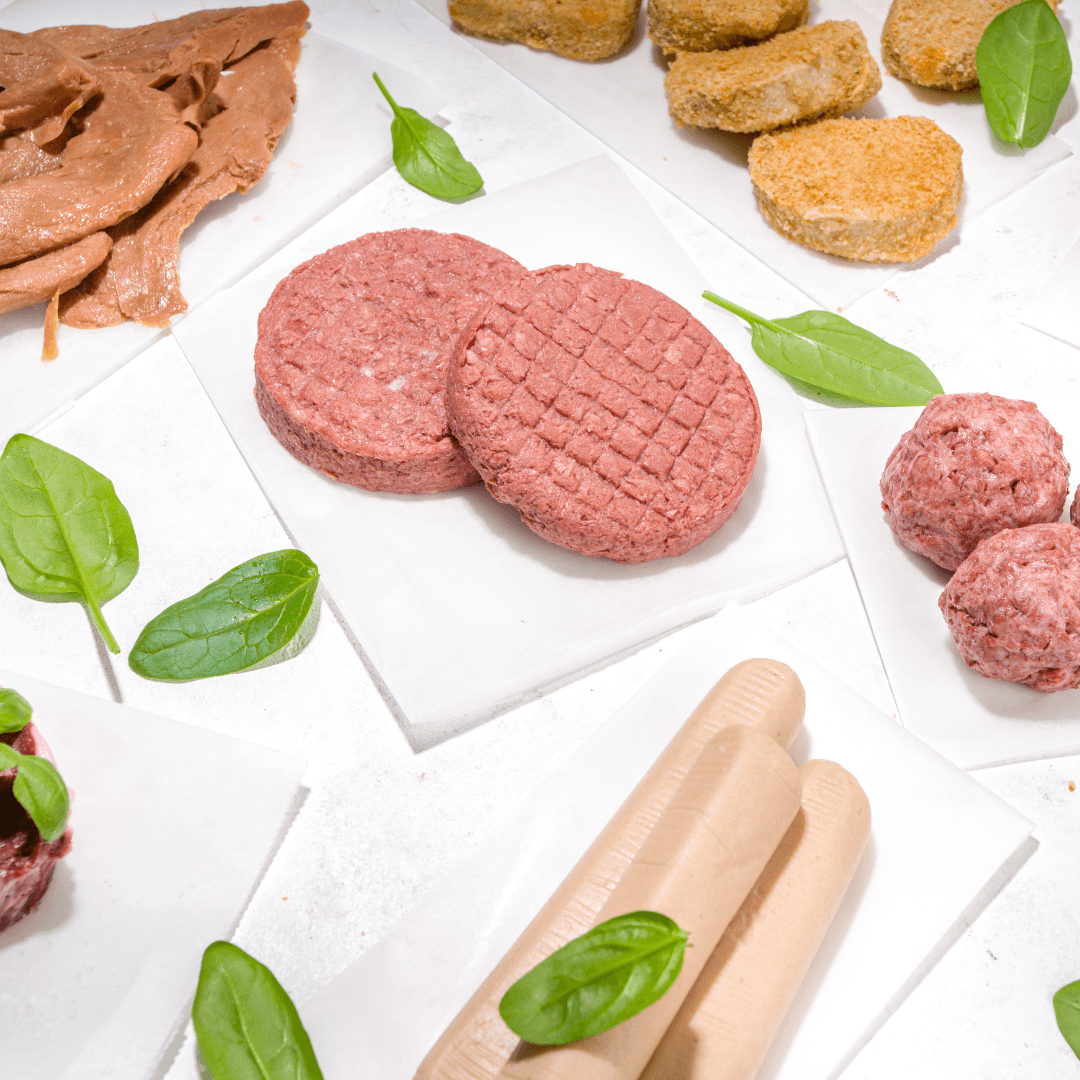
How Vegan Meat Is Made
How Vegan Meat Is Made
The need for plant-based substitutes for conventional animal products is expanding, and this need is fundamentally altering the culinary landscape.
Among the most fascinating innovations in this realm is the creation of vegan meat – a category of food products designed to replicate the taste, texture, and visual appeal of meat without animal-derived ingredients.
This emerging trend has captured the attention of vegans, vegetarians, and a broader audience interested in exploring sustainable and ethical food choices.
Delving into how vegan meat is made unveils a world of culinary creativity, scientific advancements, and a commitment to reshaping our relationship with food and the environment.
This article will unravel the behind-the-scenes magic of crafting these delicious and ethical alternatives, shedding light on the processes and ingredients that bring vegan meat to life.

Benefits Of Vegan Meat
In a world where dietary choices are no longer confined to traditional norms, the rise of vegan meat has sparked a culinary revolution.
Beyond its ability to tantalize taste buds, vegan meat offers many benefits that extend far beyond the plate.
This innovative approach to nourishment caters to ethical and environmental concerns and ushers in a new era of mindful eating. Here are the details about the benefits of vegan meat you should consider:
1. Healthier Nutritional Profile
Vegan meat often has lower cholesterol levels and saturated fat than traditional animal-derived meats. It can offer important elements such as dietary fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants to support a balanced diet.
2. Reduced Risk Of Chronic Diseases
Due to their lower concentration of saturated fat and higher consumption of fibre, vegan meat alternatives can minimize the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer.
3. Lower Environmental Impact
Vegan meat production generally requires fewer natural resources, including land, water, and energy, than conventional meat production. This reduces greenhouse gas emissions and helps mitigate environmental degradation.

4. Animal Welfare
Opting for vegan meat supports animal welfare by eliminating the need for animal slaughter and reducing demand for livestock farming, which can involve ethical concerns related to animal treatment.
5. Allergen-Friendly
Vegan meat is frequently devoid of common allergens like gluten, dairy, and eggs, making it a good alternative for anyone with dietary restrictions or allergies.
6. Ethical Considerations
Choosing vegan meat aligns with ethical beliefs and values, as it avoids contributing to the exploitation and suffering of animals raised for meat production.
7. Diverse Culinary Options
Vegan meat products are available in various forms, such as burgers, sausages, nuggets, deli slices, and more. This diversity provides consumers with versatile options for creating various dishes.
8. Cultural And Religious Sensitivities
Vegan meat can accommodate cultural and religious dietary restrictions that prohibit or limit the consumption of certain animal products.
9. Global Food Security
As the global population grows, vegan meat production could provide a more sustainable solution to food security by requiring fewer resources to produce sufficient protein sources.
10. Innovation And Variety
The growing popularity of vegan meat has led to ongoing innovation and improved taste, texture, and nutritional value. This results in an expanding range of options for consumers.
11. Supporting Food Innovation
The demand for vegan meat products drives innovation in food technology, leading to the development of plant-based alternatives that closely mimic the taste and texture of traditional meat.
12. Consumer Choice And Accessibility
Consumers have more options thanks to the increased accessibility of vegan meat in eateries, fast-food joints, and grocery shops, making it simpler for people to consume fewer animal products.
13. Positive Impact On Land Use
By shifting towards plant-based protein sources for vegan meat, the demand for land-intensive livestock farming can decrease, potentially allowing for more sustainable land-use practices.
14. Reduced Antibiotic Use
Vegan meat production does not involve raising animals for slaughter, which can reduce antibiotic use in livestock farming and help combat antibiotic resistance.
15. Personalized Diets
Vegan meat products cater to various dietary preferences and lifestyles, including vegans, vegetarians, flexitarians, and those looking to reduce meat consumption.
These benefits collectively contribute to the appeal of vegan meat options, making them an attractive and sustainable choice for individuals seeking healthier and more environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional animal-derived meats.
Discovering How Vegan Meat Is Made
Vegan meat, often called plant-based or meat alternatives, is crafted using plant-derived ingredients that mimic traditional animal meat's taste, texture, and appearance.
The production process involves various techniques and ingredients, allowing manufacturers to create products resembling animal-based meats. Here's an overview of how vegan meat is made:

1. Protein Sources
At the heart of vegan meat production lies a diverse array of plant-based proteins that build up meat-like textures and flavours.
These proteins are carefully selected for their ability to mimic the texture, mouthfeel, and nutritional profile of animal-based meats.
Soy is a well-known protein source frequently used in vegan meat products due to its versatility and high protein content.
Wheat gluten, also known as seitan, is another crucial ingredient that provides a dense and chewy texture similar to certain meat cuts.
Legumes such as peas, beans, lentils, and chickpeas are rich sources of protein that contribute not only to the texture but also to the nutritional value of vegan meats.
These legumes enhance protein content and offer dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Mushrooms often provide umami flavours and a meaty texture to vegan burgers and sausages.
Even unconventional sources like algae are being explored for their protein content and unique properties in vegan meat development.
Algae can provide a sustainable and nutrient-rich protein source while offering a distinct flavour profile.
The careful combination of these plant-based proteins allows manufacturers to recreate the chewiness, juiciness, and overall mouthfeel people associate with traditional meats.
Moreover, the diverse selection of protein sources enables a range of flavours and textures, making it possible to replicate various meat products, from tender steaks to hearty sausages.
The creativity in using these protein sources to produce a new generation of plant-based meat substitutes that please both the palate and customers' ethical concerns develops along with the popularity of vegan diets.

2. Texturization
Texturization is crucial in creating vegan meat, as it aims to replicate the intricate fibrous structure of animal-based meat.
This is achieved by employing ingredients like soy protein isolate or wheat gluten, which have unique properties that allow them to form fibrous networks when hydrated and processed.
Soy protein isolate, derived from soybeans, is often used due to its high protein content and ability to create a meat-like texture.
Similarly, wheat gluten, known as seitan, is a staple in many vegan meat recipes, particularly for its chewy and substantial texture.
The process typically involves mixing the chosen protein source with water or other liquids to create a dough-like consistency.
This mixture is then subjected to mechanical processing, which aligns the proteins and forms a fibrous matrix.
This matrix resembles the muscle fibres in animal meats and contributes to the desired chewiness and bite of the final product.
Beyond protein sources, natural binders like starches or gums may be added to improve texture and cohesion.
Additionally, incorporating fats, oils, and flavourings enhances the taste and mouthfeel, replicating the sensory experience of consuming traditional meat.
Texturization in vegan meat production requires a delicate balance of ingredients, processing techniques, and recipe formulation.
By recreating the complex fiber arrangement in animal meats, food scientists and manufacturers can craft plant-based alternatives that closely resemble the textures and eating experiences people associate with meat consumption.
This meticulous process showcases the innovation and dedication behind creating satisfying and sustainable vegan meat products that cater to consumers' evolving preferences.

3. Flavour Profile
Flavour is an essential component of meat, and in the realm of vegan meat, it plays a pivotal role in creating an authentic and satisfying eating experience.
To replicate the rich and savoury taste that meat is known for, manufacturers of vegan meat products employ a variety of ingredients and techniques.
One commonly used ingredient is yeast extract, which contains natural compounds that contribute to a meaty and umami flavour.
Similarly, soy sauce, with its salty and umami notes, enhances the depth of taste in vegan meats. Vegetable broths, made from aromatic vegetables and herbs, are also utilized to infuse a comforting and hearty flavour profile.
Incorporating an array of spices is another method to mimic the complex taste of animal-based meat.
Ingredients like garlic, onion powder, paprika, and various herbs add distinctive flavours and evoke the familiar aromas of cooking meat.
The careful selection and blending of these spices aim to achieve a balanced and robust flavour that resembles the sensory experience of consuming traditional meat.
Food scientists and chefs work meticulously to craft the ideal combination of flavour-enhancing ingredients, aiming to replicate the taste of meat and offer a unique and enjoyable culinary experience for vegans and non-vegans alike.
The intricate interplay of flavours in vegan meat products underscores the innovative techniques employed to create products that align with ethical and environmental values and cater to consumers' evolving palates and preferences seeking plant-based alternatives.

4. Colour And Appearance
The visual aspect of meat is undeniably important, as it often influences our perception and anticipation of a meal.
In vegan meat, replicating animal-based meat's natural colours and appearance is a meticulous art.
Manufacturers turn to various natural colouring agents derived from plants to achieve this. For instance, beet juice, rich in deep red pigments, infuses vegan burgers with a pinkish hue that resembles the colour of cooked beef.
Similarly, annatto, a natural dye extracted from the seeds of the achiote tree, imparts a warm, golden-brown shade to sausages and other meat substitutes.
The goal is to capture the desired colour and recreate the appealing contrast between the exterior sear and the tender interior that characterizes well-cooked meat.
Achieving this visual appeal enhances the overall sensory experience of consuming vegan meat, making it visually enticing and inviting.
It's worth noting that the efforts to replicate colour and appearance aren't solely for aesthetics; they also break down barriers for individuals transitioning to a plant-based diet, as a familiar appearance can contribute to a more comfortable and enjoyable dining experience.
The careful selection and application of natural colours underscore the dedication of food technologists and chefs to create products that satisfy our taste buds and eyes.
As the demand for vegan meat continues to grow, innovations in colour replication will likely evolve, resulting in even more convincing and captivating alternatives that align with the principles of ethical eating while catering to consumers' diverse preferences.
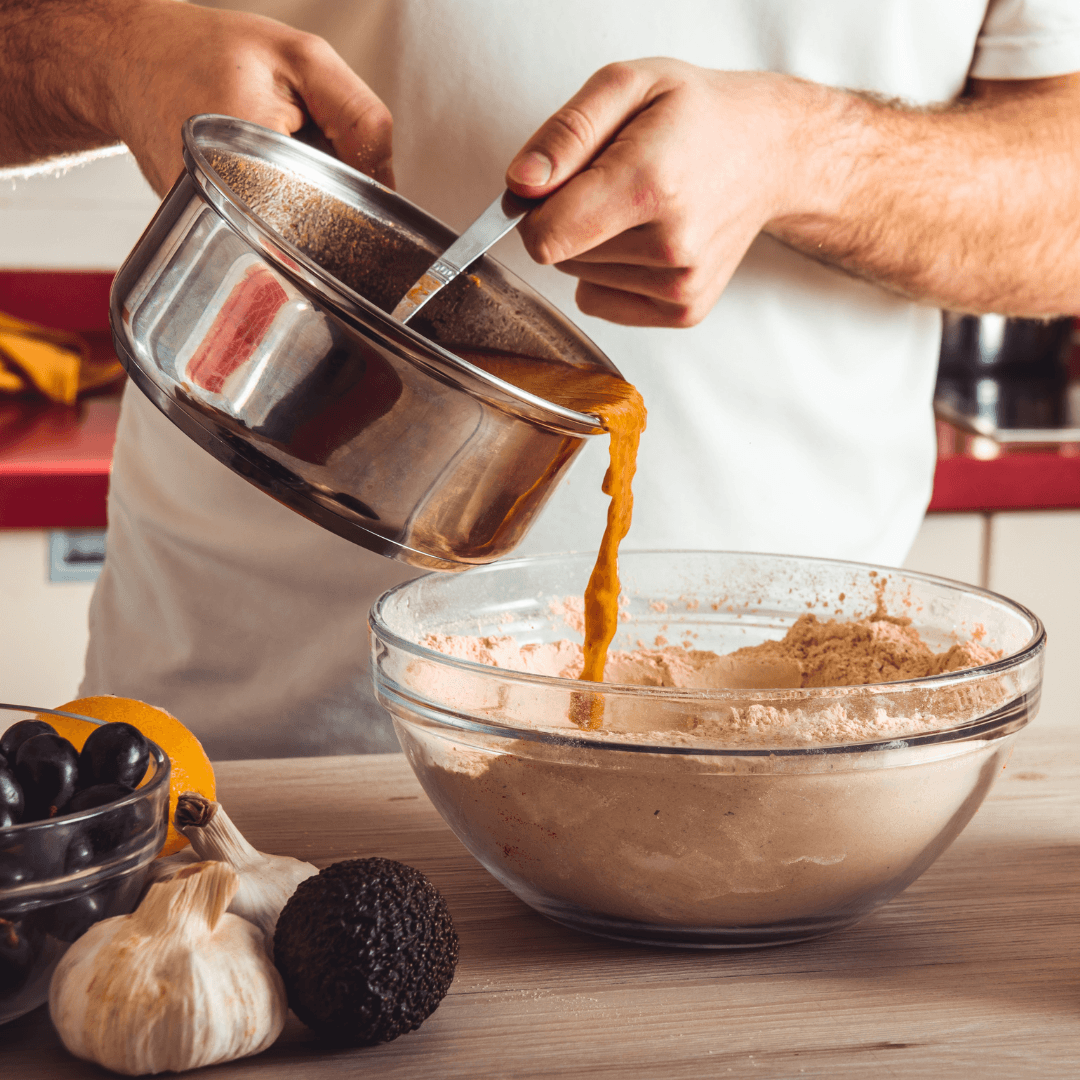

5. Binders And Fat
Creating the desired texture and mouthfeel in vegan meat products requires careful consideration of binders and fats.
Binders like methylcellulose, carrageenan, and xanthan gum are pivotal in holding the various plant-based ingredients together.
These binders create a cohesive structure that mirrors the natural fibrous composition of animal meat. They ensure that the vegan meat maintains its shape during cooking, allowing easy grilling, frying, or baking.
Plant-based fats are another essential component in replicating the succulence of animal-based meats.
Ingredients like coconut oil, which solidifies at room temperature, are used to mimic the mouthwatering juiciness associated with meat fats.
The fats contribute to the sensory experience of eating and enhance the overall flavour profile by providing a rich, satisfying taste that closely resembles animal fats.
Balancing binders and fats is crucial to achieving vegan meat's desired texture and consistency.
More binder can result in a gummy or overly dense texture, while too much fat can lead to a greasy mouthfeel.
Skilled food technologists work to strike the right balance, ensuring that the final product captures the essence of meat while remaining true to the principles of plant-based eating.
As advancements in food science continue, new binders and fat sources will likely emerge, contributing to the evolution of vegan meat products offering a compelling and delicious alternative to traditional animal-based options.
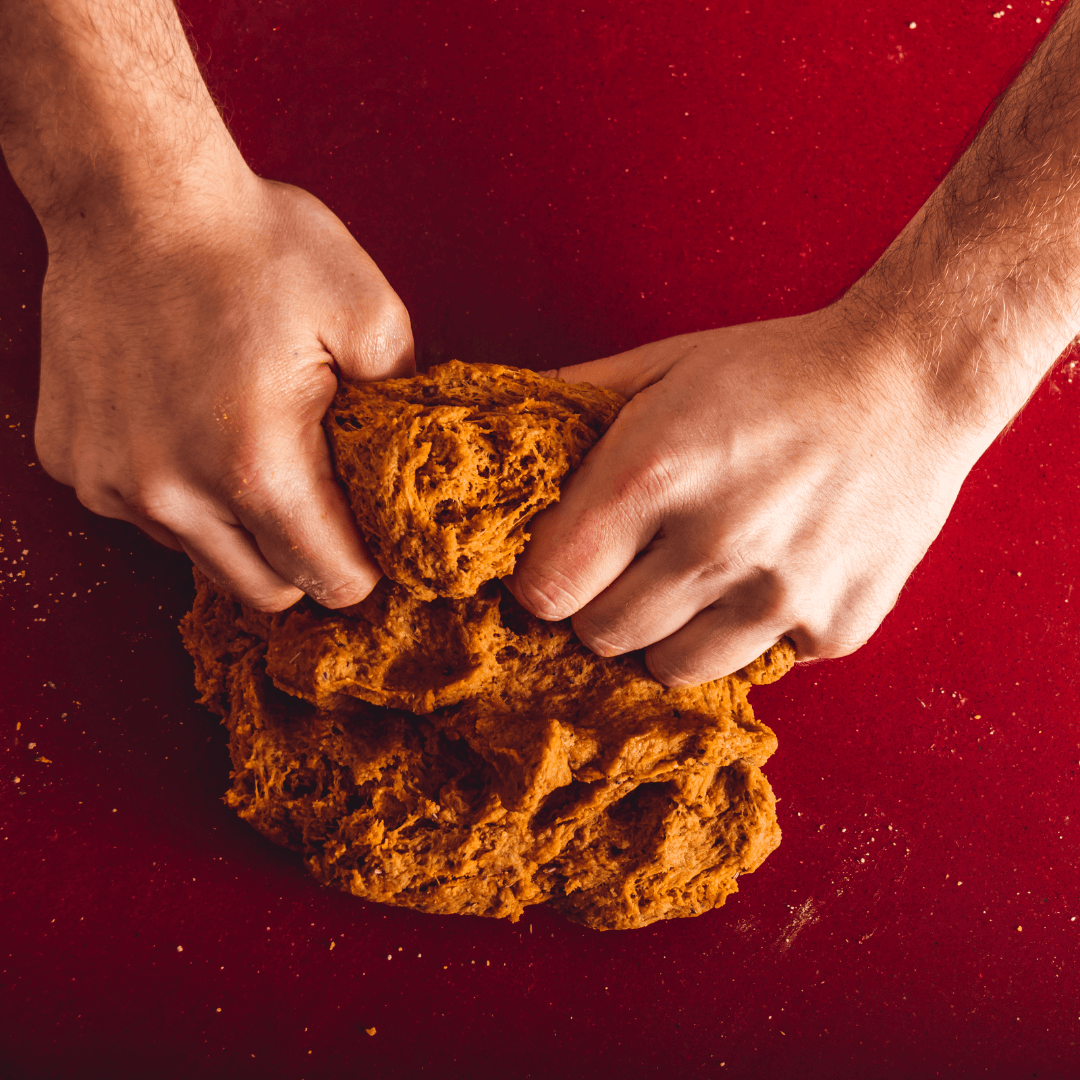

6. Processing Techniques
The manufacturing of vegan meat involves a series of processing techniques to replicate the texture and appearance of animal-based meat.
One common technique is extrusion, which involves forcing a mixture of plant-based proteins and other ingredients through a machine to create a specific texture.
The extrusion process aligns the proteins and forms the characteristic fibrous structure resembling meat's muscle fibres.
This technique is crucial for producing vegan sausages, burgers, and nuggets, giving them the desired chewiness and bite.
Mixing is another essential step in the production process. Ingredients such as proteins, fats, binders, and flavourings are combined in precise proportions to ensure uniform distribution and consistency.
Mixing helps create a cohesive mixture that can be easily shaped into various forms, such as patties or strips. Forming is the final step in shaping the mixture into the desired product.
Moulded into burger patties, sausage links, or other forms, this stage defines the appearance and size of the vegan meat.
The formed products are typically cooked by grilling, frying, or baking to develop their flavour, texture, and overall appeal.
These processing techniques are integral to achieving the familiar and satisfying qualities of meat while using plant-based ingredients.
By skillfully combining extrusion, mixing, and forming, manufacturers can create vegan meat products that taste delicious and offer a sustainable and compassionate alternative for consumers seeking to reduce their animal product consumption.
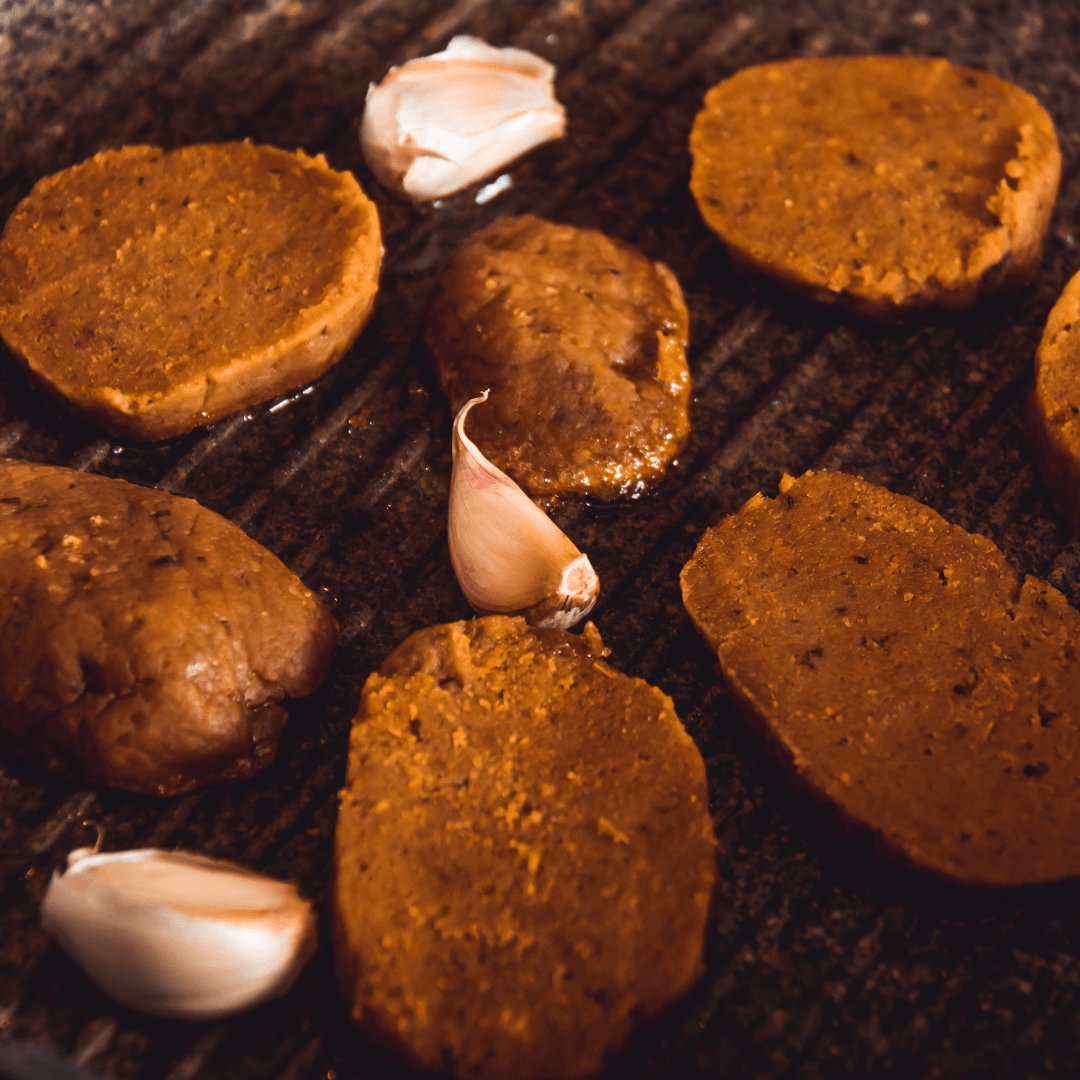

7. Cooking Instructions
Cooking vegan meat involves techniques similar to those used with animal-based meat. The appropriate cooking method depends on the specific type of vegan meat product.
For instance, vegan burgers, sausages, and patties can be grilled, baked, or pan-fried to achieve a satisfying texture and flavour.
Grilling imparts smokiness and char marks, enhancing the overall experience. Baking allows for even cooking and helps retain moisture, resulting in a tender interior. Pan-frying creates a crispy outer layer while preserving the juiciness inside.
The cooking time and temperature for vegan meat products are generally provided on the packaging or in accompanying instructions.
To get the best results, adhere to the following recommendations. Overcooking can lead to a dry or rubbery texture, while undercooking may result in an unpleasant raw taste.
Many vegan meat options can be cooked directly from frozen, offering convenience for quick meals. Experimenting with different cooking techniques and flavours can help enhance the enjoyment of vegan meat.
Adjusting seasonings, marinades, and cooking times, like cooking animal-based meat, can influence the final taste and texture.
As the popularity of vegan meat grows, culinary creativity and innovation continue to contribute to a diverse range of delicious plant-based alternatives that appeal to various tastes and preferences.

Conclusion
In conclusion, creating vegan meat is a fascinating blend of science, culinary expertise, and innovation.
The process involves a delicate balance of factors to ensure that the final product mimics the sensory aspects of meat and meets consumers' taste and nutritional value expectations.
Vegan meat has gained significant traction for its ethical, environmental, and health benefits. Plant-based proteins and processing techniques allow for the production of cruelty-free and more sustainable alternatives to traditional meat.
Moreover, vegan meat products allow people to enjoy familiar flavours and dishes while making conscious choices that align with their values.
As technology and research in plant-based foods continue to evolve, the quality and variety of vegan meat products are expected to improve even further.
The industry's commitment to enhancing taste, texture, and nutritional profiles suggests that the world of vegan meat is on a trajectory of continuous growth and innovation.
Whether for ethical, environmental, or health reasons, high-quality vegan meat options allow individuals to choose sustainable and compassionate alternatives that cater to diverse dietary preferences.
I trust you enjoyed reading the article about How Vegan Meat Is Made. Please stay tuned. I will be writing more blog posts very shortly.
JeannetteZ
>>>Please click here to read my Vegan Travel Guides To World Destinations<<<
>>>Want To Learn How To Create Delicious, Cruelty-Free, Healthy AND 100% Vegan Meals? Try These Awesome Vegan Cooking Courses With A Free 7-DAY MEMBERSHIP<<<
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Ideas? Thoughts? Questions? I would love to hear from you. Please leave me your questions, experiences and remarks about the How Vegan Meat Is Made article in the comments section below. You can also email me at Jeannette@LivingTheVeganLifestyle.org.
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. I earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate and other affiliate programs. Please read my full disclosure.