-carotene, vitamin C and antioxidants, which may help to protect against health problems like diabetes, cancer and heart disease. For adults, a typical diet should include 1-2 cups of fruit or vegetables daily (although some experts recommend up to three to four cups per day).
Meat Substitutes
One of the most misunderstood components of a healthy diet is protein. As people, we need protein in the form of meat and dairy products. But studies have shown that plant proteins, such as beans, peas, lentils, soy, nuts and seeds, don’t raise blood cholesterol as quickly and don’t clog arteries.
They have a different blood-clotting effect than animal proteins, and they don’t make you gain weight, as a protein overdose from red meat would. (This is not true for vegetarian proteins, which have higher glycemic spikes than meat.) Eating a variety of plant proteins, from avocado to quinoa to peanut butter, is crucial to supporting long-term health and combating diseases associated with a Western diet.
Many vegetarians turn to meat alternatives in order to satisfy their dietary needs. Non-meat substitutes are a great way to introduce vegetarians to meat and vegan eating. Because these products can taste so much like meat, meat eaters may find that their old favourites are satisfying with non-meat alternatives.
The ingredients used in these products vary greatly. For example, veggie burgers may use flour or vegetable shortening as their main ingredient, but bacon substitutes may use gluten and meat. This is important to be aware of before you make a purchase and to be sure that the product you are choosing will satisfy your dietary needs.
Tofu, Seitan And Tempeh
Fiber-rich, protein-packed, and filling, these versatile foods keep you feeling full for longer and have become an increasingly popular tool in the toolbox for managing diabetes, blood sugar, obesity, heart disease and other diseases that are associated with a sedentary lifestyle.
These foods can help improve digestion, aid in weight loss, decrease inflammation, improve heart health, boost brain function, and prevent allergies, irritable bowel syndrome and digestive problems. Many of the vegan foods you’ve heard of — quinoa, hemp seeds, kale, broccoli, bok choy, and cauliflower, for example — are excellent sources of many of these same key plant proteins, plus they are a delicious way to get more veggies in your diet.
Many vegetarians substitute meat-like products, including soy products such as tofu, seitan and tempeh, which have great protein and fiber content but are not meat. Soy products are low in fat, protein and calories and are a good source of B vitamins, magnesium, fiber, calcium and phytonutrients, such as omega-3 and beta-carotene.
These plant products can be a good source of protein for vegetarians who might not be eating meat. These products are also healthy options for vegans and vegetarians who are lactose intolerant or who cannot eat dairy. A vegetarian diet that includes at least one of these protein-rich foods has been shown to have some of the same health benefits as a diet that includes at least two daily servings of meat.
Beans And Lentils
Beans are the powerhouse of the plant kingdom. In one serving, you’ll get nearly a quarter of your daily requirement of fiber, almost a quarter of your daily value of Vitamin B6 and iron, and lots of iron-rich Vitamin B2, which may reduce your risk of heart disease and certain cancers. Lentils, a particularly good legume, have the power to elevate your overall health. Your body will absorb the fiber and vitamins A and C faster and more efficiently, and this helps keep your gastrointestinal tract moving.
Cacao (Chocolate)
Chocolate is a favourite, sweet treat. Cocoa beans are prepared from the bark of the Theobroma Cacao tree. The cocoa bean’s rich cocoa butter content provides a rich source of healthy monounsaturated fat, along with protein, fiber, vitamins and minerals. A small amount of real or natural cacao nibs can be used to prepare a vegan chocolate drink. Cacao powder and pure cocoa butter can be added to some recipes to achieve the rich flavour and consistency of real chocolate, along with other nuts or oats.
Fresh Pressed Juice And Smoothies
In the past, I’ve been a fan of juice bars. My go-to spot growing up was Jamba Juice and I still think the premium blends taste great and are inexpensive. But these bars typically don’t offer much nutrition beyond the juice itself, especially with added sugars and artificial ingredients, such as gums, colourants, and sweeteners.
If you want to get a good source of nutrients, the juice is no longer the answer. If you choose to juice, choose fresh-pressed juice. Real fruit juice comes from whole fruit that’s been cut up into small pieces. And all the juice should be from the fruit that’s been picked at its peak of ripeness. Avoid juice with added sugars, sweeteners and preservatives, such as fruit punch, apple juice, kiwi fruit and other fruit smoothies.
Bread And Pasta
Whole grain bread and pasta make it easy to meet your nutritional needs while still eating whole foods. Eating whole-grain foods can boost your nutrient intake, such as fiber, dietary fiber, and vitamin B, or B2, which helps control blood sugar. Whole-grain foods are high in complex carbohydrates and fiber that promote satiety and help you feel full.
Choose non-dairy milk in these categories: soy, almond, coconut, oat, rice and organic. These milk all contain less than 3 grams of fat per cup and can be a convenient source of calcium and vitamin D. However, they can contain phthalates, chemicals commonly found in cosmetics and personal care products, so be sure to read the labels.
Grains
- Wheat
- Beans
- Barley
- Oats
- Quinoa
- Rice
There are several good sources of protein. Quinoa, pumpkin seeds, peanut butter, chickpeas and beans are great, as are legumes such as lentils and beans. When you add these foods to your diet, you’re almost certain to be getting enough protein. High-quality protein includes those foods that contain at least 13 grams of protein per serving (8-ounces) and is primarily made of animal or plant sources.
Conclusion
So, what’s the difference between a healthy vegan and an unhealthy vegan? A healthy vegan, like me, follows a plant-based diet with plenty of fresh vegetables and fruits, healthy fats, and vitamins. An unhealthy vegan eats only processed meat, lots of unhealthy vegetable oils, sugary foods, and desserts.
When you eat meat, you're eating disease-causing animal cells. When you eat an animal, you're eating disease-causing animal tissues. When you eat dairy, you're eating what's inside of an animal. When you eat processed food, you're eating what's in a package. When you eat desserts, you're eating sugar. It doesn't matter what kind of food you eat — every bite of processed meat, chocolate, butter, or oil carries with it a risk of disease.
Having a well-balanced diet is important for good health. If you have difficulty meeting your nutritional needs, consider seeing your doctor for a nutrition counselling session. The American Heart Association offers some tips on what foods are good for you, what foods are bad for you and how to meet your nutritional needs for good health.
I trust you enjoyed reading the article about What Do Vegans Eat In A Day? Please stay tuned. There are more blog posts to come very shortly.
JeannetteZ
Want To Learn How To Create Delicious, Cruelty-Free, Healthy AND 100% Vegan Meals? Try These Awesome Vegan Cooking Courses With A Free 7-DAY MEMBERSHIP
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Ideas? Thoughts? Questions? I would love to hear from you. Would you please leave me your questions, experience, and remarks about this article on What Do Vegans Eat In A Day in the comments section below? You can also reach me by email at Jeannette@LivingTheVeganLifestyle.org.
Here are the links to some of my favourite articles:
The Vegan Diet And Everything To Know
What Can Vegans Take For Anemia?
A Brief History Of Veganism – Know Your Roots