How Vegan Leather Is Made
How Vegan Leather Is Made
In the ever-evolving landscape of sustainable fashion, vegan leather has emerged as a pioneering alternative, offering a cruelty-free and eco-conscious option for those seeking stylish and ethical choices.
Unlike traditional leather derived from animal hides, vegan leather is crafted from various plant-based materials, synthetic polymers, and innovative technologies.
This article delves into how vegan leather is made, unravelling the processes and materials contributing to its growing popularity.
The journey from raw materials to the finished product involves cutting-edge techniques that mimic the texture and durability of traditional leather without environmental impact or ethical concerns.
As sustainability takes center stage in consumer choices, understanding the intricate craftsmanship behind vegan leather becomes essential for those looking to make conscious and stylish decisions in fashion.
Join us on a journey through the innovative processes shaping the future of cruelty-free, planet-friendly leather alternatives.
What Is Vegan Leather?
Vegan leather, or faux or synthetic leather, is a sustainable and cruelty-free substitute for conventional leather derived from animals.
It marks a revolutionary shift in the fashion industry. Unlike its counterpart, vegan leather is crafted from diverse materials, including plant-based sources and synthetic polymers, primarily focusing on minimizing environmental impact.
Plant-based vegan leather utilizes pineapple leaves, cork, apple peels, and mushroom mycelium.
Pineapple leather, or Piñatex, repurposes the fibres from pineapple leaves, providing a durable and textured material. Mushroom leather, or mycelium leather, is grown from fungi, creating a sustainable and biodegradable option.
Apple leather harnesses the by-products of apple processing, reducing waste in the food industry.
Synthetic alternatives like polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are also commonly used in vegan leather production.
While these materials are not without environmental concerns, ongoing research focuses on developing more sustainable versions, such as water-based PU and bio-based PVC, to address their ecological footprint.
Cutting-edge technologies will continue to influence how vegan leather is developed in the future.
Biofabrication and 3D printing are revolutionizing the manufacturing process, creating materials that closely mimic traditional leather's texture, durability, and appearance.
As consumer demand for sustainable and cruelty-free fashion rises, the evolution of vegan leather redefines the industry, providing a stylish and ethical choice for conscientious consumers.
Characteristics Of Vegan Leather
Understanding the manufacturing process of vegan leather reveals a process characterized by innovation, ethical considerations, and a commitment to environmental consciousness.
Vegan leather, also known as synthetic leather or faux leather, has several characteristics that set it apart as a popular and sustainable alternative to traditional animal-derived leather:
1. Cruelty-Free
One of the primary characteristics of vegan leather is its cruelty-free nature. Unlike traditional leather, which involves animal hides, vegan leather is produced without harming animals. This aligns with ethical and compassionate practices in the fashion industry.
2. Plant-Based Or Synthetic Materials
Vegan leather can be crafted from various plant-based sources, including pineapple leaves (Piñatex), apple peels, cork, and mushroom mycelium.
Alternatively, synthetic materials such as polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are commonly used. The choice of materials contributes to the versatility and eco-friendliness of vegan leather.
3. Sustainability
Compared to traditional leather, many vegan leather varieties are made with environmental sustainability in mind.
Materials like Piñatex repurpose waste from existing industries, reducing environmental impact.
Innovations in synthetic materials aim to improve sustainability, with advancements in bio-based and water-based alternatives.
4. Versatility
Vegan leather comes in various textures, finishes, and colours, providing designers and consumers a wide range of options.
Its versatility allows for creative and stylish applications in fashion, accessories, and home goods.
5. Durability And Performance
Vegan leather can be engineered to be durable, water-resistant, and wear and tear-resistant.
Technological advancements in manufacturing processes enhance the performance of vegan leather, making it a viable and long-lasting choice for various applications.
6. Innovative Manufacturing
Vegan leather production often involves innovative manufacturing processes, including fabrication and 3D printing.
These technological advancements help produce materials that resemble traditional leather in appearance and texture.
7. Consumer Demand
The increasing demand for ethical and sustainable products has driven the popularity of vegan leather.
As consumers seek alternatives that align with their values, the characteristics of vegan leather make it an attractive choice in the evolving landscape of fashion and design.
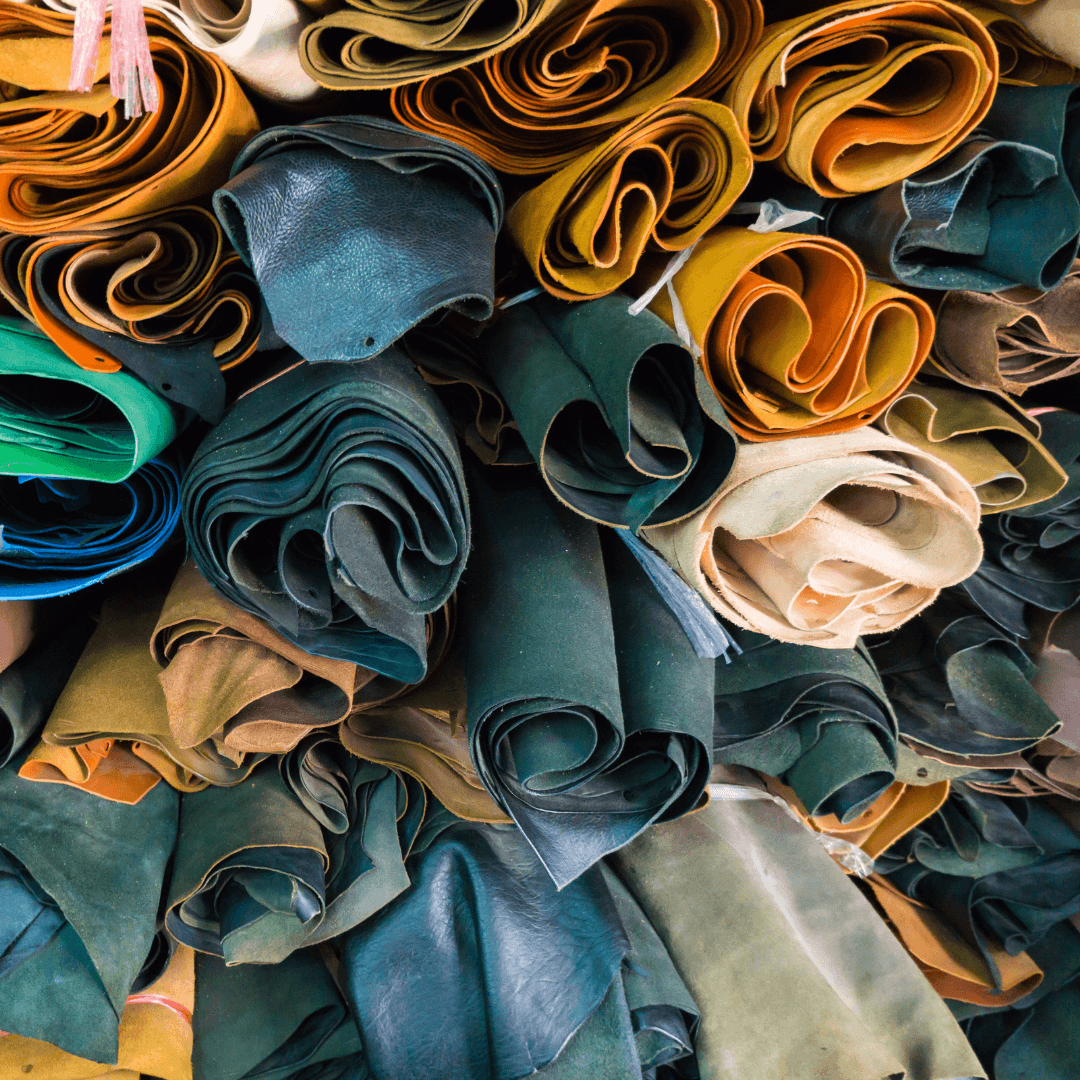

Exploring How Vegan Leather Is Made
Vegan leather is a testament to innovation, utilizing various sources and state-of-the-art technologies instead of conventional leather derived from animals.
The detailed procedures and components that go into making vegan leather are examined in this investigation, which unveils an intriguing web of ethical and sustainable decisions.
So, let’s start exploring how the vegan leader is made:
Raw Materials
The raw materials used in crafting vegan leather reflect diverse sources, each contributing to the material's unique texture, appearance, and overall sustainability.
One innovative plant-based source is pineapple leaves, giving rise to a material known as Piñatex.
Extracted from the fibres of pineapple leaves, Piñatex undergoes a meticulous process where these fibres are transformed into a mesh and coated with a resin, resulting in a durable and textured material reminiscent of traditional leather.
This not only repurposes agricultural waste but also supports local communities.
Cork, another plant-based option, offers a distinctive texture and appearance. Harvested from the bark of cork oak trees, the material is both renewable and biodegradable.
Apple peels contribute to the vegan leather landscape by utilizing by-products from the food industry that would otherwise go to waste.
Innovative processes transform apple peels into a leather-like material, providing a sustainable alternative.
Mushroom mycelium, often called mushroom leather, represents a fascinating biofabricated option.
Grown from the root structure of fungi, mycelium creates a versatile and sustainable material that can be shaped and textured to resemble traditional leather.
This process aligns with principles of environmental sustainability, as it requires less land and water compared to conventional livestock farming.
Alternatives include synthetic materials like polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyurethane (PU). PU, in particular, involves coating a fabric backing with a layer of polyurethane, creating a flexible and leather-like material.
While these synthetics have faced environmental scrutiny, ongoing developments, such as water-based PU, aim to mitigate their ecological impact.
Plant-Based Options
How vegan leather is made involves a diverse range of materials, incorporating plant-based sources like pineapple leaves, cork, apple peels, and mushroom mycelium, alongside the use of synthetic materials such as polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
1. Piñatex
Harvested from pineapple leaves, Piñatex represents a remarkable innovation sustainably. The process begins with extracting fibres from these leaves, typically discarded after the pineapple harvest.
The extracted fibres undergo a series of refining steps, including cleaning and drying, to enhance their strength and flexibility.
Subsequently, these fibres are processed into a mesh through a non-woven textile technique. The mesh is then coated with a resin derived from natural sources, such as corn or sugarcane, to create a cohesive and durable material.
The resulting Piñatex material boasts a unique texture, blending the organic appearance of plant fibres with a leather-like feel.
This innovative approach repurposes agricultural by-products, promotes resource efficiency, and reduces waste.
Additionally, Piñatex has become a sustainable economic driver in pineapple-producing regions, contributing to the livelihoods of local communities.
2. Mushroom Leather (Mycelium)
Mushroom leather, grown from mushroom mycelium, showcases fabrication possibilities in sustainable material development.
Mycelium is the root structure of fungi, and when cultivated in a controlled environment, it forms a dense network that can be harvested and shaped into a leather alternative.
The process begins by introducing mycelium to an agricultural by-product, such as wood chips or agricultural waste.
Over a period, the mycelium grows and binds these materials together, creating a solid and moldable substance.
The resulting material is then treated and processed to enhance its texture and durability, yielding a leather substitute.
Mushroom leather offers a renewable and biodegradable option for fashion and design. It requires less land and water than traditional leather production and can be tailored to various specifications.
This sustainable alternative aligns with the growing demand for cruelty-free and environmentally conscious choices in the fashion industry.
3. Recycled Materials
Recycled materials play a pivotal role in shaping the sustainability narrative of vegan leather, offering an eco-conscious alternative that addresses environmental concerns associated with traditional leather and synthetic materials.
Incorporating recycled materials, particularly from sources like plastic bottles and synthetic waste, showcases a commitment to circular economy principles within the fashion industry.
One common approach involves transforming discarded plastic bottles into a versatile, sustainable leather substitute.
Post-consumer plastic bottles are collected, cleaned, and processed into small flakes. After being melted, these flakes are extruded into fibres that can be combined with other materials to make fabric or woven.
This innovative process not only diverts plastic waste from landfills and oceans but also reduces the demand for virgin petrochemical-based materials.
Beyond plastic bottles, other forms of synthetic waste can also find new life in recycled vegan leather.
This can include repurposing industrial scraps, remnants from manufacturing processes, or decommissioned synthetic textiles.
By diverting these materials from disposal sites, the fashion industry contributes to resource efficiency and minimizes its environmental footprint.
Using recycled materials aligns with broader sustainability goals, reducing the reliance on virgin resources and mitigating the environmental impact of extraction and production.
Additionally, it addresses the challenge of waste management by giving a second life to materials that would otherwise contribute to pollution or landfill accumulation.
Integrating recycled materials into vegan leather fosters a more circular and sustainable fashion ecosystem and exemplifies a forward-thinking approach to material innovation.
This eco-friendly practice resonates with environmentally conscious consumers, reinforcing that fashion can be stylish and sustainable.
4. Synthetic Alternatives
How vegan leather is made involves using common synthetic materials like polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offering a cruelty-free and environmentally conscious alternative that combines durability and adaptability to mimic traditional leather's appearance without animal products.
Two of the most common synthetic materials used to make vegan leather are polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
Without using animal products, these materials provide an appealing combination of durability and adaptability, giving the appearance of leather.
5. Polyurethane (PU)
Polyurethane, commonly known as PU, is a prevalent synthetic alternative in vegan leather, offering a versatile and cruelty-free option.
The production of PU vegan leather involves coating a fabric backing, often made from polyester or cotton, with a layer of polyurethane.
This coating creates a material that mimics the texture and appearance of traditional leather, providing a durable and flexible substance suitable for various applications in fashion and design.
Water-based PU represents a notable eco-friendly iteration of this synthetic alternative. In traditional PU production, solvents are used in the coating process, contributing to environmental concerns.
Water-based PU, however, replaces these solvents with water, significantly reducing the environmental impact.
This shift aligns with sustainability goals by minimizing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and promoting a more environmentally conscious approach to synthetic material production.
The versatility of PU vegan leather extends to its ability to replicate different textures, from smooth finishes to textured grains, enhancing its aesthetic appeal.
This adaptability makes it a popular choice for designers and manufacturers seeking cruelty-free options that don't compromise on style.
6. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl chloride, or PVC, is another synthetic material used in vegan leather production.
While PVC vegan leather shares some similarities with PU in appearance and texture, it is considered less eco-friendly due to its manufacturing process and potential environmental impact.
The production of PVC involves coating a fabric backing with layers of PVC, creating a durable and water-resistant material.
However, environmental drawbacks are associated with the use of chlorine in PVC production, which can release harmful dioxins into the environment. Dioxins are persistent organic pollutants with known environmental and health concerns.
While PVC vegan leather is less favoured in sustainable and eco-conscious circles, ongoing research and development aim to address its environmental impact.
Innovations such as bio-based PVC, derived from renewable resources, represent efforts to create more sustainable versions of synthetic materials within the vegan leather landscape.
In summary, PU and PVC provide synthetic alternatives for vegan leather, with water-based PU offering a more environmentally friendly choice.
The ongoing exploration of sustainable variations and adoption of eco-conscious practices contribute to the evolution of synthetic vegan leather options in the fashion industry.
Innovative Technologies
Advancements in technology have ushered in a new era for sustainable materials, particularly in the realm of vegan leather.
These groundbreaking technologies, such as biofabrication and 3D printing, represent a transformative approach to the material creation, offering alternatives that mimic and enhance traditional leather's qualities.
1. Biofabrication
Biofabrication stands at the forefront of the technological revolution in vegan leather production.
This method leverages living organisms, such as bacteria, yeast, or fungi, to produce materials in a controlled environment.
In vegan leather, biofabrication often involves cultivating microbial cells to create a biomaterial resembling animal-derived leather's structure and texture.
This innovative process allows precise control over the material's properties, resulting in a sustainable, cruelty-free alternative that can revolutionize the fashion industry.
2. 3D Printing
3D printing technology has also found its way into creating vegan leather, offering precision and customization previously unseen.
This technique involves layer-by-layer deposition of materials to build a three-dimensional structure.
In the context of vegan leather, 3D printing allows for intricate designs, textures, and patterns, offering unparalleled creative freedom.
Manufacturers can experiment with different combinations of materials, producing customized vegan leather with specific characteristics tailored to meet fashion and design requirements.
How vegan leather is made reflects the intersection of innovation and sustainability, with technologies like biofabrication reducing reliance on traditional agriculture and 3D printing minimizing waste through precise production, shaping the future of cruelty-free and environmentally conscious fashion.
Biofabrication reduces reliance on traditional agriculture and allows for the creation of materials with minimal environmental impact.
3D printing reduces waste by enabling precise production, ensuring every inch of material serves a purpose.
As technology continues to evolve, the intersection of innovation and sustainability in vegan leather production will undoubtedly shape the future of cruelty-free and environmentally conscious fashion.
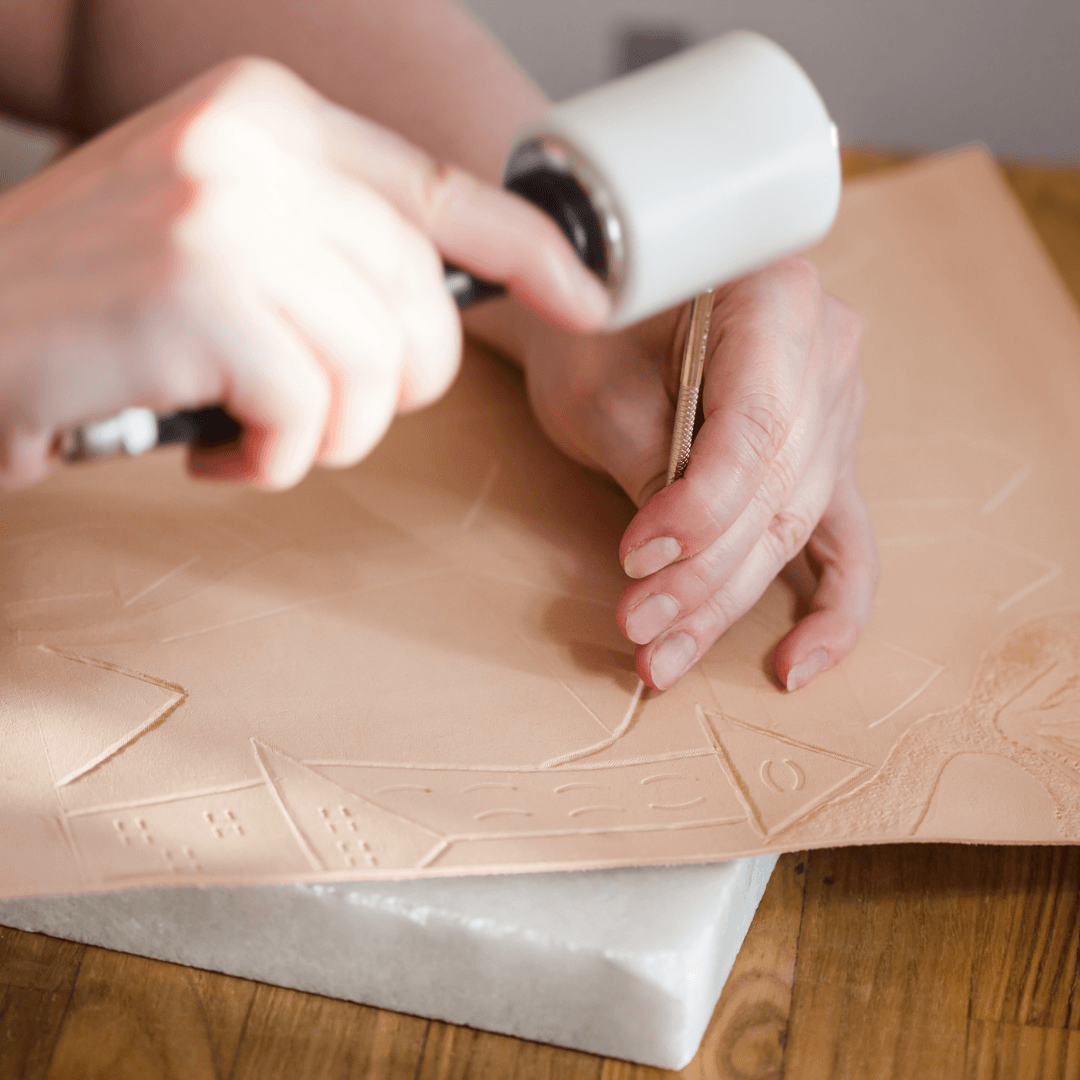

Processing And Finishing
Once the base material for vegan leather is obtained, whether derived from plant-based sources or synthetic alternatives, it undergoes meticulous processes to transform it into a final product with the desired texture, colour, and appearance.
With so many options for personalization and ingenuity, the processing and finishing phases are critical in characterizing the aesthetic appeal of vegan leather.
1. Embossing
Embossing is a technique employed to imprint patterns or textures onto the surface of vegan leather.
This process enhances the material's visual appeal, providing a distinct and often luxurious appearance.
Common patterns include faux animal prints, geometrical designs, or textures mimicking traditional leather grains.
Embossing not only adds a tactile dimension to the material but also allows for replicating intricate details found in natural hides.
2. Dyeing
Dyeing is pivotal in creating vegan leather, incorporating various colours to suit diverse design preferences.
Water-based dyes are often preferred for their reduced environmental impact compared to traditional solvent-based options.
This step allows for creating vibrant, consistent, and fade-resistant hues, ensuring that vegan leather meets the aesthetic standards expected in the fashion industry.
3. Coatings
Coatings are applied to vegan leather to enhance its durability, resistance to water, and overall performance.
These coatings can include protective layers that shield the material from wear and tear, making it suitable for various applications.
Additionally, coatings contribute to the material's sheen or matte finish, adding to its visual appeal.
Water-based and eco-friendly coatings align with sustainability goals, further reinforcing the commitment to environmentally conscious practices in vegan leather production.
How vegan leather is made involves processing and finishing as the artistic strokes that breathe life into the material, transforming raw components into a versatile and aesthetically pleasing alternative that meets the diverse demands of the fashion and design industries while adhering to ethical and sustainable principles.
These techniques contribute to the material's visual richness and play a crucial role in meeting the diverse demands of the fashion and design industries while adhering to ethical and sustainable principles.

Checking Durability And Texture
The quest for a credible alternative to traditional leather has driven manufacturers to prioritize two critical aspects: durability and texture.
Vegan leather aims to emulate the visual appeal of animal-derived leather and offer a high-quality, functional, and sustainable substitute.
1. Mimicking Durability
One of the primary goals in vegan leather production is replicating the durability associated with traditional leather.
The material is engineered to withstand daily wear and tear, ensuring longevity and resilience comparable to its animal-based counterpart.
Manufacturers achieve this by selecting robust base materials and incorporating reinforcement techniques during processing.
The focus on durability is crucial to position vegan leather as a viable option for various applications, from fashion accessories to upholstery and beyond.
2. Texture Replication
The texture of traditional leather is a sensory experience that manufacturers aim to replicate in vegan alternatives faithfully.
Through embossing techniques, vegan leather can mimic the grain patterns, wrinkles, and suppleness characteristic of animal hides.
By offering a tactile sensation similar to real leather, this attention to detail enhances the user experience overall rather than just being aesthetically pleasing.
Vegan substitutes offer a wide range of textures to suit various tastes, whether it's the luxurious, soft feel of Nappa leather or the grainy texture of full-grain leather.
3. Innovations In Microfibre Technology
Advancements in microfiber technology have played a pivotal role in enhancing the texture of vegan leather.
Microfibers, often made from polyurethane or polyester, can be engineered to replicate the natural pores and softness of leather.
This innovation contributes to the visual and tactile appeal of vegan leather. It aligns with sustainability goals, as microfiber production can be more resource-efficient than traditional leather tanning processes.
4. Functional And Versatile
Durability and texture in vegan leather are not just about imitating traditional leather but ensuring the material is functional and versatile.
Vegan leather is crafted to meet the demands of various industries, from fashion and accessories to automotive interiors and home furnishings—the adaptability of vegan leather positions it as a practical choice without compromising aesthetic and tactile qualities.
The pursuit of durability and texture in vegan leather underscores the commitment to providing a sustainable, cruelty-free alternative that not only meets but exceeds the expectations set by traditional leather.
As innovations continue to evolve, vegan leather is poised to become a cornerstone in the future of ethical and environmentally conscious materials.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey through the creation of vegan leather unveils a tapestry woven with innovation, sustainability, and ethical consciousness, showcasing how vegan leather is made and emphasizing strides towards a future where fashion seamlessly harmonizes with compassion for animals and environmental stewardship.
In this exploration, we witness not only the craftsmanship involved in mimicking the qualities of animal-derived leather but also the strides made toward a future where fashion harmonizes with compassion for animals, environmental stewardship, and the ever-growing desire for sustainable choices.
Vegan leather emerges as a material and a symbol of a transformative journey towards a more ethical and environmentally conscious approach to fashion and design.
As the fashion industry evolves, vegan leather becomes a cornerstone in reshaping consumer choices, proving that style and sustainability coexist seamlessly.
This exploration into the intricacies of vegan leather production invites us to envision a future where ethical, cruelty-free materials play a central role in defining the aesthetics of our evolving world.
I trust you enjoyed reading the article about How Vegan Leather Is Made. Please stay tuned? There are more blog posts to come very shortly.
JeannetteZ
>>>Please click here to read my Vegan Travel Guides To World Destinations<<<
>>>Want To Learn How To Create Delicious, Cruelty-Free, Healthy AND 100% Vegan Meals? Try These Awesome Vegan Cooking Courses With A Free 7-DAY MEMBERSHIP<<<
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Ideas? Thoughts? Questions? I would love to hear from you. Would you mind leaving me your questions, experiences and remarks about How Vegan Leather Is Made in the comments section below? You can also reach me by email at Jeannette@LivingTheVeganLifestyle.org.
>>>Please click here to read more about Vegan Leather on Peta.org<<<
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. I earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate and other affiliate programs. Please read my full disclosure.
You might also enjoy these blog posts:
Best Eco-Friendly Vegan Leather Alternatives
Best Online Shops To Buy Vegan Leather Products
Best Places To Buy Vegan Leather







