Ultimate Guide To Vegan Sources of Zinc: Boosting Immunity
Zinc is essential for immunity, cell repair, and overall vitality. Finding adequate sources can be challenging for those following a plant-based diet, but it is achievable with the right foods.
This ultimate guide explores the best vegan sources of zinc, complete with tips and benefits, to help you incorporate more of this crucial nutrient into your meals for enhanced health and well-being.
Why Is Zinc Important?
Zinc is an essential mineral involved in:
1. Immune Function
Zinc is critical for the development and function of immune cells, helping your body fight infections and inflammation.
2. Cell Division And Growth
It plays a significant role in cellular growth and division, essential for skin, muscle, and bone health.
3. Protein And DNA Synthesis
It is necessary for DNA and protein synthesis, which impacts tissue repair and healing.
4. Enzymatic Function
Zinc activates over 100 enzymes that aid metabolism, digestion, and nerve function.
Zinc Requirements For Vegans
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for zinc varies by age and gender:
- Men: 11 mg per day
- Women: 8 mg per day
- Pregnant and Lactating Women: 11-12 mg per day
Since plant-based foods contain phytates, compounds that can inhibit zinc absorption, vegans may need to aim for slightly higher zinc intakes.
Want to Share Your Passion for Vegan Living?
Discover how easy and fulfilling vegan living can be —
from recipes and travel to lifestyle and sustainability tips.
Read this blog post next:
How to Start a Vegan Blog (and Turn Your Passion into Purpose).
Top Vegan Sources Of Zinc
1. Legumes
Types Of Legumes
Chickpeas, lentils, black beans, kidney beans, and peas are popular, nutrient-dense legumes that are easy to incorporate into meals.
Zinc Content In Legumes
Lentils, for instance, offer about 1.3 mg of zinc per 100g cooked serving, with other legumes providing similar amounts.
Benefits Of Legumes
These legumes are packed with fibre, protein, and essential vitamins and minerals, which support energy, digestion, and immunity.
Tips
Soaking, sprouting, or fermenting legumes helps break down phytates, making zinc and other minerals more bioavailable for absorption.

2. Nuts And Seeds
Types Of Nuts And Seeds
Popular zinc-rich nuts and seeds include pumpkin, hemp, chia, sesame, cashews, and almonds.
Zinc Content In Nuts And Seeds
Pumpkin seeds are exceptionally high in zinc, with about 7.81 mg per 100 g, making them one of the best plant-based sources.
Benefits Of Nuts And Seeds
Nuts and seeds offer healthy fats, protein, and antioxidants, supporting heart health and immunity while adding flavour and crunch to meals.
Tips
Lightly roasting seeds can reduce phytates, and pairing them with vitamin C-rich foods, such as citrus, can enhance zinc absorption.

3. Whole Grains
Types Of Whole Grains
Zinc-containing whole grains, such as oats, quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat, are staples in many diets.
Zinc Content In Whole Grains
Oats, for example, provide around 2.97 mg of zinc per 100g, contributing a solid dose to a plant-based diet.
Benefits Of Whole Grains
Whole grains deliver lasting energy, fiber for digestive health, and essential nutrients like B vitamins and minerals, supporting overall wellness.
Tips
Choosing sprouted grain products can reduce phytates, enhance zinc absorption, and make the minerals in these grains more bioavailable.

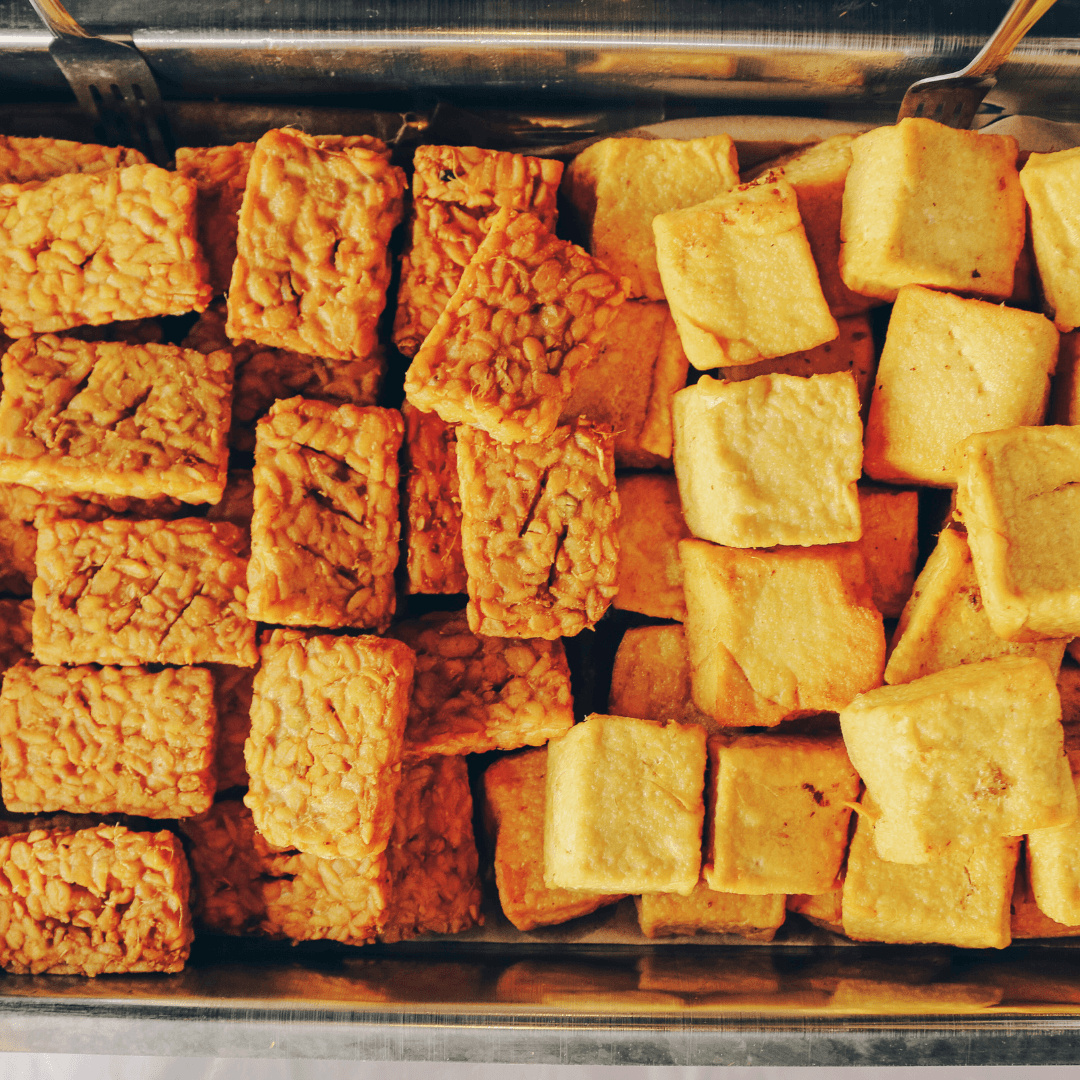
4. Tofu And Tempeh
Zinc Content In Tofu And Tempeh
Tempeh provides approximately 1.1 mg of zinc per 100 g serving, while tofu offers around 0.5 mg, contributing to daily zinc intake.
Benefits Of Tofu And Tempeh
Tofu and tempeh are rich in plant-based protein and contain isoflavones, which support heart health and hormone balance. Thus, they are valuable additions to vegan diets.
Tips
Tempeh’s fermentation process reduces its phytate levels, allowing for better zinc absorption than non-fermented soy products like tofu, making it a preferred choice for zinc intake.

5. Vegetables
Types Of Vegetables
Zinc-rich vegetables include spinach, kale, broccoli, mushrooms, and garlic, adding essential nutrients to meals.
Zinc Content In Vegetables
Spinach contains about 0.53 mg of zinc per 100 g, while shiitake mushrooms are higher at 1.33 mg per 100 g, making them valuable for boosting zinc intake.
Benefits Of Vegetables
Leafy greens and vegetables contain vitamins, antioxidants, and minerals that promote immunity, heart health, and energy.
Tips
Combine vegetables with zinc-rich nuts or seeds in salads or stir-fries to enhance overall zinc intake and create balanced, nutrient-dense meals.

6. Fortified Foods
Types Of Fortified Foods
Common zinc-fortified foods include breakfast cereals, plant-based milk, and nutritional yeast, often enriched for added nutrition.
Zinc Content In Fortified Foods
Fortified cereals can offer up to 4-5 mg of zinc per serving, substantially boosting daily intake.
Benefits Of Fortified Foods
Fortified foods are convenient for filling nutrient gaps, especially in vegan diets where natural sources of zinc may be limited.
Tips
Look for zinc-fortified options with minimal added sugars to keep your diet balanced and nutritious.

7. Dried Fruits
Types Of Dried Fruits
Dried fruits like prunes, apricots, and raisins offer trace amounts of zinc, making them a light zinc source.
Zinc Content In Dried Fruits
Though not as zinc-rich as other foods, dried fruits contribute small amounts of zinc, fibre, iron, and other essential minerals.
Benefits Of Dried Fruits
Dried fruits are portable, naturally sweet, and provide quick energy, making them a convenient snack or meal addition.
Tips
Add dried fruits to oatmeal, salads, or trail mix to enhance flavour and boost the nutrients in your meals.

8. Sea Vegetables
Types Of Sea Vegetables
Sea vegetables like nori, kelp, dulse, and wakame are excellent sources of trace minerals, including zinc.
Zinc Content In Sea Vegetables
Nori, a popular type of seaweed, contains about 1 mg of zinc per 100g, contributing to daily intake.
Benefits Of Sea Vegetables
Sea vegetables are nutrient-dense, providing essential minerals like iodine, which support thyroid health, and other vitamins and antioxidants.
Tips
To boost your meal's nutrient profile, use seaweed sheets for sushi wraps, sprinkle dried flakes on soups and salads, or blend into smoothies.

9. Nutritional Yeast
Zinc Content In Nutritional Yeast
Nutritional yeast provides approximately 2 mg of zinc per tablespoon, although the content can vary by brand.
Benefits Of Nutritional Yeast
Popular in vegan diets for its cheesy, nutty flavour, nutritional yeast is also rich in B vitamins, protein, and fiber, supporting energy and overall health.
Tips
Sprinkle nutritional yeast on popcorn, pasta, or salads or mix it into sauces to boost flavour and zinc intake. This versatile addition to various dishes is a great way to increase nutrients.

10. Amaranth And Quinoa
Zinc Content In Amaranth And Quinoa
Quinoa provides around 1.1 mg of zinc per 100g, while amaranth offers a similar amount, making both grains excellent sources of this essential mineral.
Benefits Of Amaranth And Quinoa
Quinoa and amaranth are complete proteins, offering all nine essential amino acids. They are also rich in iron, magnesium, and fiber, supporting overall health and muscle repair.
Tips
Use quinoa or amaranth as a base for salads, grain bowls, or side dishes. Amaranth can also be eaten as porridge or mixed into baked dishes for an extra nutritional boost.

11. Wild Rice
Zinc Content In Wild Rice
Wild rice provides approximately 1.3 mg of zinc per 100 g, contributing to your daily zinc intake.
Benefits Of Wild Rice
Wild rice is a fiber and protein powerhouse, surpassing many grains in these nutrients. It also contains antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, promoting heart health and digestion.
Tips
Swap wild rice for white rice in stir-fries, casseroles, or stuffed vegetables. Its chewy texture and nutty flavour enhance dishes and boost your zinc intake.

12. Green Peas
Zinc Content In Green Peas
Green peas provide around 1.2 mg of zinc per cup (cooked), contributing to daily zinc needs.
Benefits Of Green Peas
Besides zinc, green peas are rich in protein, fiber, and essential vitamins like vitamins C and K, which support immune function and digestive health.
Tips
Add green peas to soups, stews, or salads for a nutrient boost, or blend them into a creamy pea spread for a tasty, zinc-packed snack.

13. Cashews
Zinc Content In Cashews
Cashews provide approximately 5.6 mg of zinc per 100g, making them a good mineral source.
Benefits Of Cashews
Cashews are rich in healthy fats, antioxidants, and magnesium, which support the brain, heart, and overall well-being.
Tips
Enjoy cashew butter as a toast spread, or add it to smoothies. Snack on raw cashews or incorporate them into curries and stir-fries for a creamy texture and a boost of nutrition.

14. Sunflower Seeds
Zinc Content In Sunflower Seeds
Sunflower seeds provide around 5 mg of zinc per 100g, contributing to your daily zinc intake.
Benefits Of Sunflower Seeds
Rich in vitamin E, antioxidants, and healthy fats, sunflower seeds help support skin health, reduce inflammation, and promote overall wellness.
Tips
Sprinkle sunflower seeds on salads, mix them into granola, or use sunflower seed butter as a spread or to boost your smoothie’s nutritional value. They add both texture and health benefits to various dishes.

15. Dark Chocolate
Zinc Content In Dark Chocolate
Dark chocolate (70-85%) provides about 3.3 mg of zinc per 100g, offering a tasty way to boost zinc intake.
Benefits Of Dark Chocolate
Dark chocolate, which is high in antioxidants, magnesium, and iron, supports heart health, brain function, and overall well-being.
Tips
Enjoy a small piece of dark chocolate as a satisfying treat, or incorporate dark chocolate chips into baking, oatmeal, or smoothies for added flavour and nutritional benefits.

16. Asparagus
Zinc Content In Asparagus
Asparagus contains about 0.6 mg of zinc per 100g, adding a small but valuable amount to your diet.
Benefits Of Asparagus
Rich in vitamins A, C, E, and K, asparagus provides powerful antioxidants that help boost the immune system and promote overall health.
Tips
Grill or roast asparagus for a delicious side dish, or add it to stir-fries, salads, or pasta to enhance its flavour and nutritional value. Its tender texture and mild taste complement a variety of meals.

17. Acorn Squash
Zinc Content In Acorn Squash
Acorn squash contains approximately 0.6 mg of zinc per cup (cooked), contributing to your daily zinc intake.
Benefits Of Acorn Squash
Acorn squash is high in fiber, vitamin C, and antioxidants, which support immune health, reduce inflammation, and promote digestive health.
Tips
Roast acorn squash for a wonderful side dish, or add it to salads, soups, or filled meals to boost flavour and zinc consumption. Its naturally sweet taste complements a wide range of foods.
Sample Meal Plan For Optimal Zinc Intake
To ensure a balanced and zinc-rich diet, here's a meal plan that includes various plant-based sources of zinc throughout the day:
Breakfast: Oatmeal with Chia, Pumpkin, and Fresh Berries
Begin the day with a hearty dish of oats. Oats are a great source of zinc, providing around 2.97 mg per 100g. Combine them with chia seeds, which contain zinc and omega-3 fatty acids, and pumpkin seeds, which are one of the highest plant-based sources of zinc (7.81 mg per 100g).
Fresh berries, such as blueberries or raspberries, are abundant in antioxidants and vitamin C, which improve their flavour and strengthen the immune system.
This meal contains fiber, healthy fats, and critical nutrients to keep you pleased and energized throughout the morning.
Lunch: Chickpea And Vegetable Stir-Fry With Quinoa
For lunch, prepare a chickpea and vegetable stir-fry with quinoa. Chickpeas provide approximately 1.3 mg of zinc per 100g and are packed with protein and fiber, while quinoa is a complete protein and a good source of zinc (1.1 mg per 100g).
Stir-fry your favorite vegetables, such as bell peppers, spinach, and broccoli. These are all packed with vitamins and minerals that promote overall health.
This meal offers a high-protein, plant-based combination that ensures you get zinc and other essential nutrients, such as iron and magnesium. Serve over quinoa for added fiber and amino acids.
Snack: Mixed Nuts and Dried Apricots
For a satisfying snack, mix a handful of nuts (cashews, almonds, and sunflower seeds) with dried apricots.
Dried apricots are excellent sources of zinc and healthy fats, and they also provide a small amount of zinc, potassium, and vitamin A.
This portable and nutrient-dense snack offers a balance of protein, healthy fats, and carbohydrates to curb your hunger between meals while boosting your zinc intake.
Dinner: Tempeh And Vegetable Bowl With Kale, Brown Rice, And Tahini Dressing
For dinner, enjoy a tempeh and vegetable bowl with kale, brown rice, and tahini dressing. Tempeh is fermented and a great source of zinc (1.1 mg per 100g), and kale is rich in vitamins A, C, and K, which support the immune system. Brown rice is another good source of zinc and fiber.
Drizzle tahini dressing over this dish for more flavour and healthy fats. This nutrient-dense dinner provides a balanced combination of protein, fiber, and essential minerals, ensuring an optimal zinc intake to support overall health.

Maximizing Zinc Absorption On A Vegan Diet
Several factors can impact zinc absorption. Here are some tips to ensure you’re getting the most from your plant-based zinc sources:
1. Reduce Phytates
Phytates in whole grains and legumes can reduce zinc absorption by binding to minerals. Techniques like soaking, sprouting and fermenting break down phytates, enhancing zinc bioavailability and making it easier for the body to absorb this essential mineral.
2. Eat Vitamin C-Rich Foods
Combining zinc-rich foods with vitamin C sources, such as citrus fruits, bell peppers, and strawberries, can boost zinc absorption.
Vitamin C helps convert zinc into a more absorbable form, making it easier for the body to utilize this critical mineral.
3. Avoid Excessive Iron Intake
Excessive iron can interfere with zinc absorption, as the two minerals compete within the body. To optimize zinc levels, avoid high-dose iron supplements unless necessary, and aim to balance meals containing both iron and zinc-rich foods for better nutrient harmony.
4. Use Cookware That Adds Zinc
Cooking with certain types of stainless steel or cast-iron cookware can add small amounts of zinc to your meals, especially when preparing acidic foods like tomatoes. This technique naturally boosts zinc intake, making it a simple way to enrich your diet.
5. Consider Zinc Supplements
A vegan supplement can help fill the gap if meeting daily zinc needs is challenging. Speaking with a healthcare expert before selecting the appropriate supplement and dosage is critical to ensure it meets your nutritional requirements.
FAQs
Q1: Can Zinc Be Absorbed From Plant-Based Foods?
Answer: Yes, although plant-based sources of zinc contain phytates, which can reduce absorption, methods like soaking, sprouting, and fermenting can help enhance bioavailability and improve zinc absorption.
Q2: Are There Any Risks Of Zinc Deficiency On A Vegan Diet?
Answer: If zinc intake is insufficient, it can lead to immune dysfunction, poor wound healing, and hair loss. However, with careful meal planning, vegans can quickly meet their zinc needs through plant-based sources.
Q3: Can I Take A Zinc Supplement If I'm Not Getting Enough?
Answer: A vegan zinc supplement may be helpful if you’re struggling to meet your zinc needs through food. Always consult your healthcare professional before taking any supplements to ensure you are taking the correct dosage.
Q4: Are There Any Foods To Avoid With Zinc Intake?
Answer: When consumed in excess, foods high in calcium or iron can compete with zinc for absorption. It's best to balance your intake of these minerals and not take high-dose iron supplements without a doctor’s advice.
Q5: Does Cooking Affect The Zinc Content In Food?
Answer: Cooking can impact zinc levels in food, but it’s generally not significant enough to drastically reduce zinc content. However, soaking or sprouting grains, legumes, and seeds before cooking can improve zinc absorption.
Q6: Are There Any Symptoms Of Zinc Deficiency To Watch For?
Answer: Common symptoms of zinc deficiency include frequent illness or infections, slow wound healing, hair loss, poor appetite, and skin issues like acne. If you experience these symptoms, it’s worth getting your zinc levels checked.
Conclusion
Incorporating enough zinc into a vegan diet is achievable and beneficial for maintaining a strong immune system, energy levels, and overall health.
You can ensure a well-rounded intake of this essential mineral by choosing various vegan sources of zinc, like nuts, seeds, legumes, whole grains, and fortified foods.
Straightforward preparation tips, such as soaking, sprouting, and pairing zinc-rich foods with vitamin C sources, will enhance zinc absorption. Prioritizing these nutrient-packed foods will help you thrive on a plant-based diet.
I trust you enjoyed this article on the Ultimate Guide To Vegan Sources of Zinc: Boosting Immunity. Please stay tuned for more plant-based recipes, vegan travel tips, and lifestyle inspiration.
Take care!
— JeannetteZ 🌿
💬 Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I’d love to hear from you. Please leave your comments below, or email me directly at Jeannette@LivingTheVeganLifestyle.org.
📚 More Vegan Lifestyle Reads
🌱 My #1 Recommendation for Online Success
Sharing my passion for vegan living — from food to fashion — has been such a rewarding journey.
If you’ve ever dreamed of building your own ethical lifestyle brand or blog, this is the best place to start.
🌟 See How Vegan Bloggers Build Online Income — Try WA Free (No Credit Card Needed)
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate and participant in other affiliate programs, I earn from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you. Please read my full affiliate disclosure.