Is Vegan Meat Healthy
Is Vegan Meat Healthy?
With the rising popularity of plant-based diets and the increasing demand for sustainable food options, vegan meat has become a prominent player in the modern culinary landscape.
As more people seek alternatives to traditional animal-based products, questions arise about the health implications of incorporating vegan meat into one's diet.
Advocates praise its ethical and environmental benefits, but skeptics question its nutritional value and potential health risks.
In this article, we delve into the debate surrounding vegan meat's healthiness, exploring its nutritional profile, health benefits, and potential drawbacks.
By shedding light on various perspectives and backed by scientific research, we aim to offer readers a well-rounded understanding of whether vegan meat aligns with their dietary goals and lifestyle choices.
Whether you are a seasoned vegan, a curious flexitarian, or a steadfast meat-eater exploring alternatives, join us on this journey to uncover the truth behind the question: Is vegan meat truly a healthy option?
The Story Of Vegan Meat's Discovery
The discovery of vegan meat is a fascinating journey that traces back to ancient civilizations and continues to evolve in the modern world.
While the concept of plant-based meat may seem like a recent phenomenon, its roots can be found in various cultures and traditions across the globe.
Ancient civilizations like the Greeks and Romans experimented with meat alternatives made from wheat gluten and other plant-based ingredients.
Tofu and tempeh have been staples in Asia for centuries, providing rich plant-based protein sources. However, in the 19th and 20th centuries, vegan meat alternatives began gaining more attention.
In the 19th century, plant-based meat substitutes like seitan, a protein-rich wheat gluten, gained popularity in China and Japan.
Later, during World War II, food shortages led to the development of textured vegetable protein (TVP) as a protein source.
The rise of vegetarianism and environmental consciousness in the 20th century further fueled the exploration of meat alternatives.
One of the most significant milestones in the discovery of vegan meat was the creation of the Impossible Burger and Beyond Burger in the 2010s.
These innovative products utilized advanced plant-based technologies to mimic the taste and texture of real meat, attracting widespread attention and sparking a plant-based revolution in the food industry.
Today, the story of vegan meat continues to unfold as scientists, chefs, and food companies collaborate to perfect the art of creating delicious and sustainable plant-based alternatives to meat.
The discovery of vegan meat reflects our evolving culinary preferences and our growing awareness of meat consumption's environmental and ethical impacts, inspiring a shift towards more compassionate and sustainable food choices.
As technology and culinary expertise continue to advance, the future of vegan meat holds the promise of even more exciting and delectable possibilities for a healthier planet and a more compassionate world.
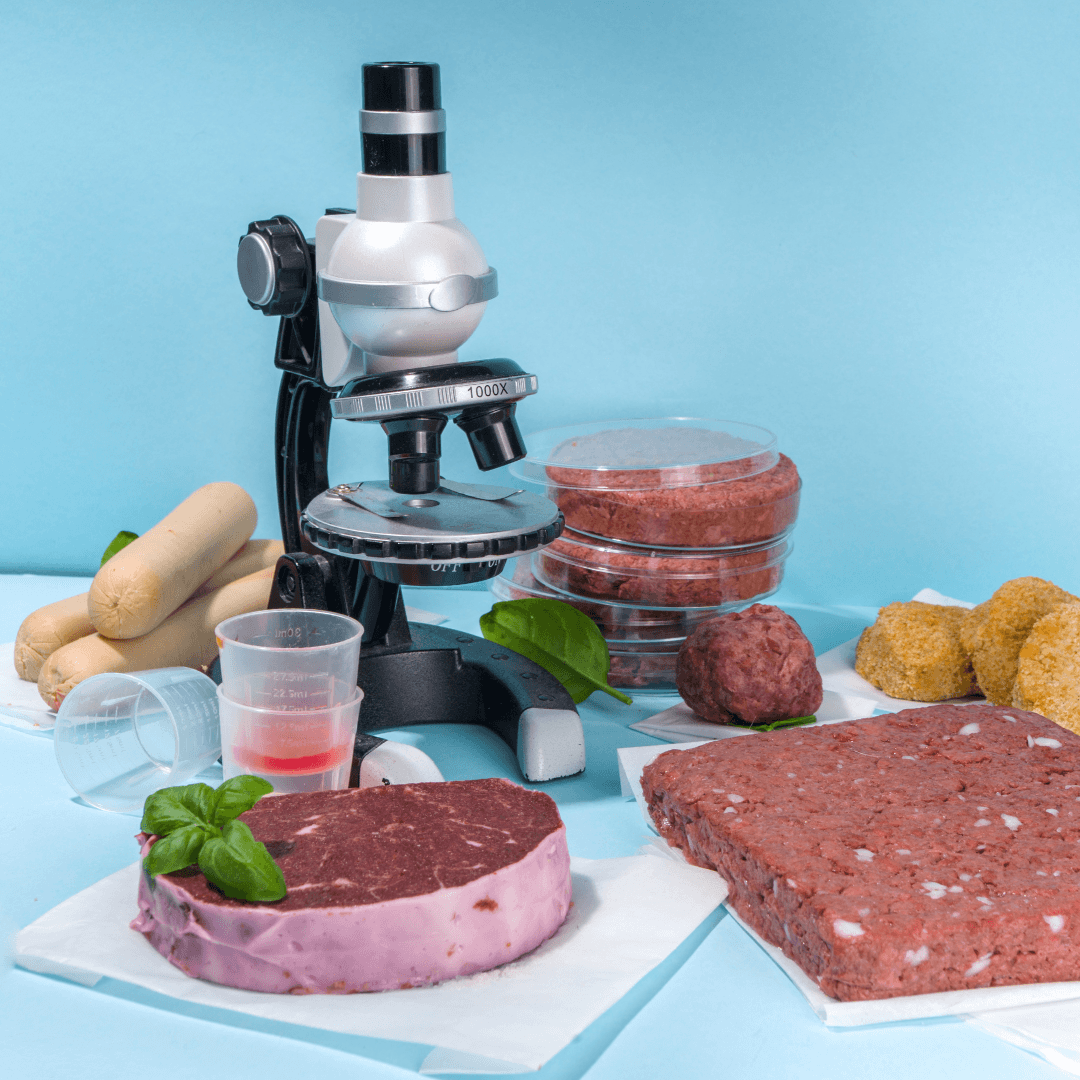

How Is Vegan Meat Prepared?
Vegan meat, also known as plant-based or meat alternatives, is crafted through culinary artistry and cutting-edge food technology.
The process involves using various plant-based ingredients to recreate animal-based meats' taste, texture, and appearance.
The primary base for many vegan meats is protein-rich plant sources such as soy, wheat gluten (seitan), pea protein, or mycoprotein (a fungus-based protein).
These plant proteins serve as the foundation for mimicking the fibrous structure found in animal muscle tissue.
Vegan meat manufacturers incorporate various natural ingredients, such as vegetable oils, herbs, spices, and seasonings, to enhance the flavour, aroma, and appearance.
These additions contribute to replicating the savoury, umami taste characteristic of conventional meat.
Next comes the crucial step of texturizing plant proteins. This can involve extrusion, a process where the mixture is subjected to high pressure and heat to create a fibrous texture.
Alternatively, some manufacturers use 3D printing technology to arrange plant proteins precisely into meat-like structures.
Once the base and texture are perfected, vegan meats may undergo additional processes, such as marinating or smoking, to enhance taste and create a more authentic meaty experience.
The result is various vegan meat products, including plant-based burgers, sausages, nuggets, and even faux seafood options.
From taste and texture to appearance and nutritional content, vegan meat preparation aims to provide consumers with a delicious and sustainable alternative to conventional meat while catering to diverse dietary preferences and ethical considerations.
Vegan Meat: The Pros For Your Well-Being
Vegan meat has taken center stage in the contemporary culinary scene as plant-based diets have grown in popularity, and consumer desire for sustainable food options has increased.
The healthiness of vegan meat depends on various factors, and here are some key points to consider:
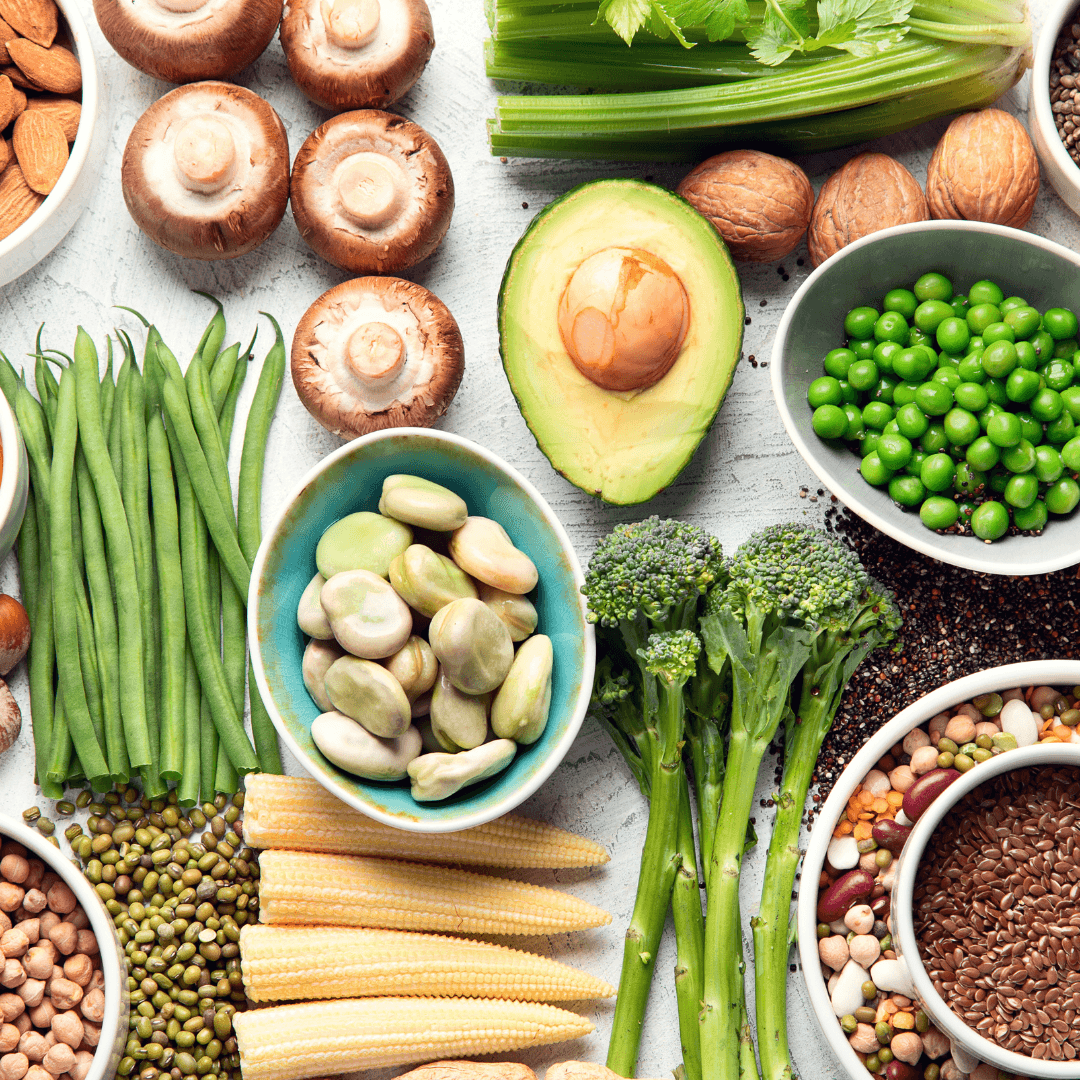

1. Plant-Based Ingredients
Vegan meat, a burgeoning trend in the food industry, owes its existence to a diverse range of plant-based ingredients. Soy, pea protein, wheat gluten, and other plant sources are pivotal in crafting these meat alternatives.
One of the key advantages lies in the abundance of essential nutrients they offer. These ingredients are excellent protein sources, meeting the dietary needs of vegans and those seeking to reduce their meat consumption.
Moreover, they provide dietary fiber, which aids digestion and promotes a healthy gut. These plant-based substances support general health since they are rich in vitamins and minerals like iron, zinc, and B vitamins.
Not only are they nutritionally beneficial, but they also address environmental and ethical concerns surrounding traditional meat production.
Using plant-derived components, vegan meats help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and deforestation associated with livestock farming.
As consumer awareness about health and sustainability grows, these plant-based ingredients are poised to revolutionize how we perceive and consume meat, paving the way for a more compassionate and eco-friendly future.

2. Vegan Meat Is Lower In Saturated Fat
One of the significant health benefits of vegan meat is its lower saturated fat content when compared to real meat.
The risk of heart disease and the development of atherosclerosis are increased by saturated fats, known to increase blood levels of LDL cholesterol, also known as “bad” cholesterol.
Using plant-based ingredients, vegan meat products can effectively reduce saturated fat intake, promoting better heart health and overall well-being.
Traditional animal-based meats, such as beef, pork, and lamb, are typically higher in saturated fat, especially in the visible fat and marbling within the meat.
On the other hand, vegan meats rely on plant sources that inherently contain lower levels of saturated fat.
Ingredients like soy, peas, and wheat protein are naturally low in saturated fat, making them excellent alternatives for individuals seeking to lower their saturated fat intake.
The reduced saturated fat offered by vegan meat aligns with dietary recommendations from health organizations worldwide.
Reducing saturated fat consumption is frequently advised to control cholesterol levels and lower the risk of cardiovascular illnesses.
By choosing plant-based alternatives, individuals can enjoy the flavours and textures of meat without compromising their heart health, making vegan meat a favourable option for those looking to adopt a heart-healthy diet.
3. Vegan Meat Is Cholesterol-Free
One of the key health advantages of consuming vegan meat is its cholesterol-free nature, primarily due to its plant-based origins.
Unlike animal-based meats, which can be high in cholesterol, vegan meat products are entirely free from this potentially harmful lipid. A waxy substance called cholesterol is present in animal tissues and food products.
Individuals can effectively manage their cholesterol intake and support heart health by eating cholesterol-free vegan meat.
Plant-based ingredients like soy, peas, and wheat protein naturally lack cholesterol, making them excellent alternatives for those looking to reduce or eliminate cholesterol from their diet.
The absence of cholesterol in vegan meat benefits heart health and aligns with dietary recommendations from health organizations advocating reducing dietary cholesterol intake.
Additionally, selecting cholesterol-free vegan meat might be especially advantageous for people with specific health issues, such as excessive cholesterol levels or a family history of heart disease.
By making this dietary switch, people can still enjoy delicious and familiar meat-like dishes while proactively protecting their cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
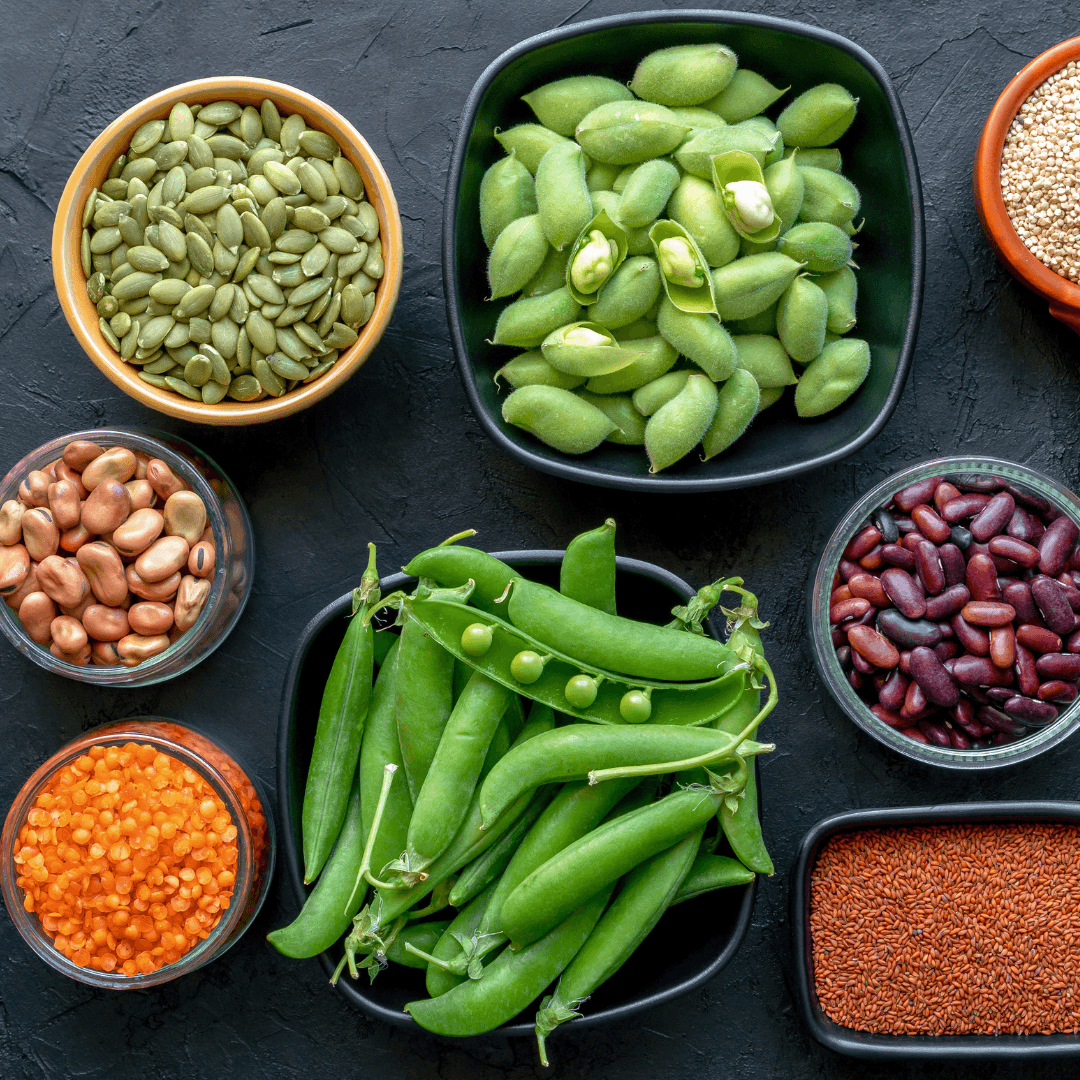

4. Vegan Meat Has A High Protein Content
Vegan meat offers a compelling solution for individuals seeking to maintain or increase their protein intake while avoiding animal sources.
Many vegan meat products are specifically formulated to provide a protein content similar to real meat, making them an excellent alternative for protein-conscious individuals, including vegans, vegetarians, and those looking to reduce their meat consumption.
The primary protein sources used in these products, such as soy, peas, and wheat gluten, are rich in essential amino acids, making them nutritionally complete and comparable to animal-based proteins.
Protein is crucial in various bodily functions, including muscle repair and growth, enzyme production, and immune system support.
By offering a comparable protein content to real meat, vegan meat enables individuals to meet their daily protein requirements while adhering to a plant-based diet.
This is particularly beneficial for athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and individuals with active lifestyles who rely on protein for muscle recovery and development.
5. Vegan Meat Has A Lower Risk Of Foodborne Illnesses
By virtually eliminating the risk of foodborne infections, vegan meat provides a huge benefit over actual meat in terms of food safety.
Vegan meat is created from plant-based ingredients that do not contain these hazardous bacteria, unlike animal-based meats that may be infected with infections like Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria.
Foodborne illnesses from contaminated meat can cause severe health issues, ranging from gastrointestinal discomfort to life-threatening conditions.
However, vegan meat production processes involve minimal risk of pathogen contamination, as the raw materials used are not prone to carrying such bacteria.
Moreover, since vegan meat does not require cooking to kill bacteria like traditional meat, there is a reduced risk of cross-contamination in the kitchen during food preparation.
This makes vegan meat safer, especially for individuals with weakened immune systems, pregnant women, children, and the elderly, who are more susceptible to foodborne illnesses.
Choosing vegan meat can offer peace of mind and confidence in food safety while enjoying delicious and satisfying meat-like dishes.
6. Processing And Additives
While vegan meat presents a healthier and more sustainable alternative to animal-based products, some vegan meat options may include processed ingredients and additives to mimic the taste and texture of real meat.
Processing methods like extrusion and high-temperature cooking often transform plant-based ingredients into familiar meat-like forms, such as patties, sausages, and nuggets.
Additionally, additives like preservatives, flavour enhancers, and stabilizers might be incorporated to improve taste, shelf life, and overall product consistency.
While these techniques can create more appealing vegan meat products, consumers should be mindful of the potential drawbacks of excessive processing and additives in their diet.
A high intake of processed foods has been related to adverse health impacts, including a higher chance of developing chronic diseases.
To make healthier choices, consumers can opt for more natural and minimally processed vegan meat alternatives, which typically have shorter ingredient lists and contain recognizable whole-food ingredients.
Prioritizing products with limited or no additives ensures a diet that aligns better with overall health and well-being while enjoying plant-based protein benefits and reduced environmental impact.

7. Sodium Content
While vegan meat offers numerous health benefits, consumers must know its sodium content. Some vegan meat products may have higher sodium levels than real meat, posing potential health risks.
High blood pressure, a significant risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular disorders, has been linked to excessive sodium consumption.
While sodium is a necessary mineral for the body, consuming too much can lead to water retention and increased pressure on blood vessel walls.
Consumers should diligently read product labels and nutritional information to make informed choices.
Opting for lower-sodium vegan meat alternatives can help individuals maintain a balanced sodium intake and support heart health.
Additionally, incorporating fresh, whole plant-based foods into the diet, such as fruits, vegetables, and grains, can naturally contribute to a lower sodium intake while still enjoying the benefits of a vegan diet.
By being mindful of sodium levels and making conscious choices, individuals can continue savouring the flavours of vegan meat without compromising their overall well-being.

9. Nutritional Fortification
Nutritional fortification is a significant aspect of some vegan meat products, addressing potential nutrient gaps in plant-based diets. Vitamin B12 and iron are essential nutrients predominantly found in animal-based foods.
As these nutrients are crucial for various bodily functions, their presence in vegan diets is vital for overall health.
To bridge this nutritional gap, manufacturers often fortify vegan meat products with vitamin B12 and iron, ensuring that consumers receive adequate nutrients without relying on animal sources.
Fortified vegan meats offer a convenient and accessible way for vegans and vegetarians to obtain these nutrients and prevent deficiencies.
However, checking product labels and choosing fortified options is essential to ensure these nutrients are included appropriately.
In addition to fortified foods, individuals can consider vitamin B12 supplements and include iron-rich plant-based foods like legumes, nuts, seeds, and leafy greens to support a well-rounded and nutritionally balanced vegan diet.

10. Overall Diet Quality
The healthiness of vegan meat is not solely determined by its attributes but rather by how it complements an individual's overall diet.
While vegan meat offers numerous benefits, such as lower saturated fat, cholesterol-free content, high protein, and reduced foodborne illness risk, it is essential to remember that it is just one component of a broader dietary pattern.
Individuals should adopt a well-balanced diet incorporating diverse plant-based foods for optimal health and well-being.
This includes abundant fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, providing essential nutrients, vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber.
Emphasizing variety ensures the body receives a wide spectrum of nutrients necessary for various bodily functions.
Moreover, a balanced diet also supports gut health and a robust immune system. While vegan meat can be a valuable addition to the diet, it should be enjoyed in moderation alongside other nutrient-dense plant-based foods.
By focusing on a holistic approach to nutrition and adopting a well-balanced plant-based diet, individuals can maximize the health benefits of vegan meat and promote overall health and vitality.

11. Culinary Versatility
The culinary versatility of vegan meat is one of its standout features, making it an exciting and appealing choice for individuals transitioning to a plant-based diet or seeking to incorporate more plant-based options into their meals.
Vegan meat products are available in various forms, including burgers, sausages, nuggets, and ground meat, mimicking the textures and flavours of traditional animal-based meats.
This adaptability allows home cooks and chefs to experiment with many creative and diverse meal preparations.
The possibilities are endless, from classic comfort foods like vegan burgers and hot dogs to flavorful curries, stir-fries, and pasta dishes featuring vegan ground meat.
Vegan meat also extends to international cuisines, such as tacos, sushi, and dumplings, enabling individuals to explore new cultural dishes without compromising their dietary choices.
Moreover, the ability to customize vegan meat with different spices, herbs, and sauces adds a layer of versatility, catering to various taste preferences and culinary styles.
The accessibility of vegan meat products empowers individuals to craft delicious, nutritious, and satisfying plant-based meals that rival traditional meat-based dishes, making it an exciting addition to any kitchen.
Conclusion
In conclusion, vegan meat can be healthy when incorporated into a well-balanced and varied plant-based diet.
It offers several health benefits, such as lower saturated fat content, no cholesterol, and reduced risk of foodborne illnesses compared to traditional animal-based meats.
Additionally, many vegan meat products are designed to provide a similar protein content to real meat, making them suitable for those looking to maintain or increase their protein intake without relying on animal sources.
Vegan meat also eliminates the ethical concerns of animal agriculture, contributing to a more compassionate and sustainable food system.
As with any dietary choice, moderation and balance are key. By making thoughtful and informed decisions, individuals can enjoy vegan meat's health benefits and culinary versatility while supporting a lifestyle that aligns with their values and health goals.
I trust you enjoyed reading the article about Is Vegan Meat Healthy? Please stay tuned. More blog posts will be posted very shortly.
JeannetteZ
>>> Please click here to read my Vegan Travel Guides To World Destinations <<<
>>> Want To Learn How To Create Delicious, Cruelty-Free, Healthy AND 100% Vegan Meals? Try These Awesome Vegan Cooking Courses With A Free 7-DAY MEMBERSHIP<<<
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Ideas? Thoughts? Questions? I would love to hear from you. Would you mind leaving me your questions, experiences and remarks about the article on Is Vegan Meat Healthy in the comments section below? You can also reach me by email at Jeannette@LivingTheVeganLifestyle.org.
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. I earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate and other affiliate programs. Please read my full disclosure.







