Do Vegans Drink Milk?

Do Vegans Drink Milk? – A Deep Dive Into Dairy Alternatives
In recent years, veganism has moved from a niche dietary choice to a mainstream lifestyle millions worldwide embrace.
At the core of veganism is excluding all animal products, including milk. This raises a common question: do vegans drink milk?
The short answer is no. Vegans do not consume traditional dairy milk.
However, the reasons behind this choice are complex and multifaceted, encompassing ethical, environmental, and health considerations.
Additionally, the increasing popularity of veganism has led to a diverse selection of dairy alternatives being available in stores.
This article explores why vegans avoid milk and delve into the various plant-based milk alternatives they choose instead.
Reasons Vegans Don’t Drink Milk
Vegans avoid milk for various reasons, encompassing ethical, environmental, and health concerns. Here are some of the primary motivations for why milk is excluded from a vegan diet:

1. Ethical Concerns
Vegans abstain from consuming milk primarily due to ethical concerns. The dairy industry often involves practices that vegans find objectionable, such as the separation of calves from their mothers shortly after birth, which distresses both.
Additionally, dairy cows are frequently confined and subjected to continuous impregnation to maintain milk production.
These practices are seen as exploitative and inhumane, leading vegans to avoid dairy products altogether.
2. Animal Welfare
The well-being of dairy cows is a major concern for vegans. Cows are often bred for high milk production, which can lead to physical strain and health issues.
Many vegans believe that it is morally wrong to exploit animals for human benefit, particularly when it results in suffering.
The living conditions and treatment of dairy cows in factory farms are often far from natural, and the animals' well-being is compromised to maximize production and profit.
3. Environmental Impact
The dairy industry has a considerable environmental footprint. Deforestation, water pollution, soil deterioration, and greenhouse gas emissions are all impacted by dairy farming.
Producing dairy requires significant resources, including land, water, and feed for the cows. For vegans who prioritize sustainability, avoiding dairy is a way to reduce their environmental impact and promote more sustainable agricultural practices.

4. Health Concerns
Some vegans abstain from milk due to health concerns. Dairy products' high cholesterol and saturated fat content have been linked to a range of health issues, including heart disease.
Additionally, many people are lactose intolerant or have a dairy allergy, making milk consumption uncomfortable or harmful.
Vegans often turn to plant-based alternatives, which can offer nutritional benefits without the adverse health effects of dairy.
5. Hormones And Antibiotics
Dairy cows are frequently given hormones and antibiotics to increase milk production and prevent disease.
These compounds may find their way into milk, which raises questions about how they can affect people's health.
Dairy products contain hormones that have been connected to several health problems, such as hormone imbalances and an elevated risk of cancer. Vegans prefer to avoid these potential risks by choosing plant-based milk alternatives.
6. Lactose Intolerance
Many individuals are lactose intolerant due to a lack of lactase, the enzyme required to digest lactose, and sugar in milk.
Consumption of dairy products can result in symptoms such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, and stomach cramps.
Choosing lactose-free alternatives allows both vegans and those with lactose intolerance to avoid these uncomfortable and sometimes severe reactions.
7. Dietary Preferences
This dietary choice is often rooted in a broader lifestyle philosophy that promotes compassion, health, and sustainability.
By eliminating animal products, vegans align their food choices with their ethical beliefs and personal values.
For many individuals, this choice extends beyond their diet to include other aspects of their lives, such as clothing and cosmetics.

8. Nutritional Preferences
Vegans prefer plant-based milk for its nutritional benefits. Thanks to fortification with vitamins and minerals like calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin B12, the nutritional profile of many plant-based milks is comparable to or better than that of cow's milk.
Additionally, plant-based milk can be tailored to specific dietary needs, providing a versatile and nutritious option for those seeking to avoid dairy.
9. Allergies
Certain people have allergies to proteins found in milk, such as casein and whey. Hives, stomach problems, and anaphylaxis are mild to severe symptoms of dairy allergies.
Consuming dairy is not an option for those with a milk allergy. Vegans and those with allergies often find plant-based milk alternatives a safe and satisfying replacement.
10. Cruelty-Free Lifestyle
Vegans strive to live a cruelty-free lifestyle, which involves avoiding products and practices that harm animals.
This philosophy extends beyond diet to clothing, cosmetics, and other consumer goods. By choosing plant-based milk alternatives, vegans reduce their reliance on industries that exploit animals, promoting a more compassionate and ethical way of life.
11. Sustainability
For many vegans, sustainability is a top priority. Producing dairy milk is resource-intensive, requiring extensive water, land, and feed, whereas plant-based milk alternatives generally have a lower environmental footprint.
By opting for these alternatives, vegans support more sustainable food systems that are less taxing on the planet's resources and ecosystems.

12. Carbon Footprint
Many vegans prioritize reducing their carbon footprint. Dairy production produces substantial greenhouse gas emissions, which contribute to climate change.
Livestock farming, which includes dairy production, contributes significantly to methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas.
Choosing plant-based milk alternatives helps vegans lower their carbon footprint and mitigate their impact on global warming.
13. Resource Efficiency
Plant-based milk production is often more resource-efficient than dairy farming. Growing almonds, oats, and soy plants requires less water and land than raising dairy cows.
This efficiency is crucial in a world facing increasing pressure on natural resources. By consuming plant-based milks, vegans contribute to a more efficient and sustainable use of resources.
14. Waste Reduction
The dairy industry generates considerable waste, including manure, which can pollute waterways and contribute to environmental degradation.
Plant-based milk production tends to produce less waste and pollution. For vegans committed to reducing their environmental impact, choosing plant-based alternatives is a logical step toward minimizing waste and promoting cleaner production methods.
15. Innovation And Variety
The growing popularity of veganism has spurred innovation in the food industry, leading to various plant-based milk alternatives.
These products cater to diverse tastes and dietary needs, providing almond, soy, oat, and coconut milk options.
This variety allows vegans to enjoy different flavours and nutritional profiles while adhering to their ethical and dietary choices.
16. Market Availability
The growing popularity of plant-based products has led to a significant rise in the availability of dairy alternatives.
Supermarkets and health food stores now offer various plant-based milks, cheeses, yogurts, and other products.
This accessibility makes it easier for vegans to maintain their dietary choices without feeling deprived, encouraging them to adopt a vegan lifestyle.
17. Influence Of The Vegan Community
The vegan community and advocacy groups play a significant role in educating people about why to avoid dairy.
Documentaries, books, social media influencers, and activists highlight dairy consumption's ethical, environmental, and health implications.
This collective awareness and support from the vegan community encourage more people to adopt a vegan lifestyle and explore plant-based alternatives.
18. Cultural Shifts
There is a growing shift in cultural attitudes towards food and diet, leading to greater acceptance and normalization of veganism.
As societal norms evolve, more people are open to exploring plant-based diets, including avoiding dairy.
The increasing availability of vegan options in restaurants, cafes, and supermarkets reflects this shift, making it easier for individuals to choose plant-based alternatives.
How Do Vegans Get Milk?
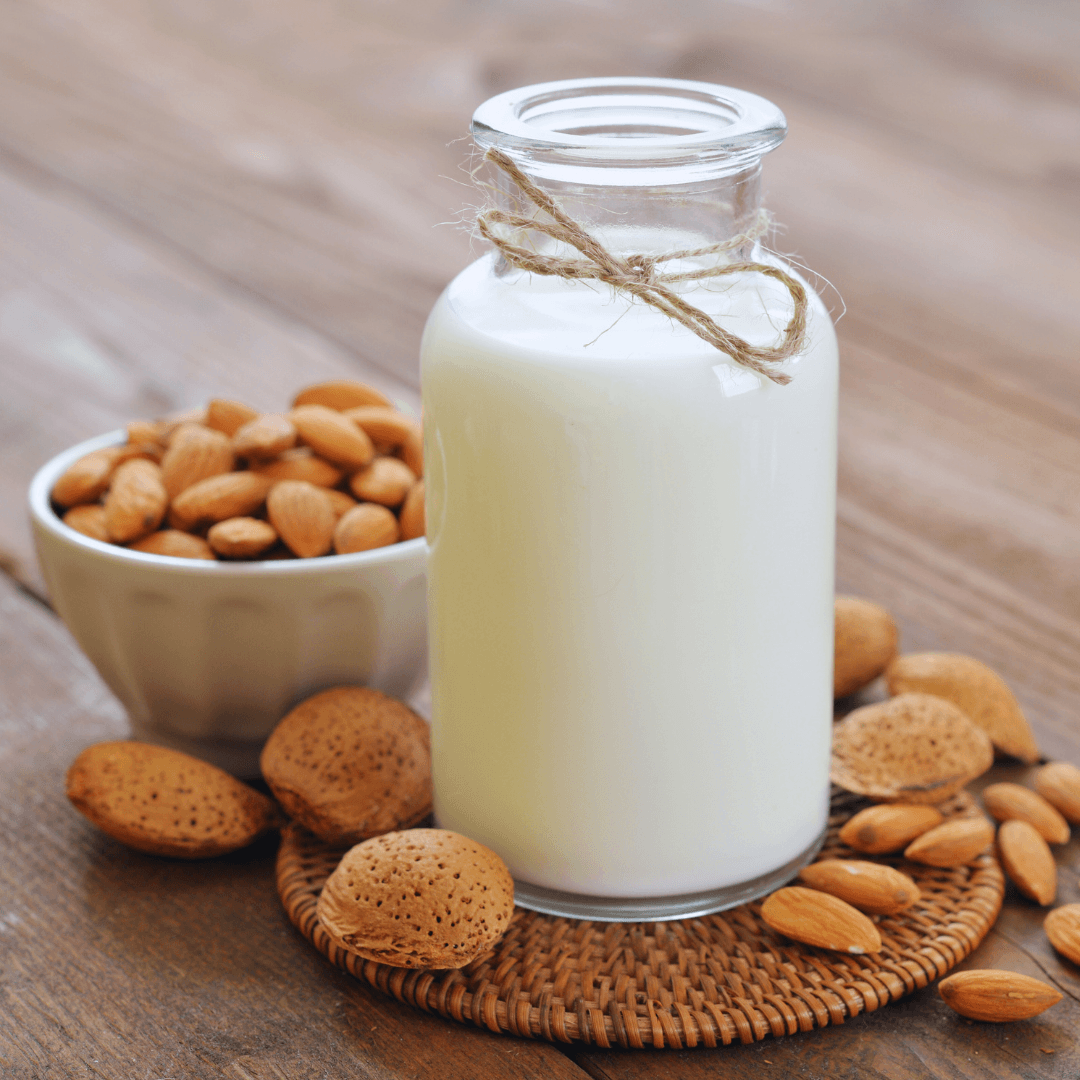

1. Almond Milk
Almond milk is renowned for its creamy texture and light, nutty flavour. It is made by mixing almonds with water and then filtering the liquid.
It is low in calories and contains essential nutrients like vitamin E and calcium. Almond milk is versatile and suitable for drinking alone, adding to coffee, or using it in recipes.
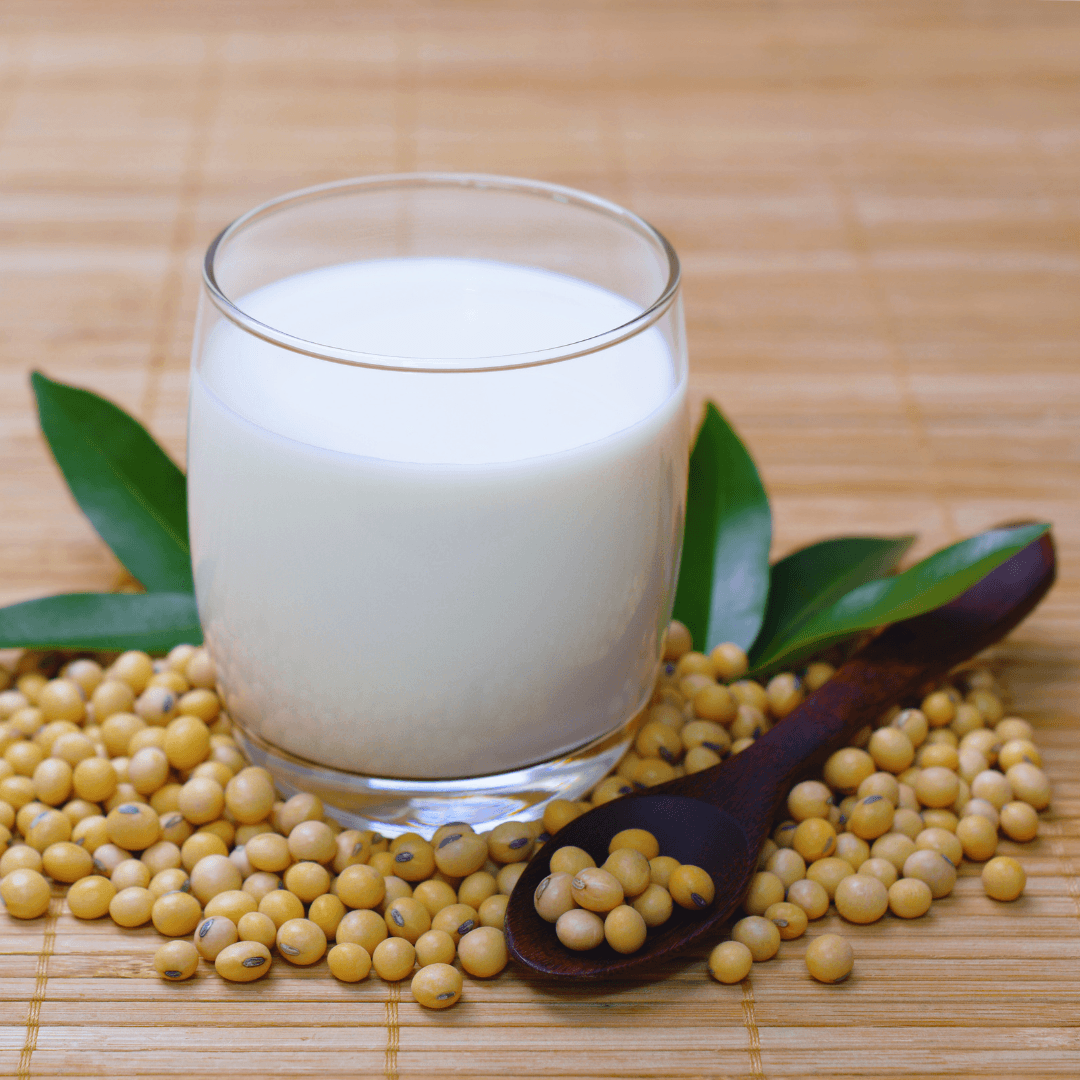

2. Soy Milk
Soy milk, made from soybeans, is a staple in many vegan diets. It has a creamy consistency and a slightly bean-like flavour, varying depending on the brand and any added flavours.
Like cow's milk in protein content, soy milk is frequently enhanced with vital nutrients like calcium and vitamin D. It serves well in cooking, baking, and beverages, offering versatility in various recipes.
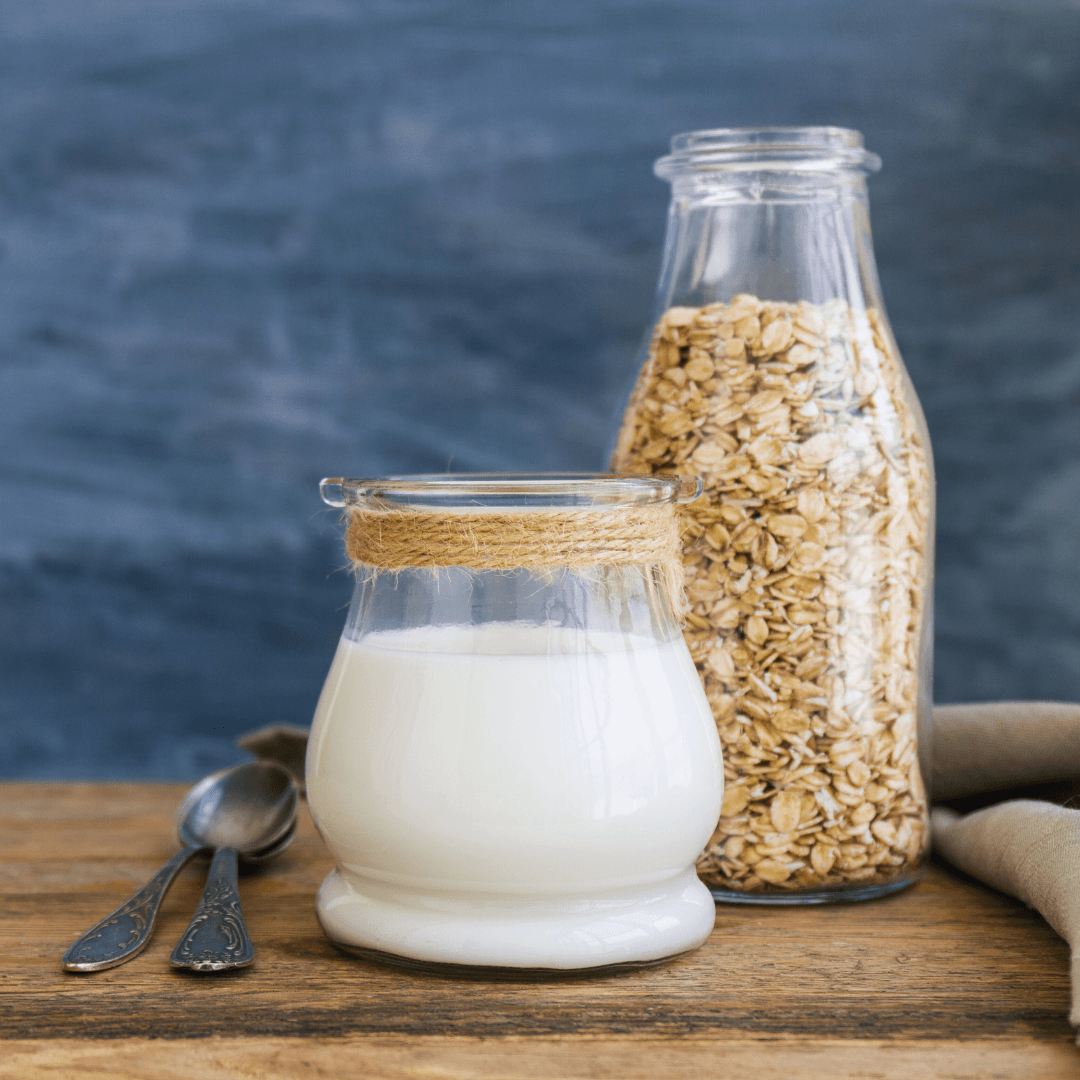

3. Oat Milk
Oat milk is popular for its rich, creamy texture and mild flavour. Derived from soaked and blended oats, this milk alternative is widely recognized for its sustainability, as oats typically require less water to cultivate than almonds.
Oat milk is naturally sweet and can be used in coffee, smoothies, cereals, and baking. Additionally, it provides a good amount of fiber and can be fortified with extra nutrients.
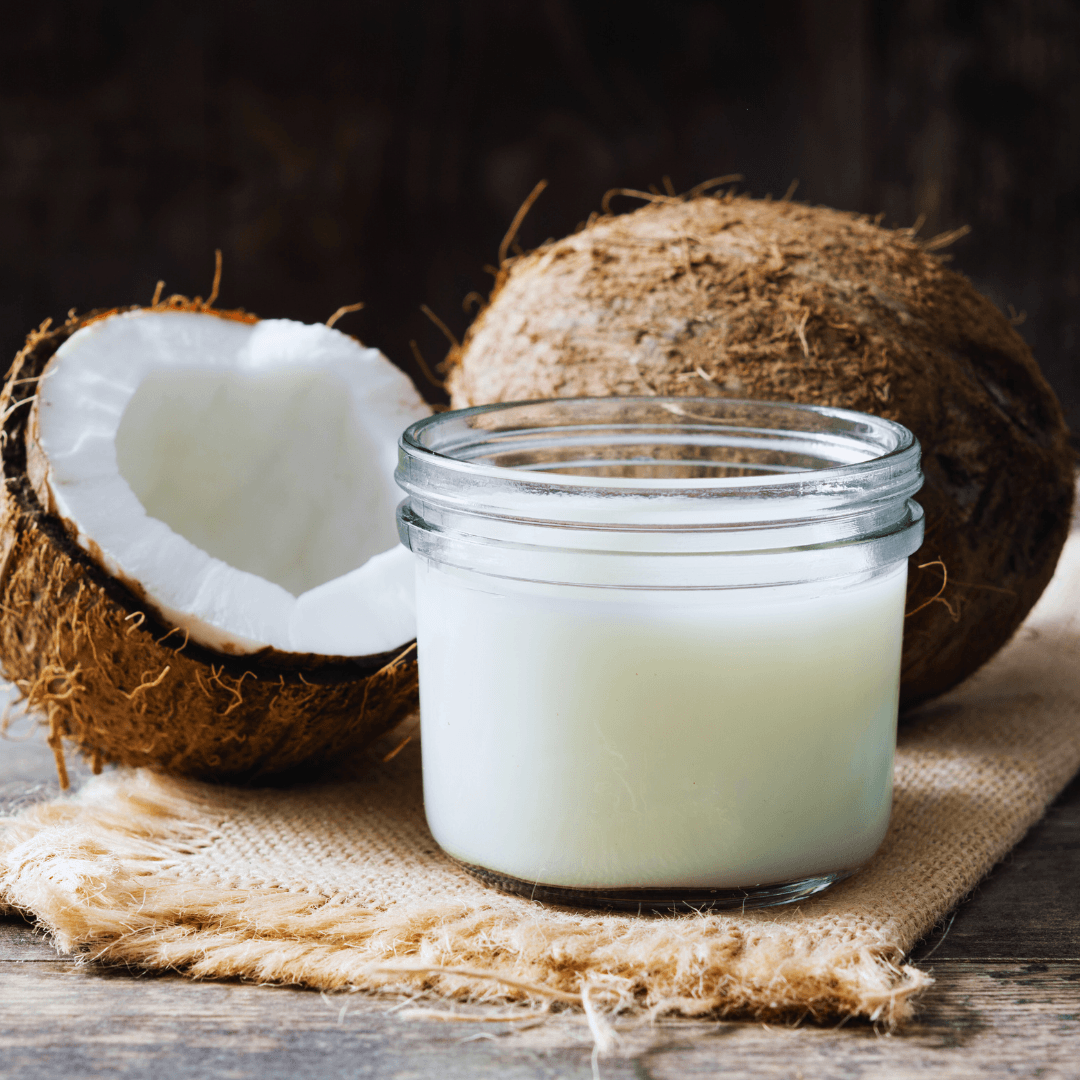

4. Coconut Milk
Coconut milk is a popular plant-based alternative derived from the white flesh of mature coconuts.
It is a common ingredient in cooking, especially in Southeast Asian cuisine, because of its unique, sweet flavour and creamy consistency.
Coconut milk comes in two varieties: canned and carton, with the carton being more diluted and palatable. It provides healthy fats but is lower in protein than other plant-based milks.
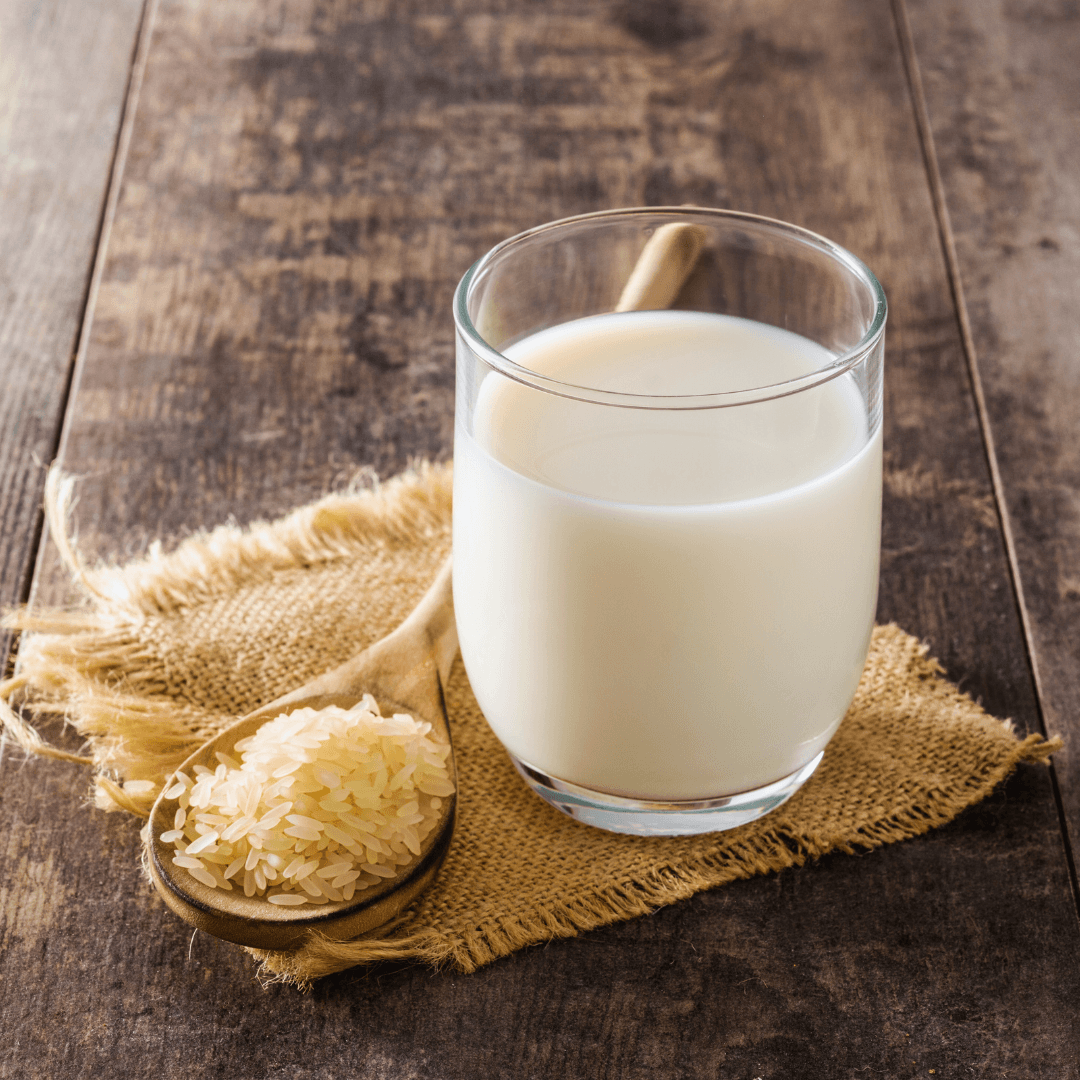

5. Rice Milk
Milling rice and adding water creates a naturally sweet and thin substitute. It is a hypoallergenic option, making it suitable for those with soy, nut, or gluten allergies.
While rice milk contains less protein, it is commonly fortified with additional vitamins and minerals. Its mild flavour makes it a good choice for drinking, cereal, and light cooking.
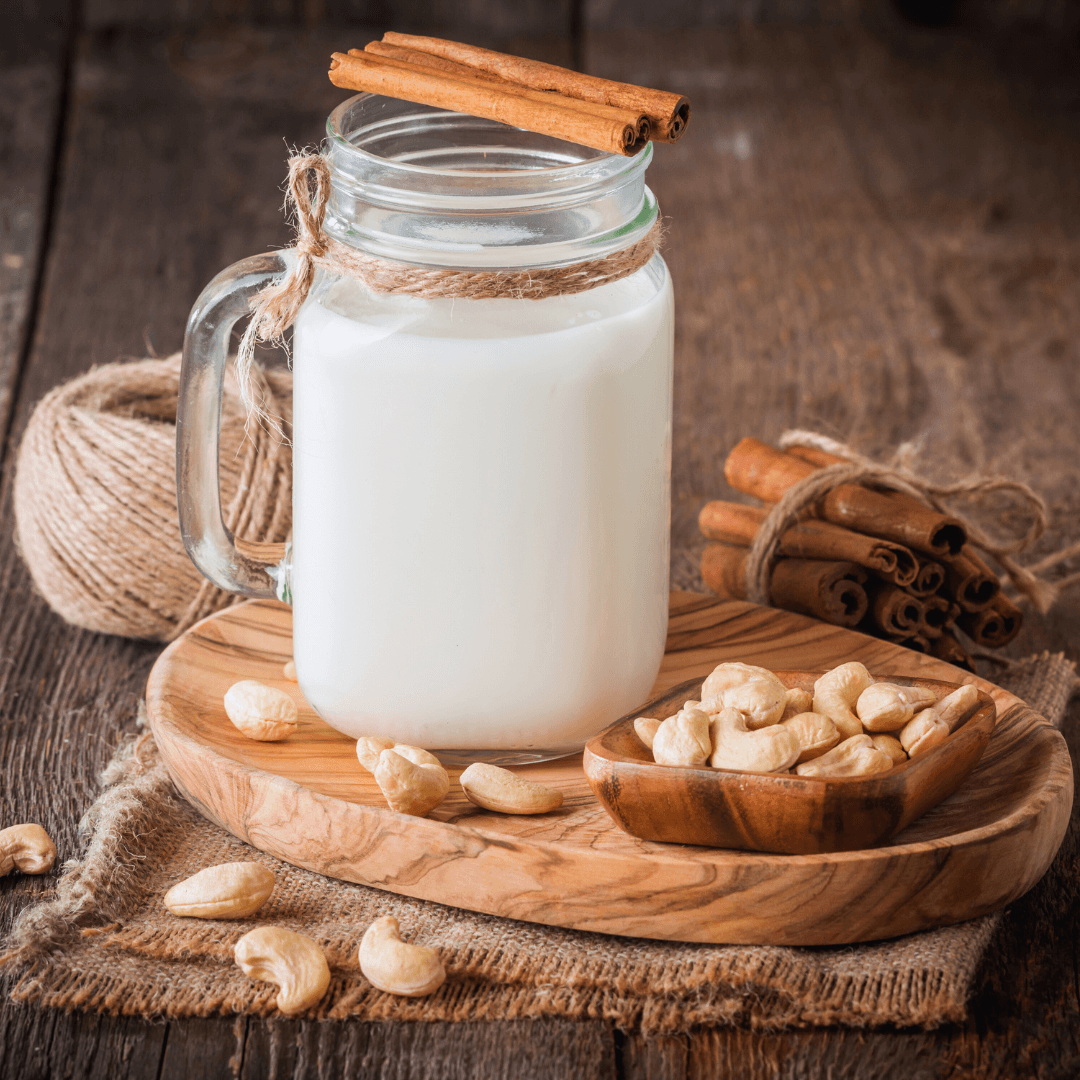

6. Cashew Milk
Cashew milk has a moderate, nutty flavour and a creamy texture. It is made by blending cashews with water.
This adaptable milk substitute tastes great in sauces, soups, and coffee. Compared to other plant-based milks, it has fewer calories and fat and can be enhanced with additional nutrients like calcium and vitamin D.
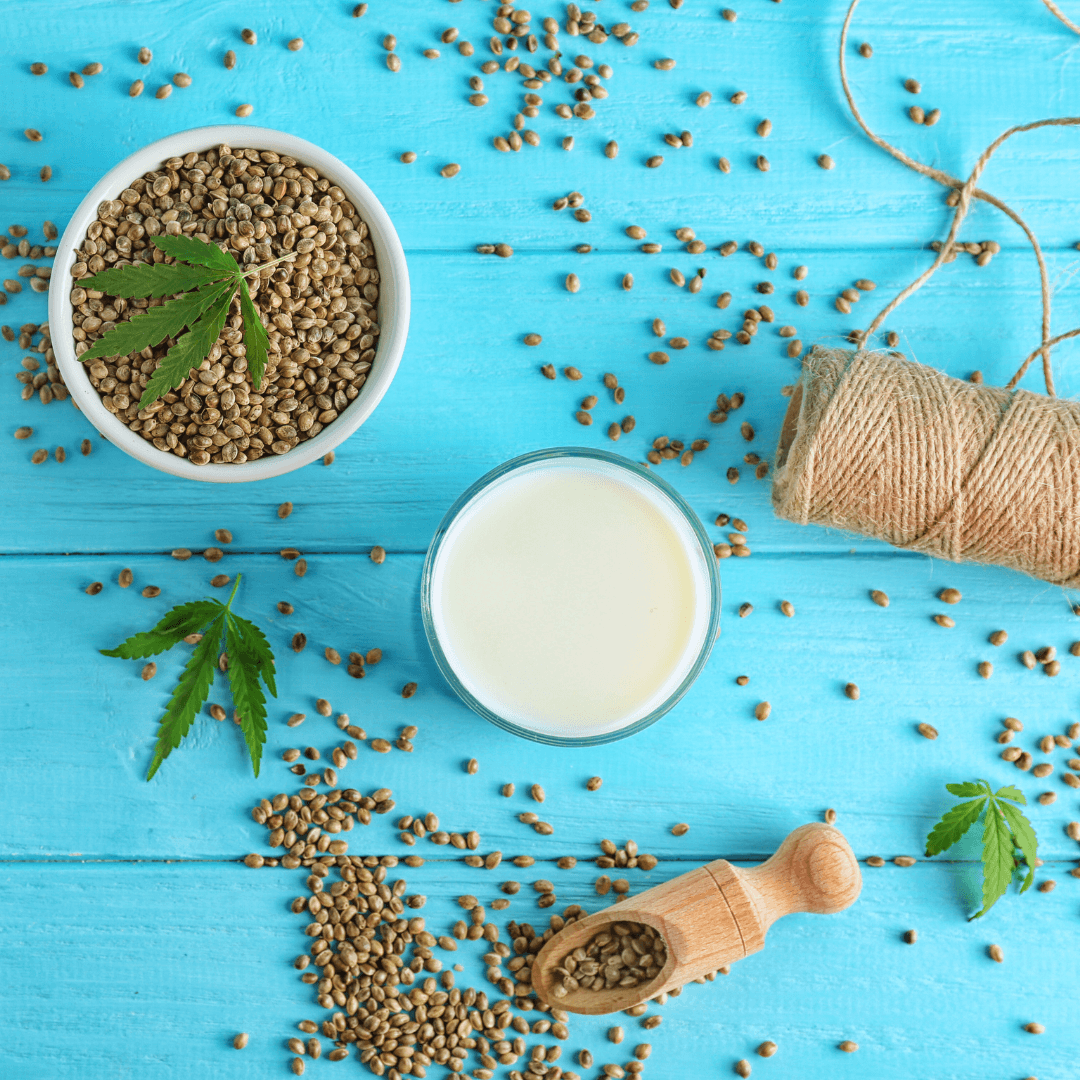

7. Hemp Milk
Hemp milk has a creamy texture and a mildly nutty flavour. It is made by blending hemp seeds with water.
Nutritionally, hemp milk is rich in omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids and offers a good source of plant-based protein.
Furthermore, it can be enriched with additional vitamins and minerals. It is ideal for drinking, blending into smoothies, and using in various recipes.
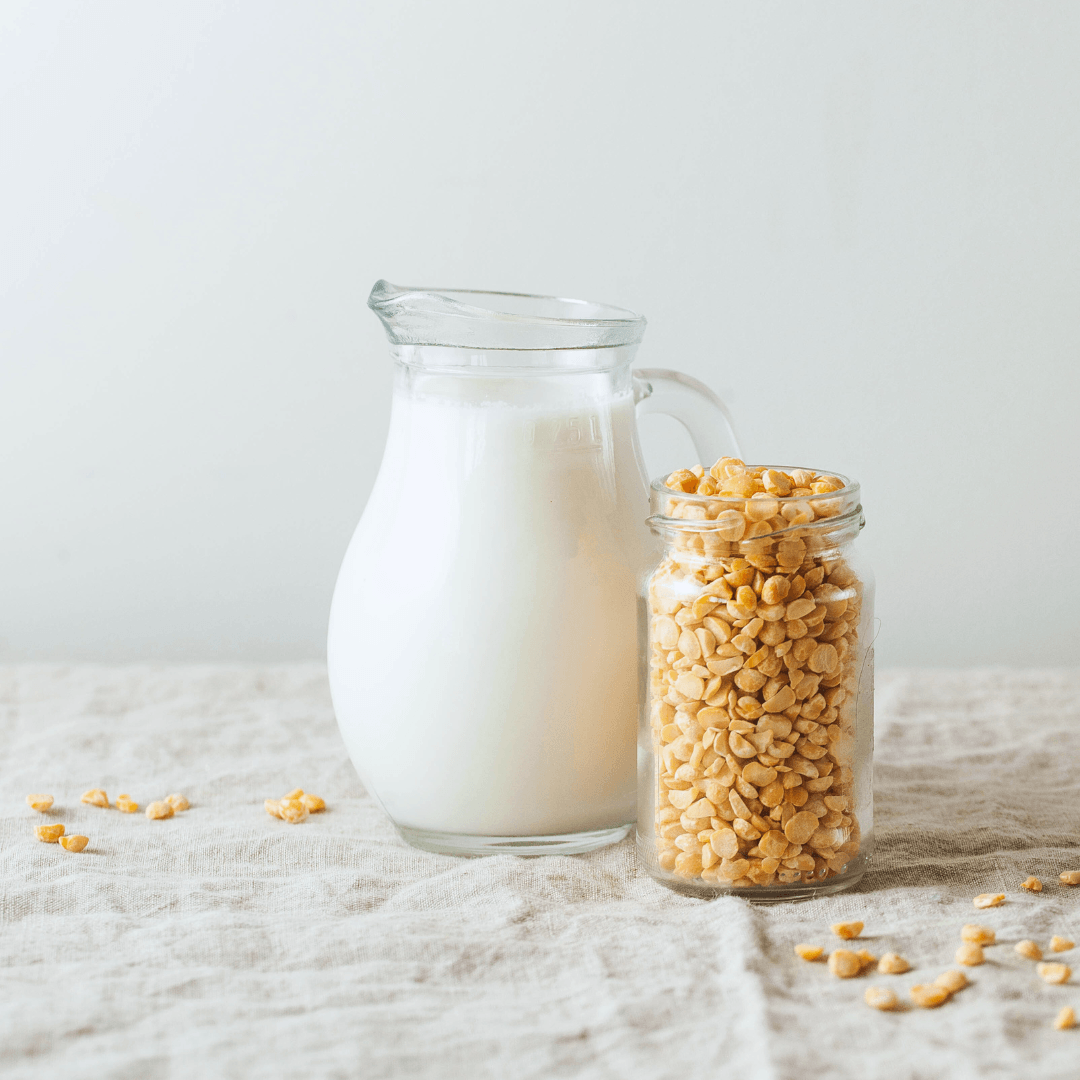

8. Pea Milk
A more recent product on the plant-based milk scene is pea milk, produced from yellow split peas. It has a creamy texture and a neutral flavour, making it versatile for various uses.
Pea milk is highly protein and often fortified with calcium, vitamin D, and other nutrients. It is an environmentally friendly option, as peas require less water and fertilizer than other crops.
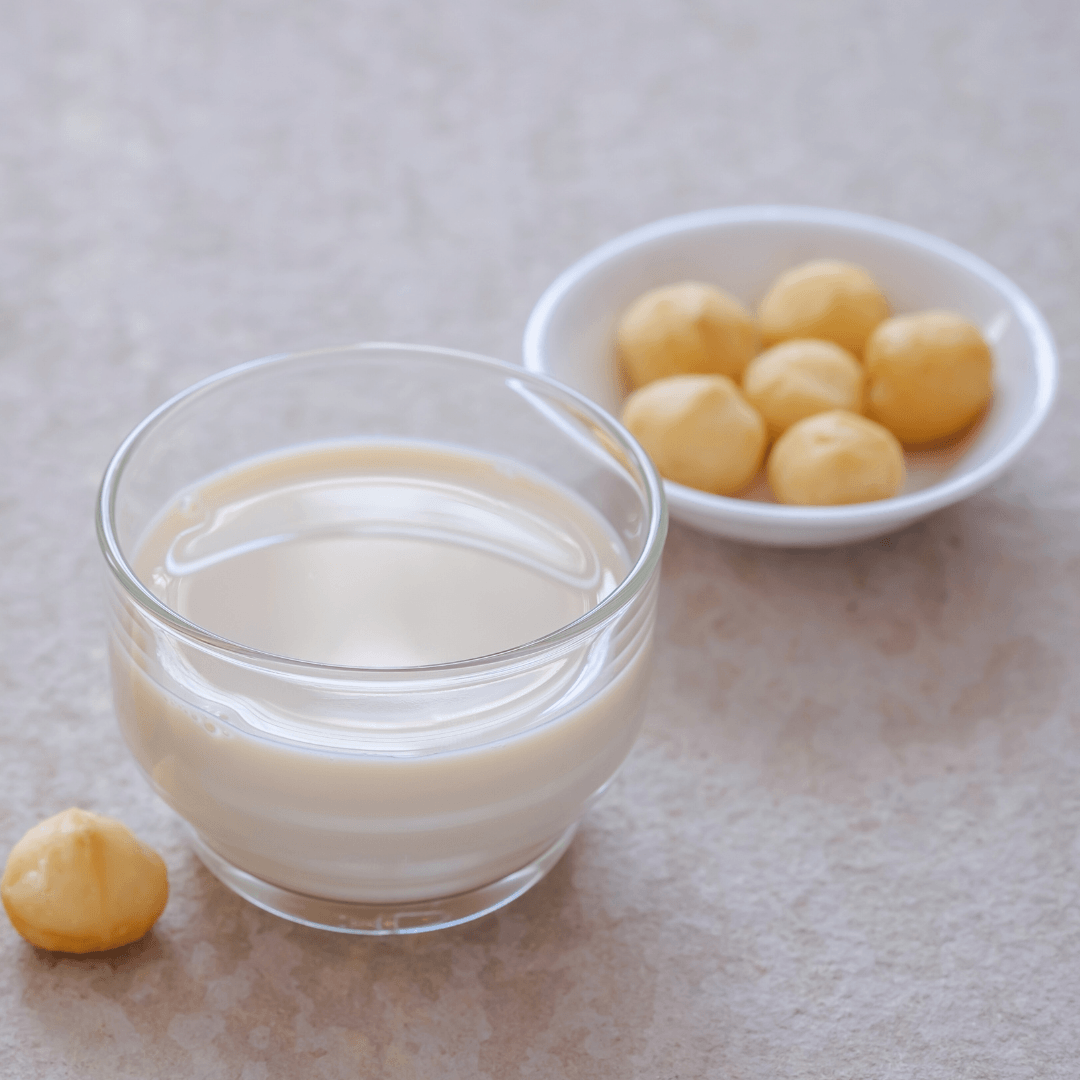

9. Macadamia Milk
Macadamia milk is made from nuts and water, producing a rich, creamy alternative with a slightly sweet, nutty flavour.
It has fewer calories and carbohydrates than dairy milk and can be fortified with extra nutrients. Macadamia milk is a luxurious option for drinking, adding to coffee, using in desserts, and cooking.
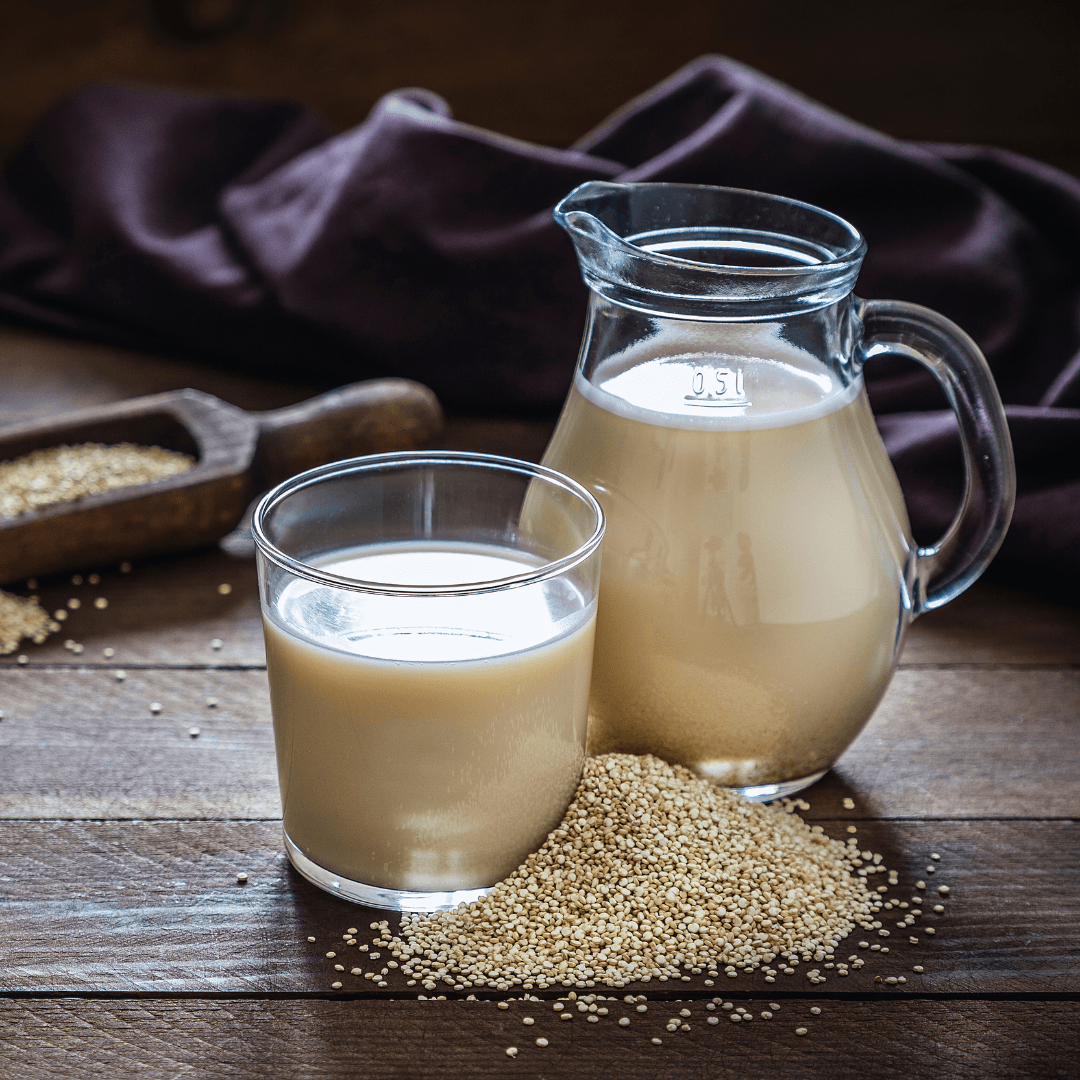

10. Quinoa Milk
Quinoa milk, made from the nutrient-dense quinoa grain, offers a slightly nutty flavour and a light texture.
It is a nutrient-dense option that is high in vital amino acids and a superb source of protein. Quinoa milk is often fortified with vitamins and minerals and can be used for drinking, adding to cereals, and in light cooking.
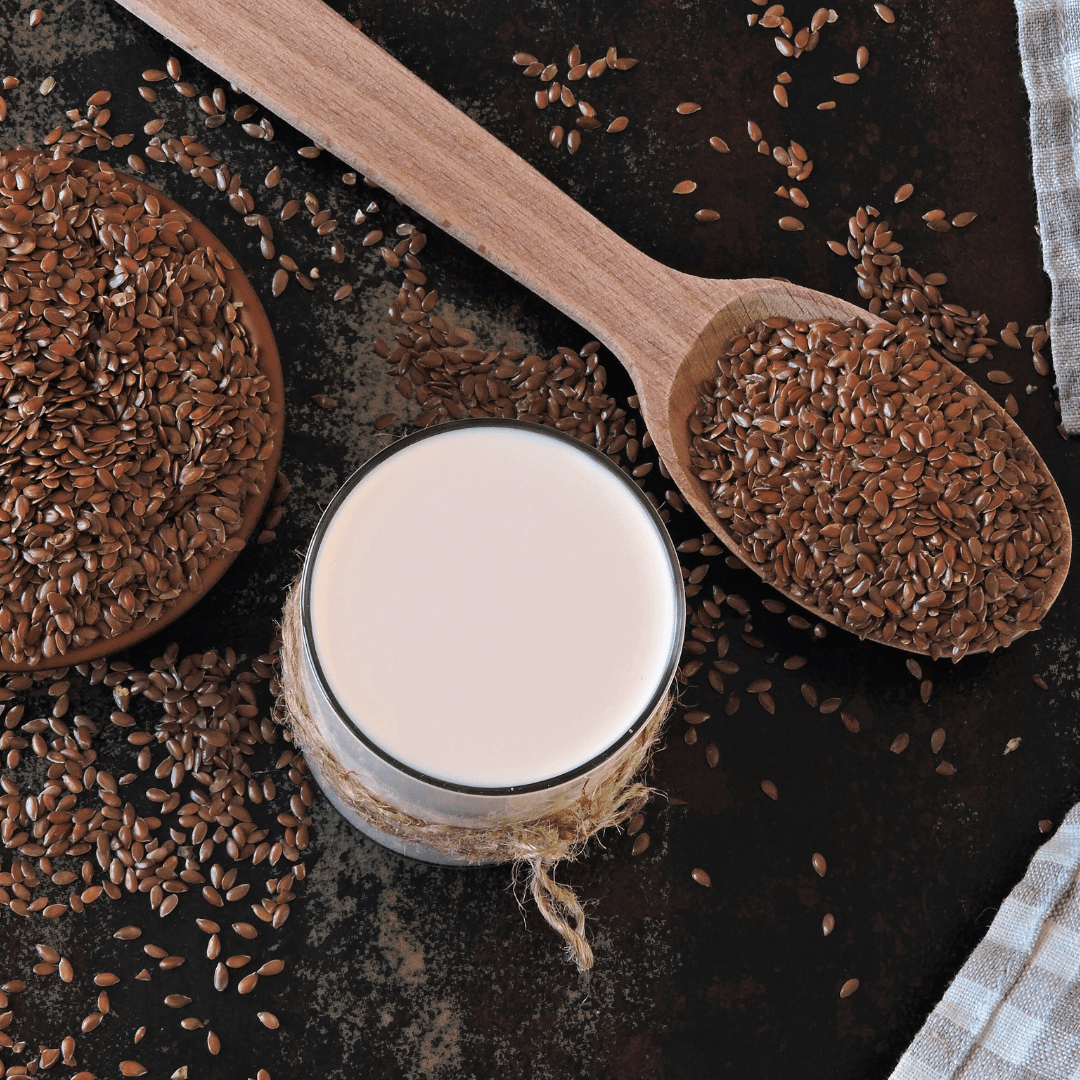

11. Flax Milk
Flax milk is made from flaxseeds and water, providing a light, slightly nutty flavour. It is abundant in omega-3 fatty acids, which are good for the heart.
Calcium and vitamin D are two common vitamins and minerals added to flax milk for fortification. This versatile milk alternative makes it ideal for drinking, adding to smoothies, and incorporating into recipes.
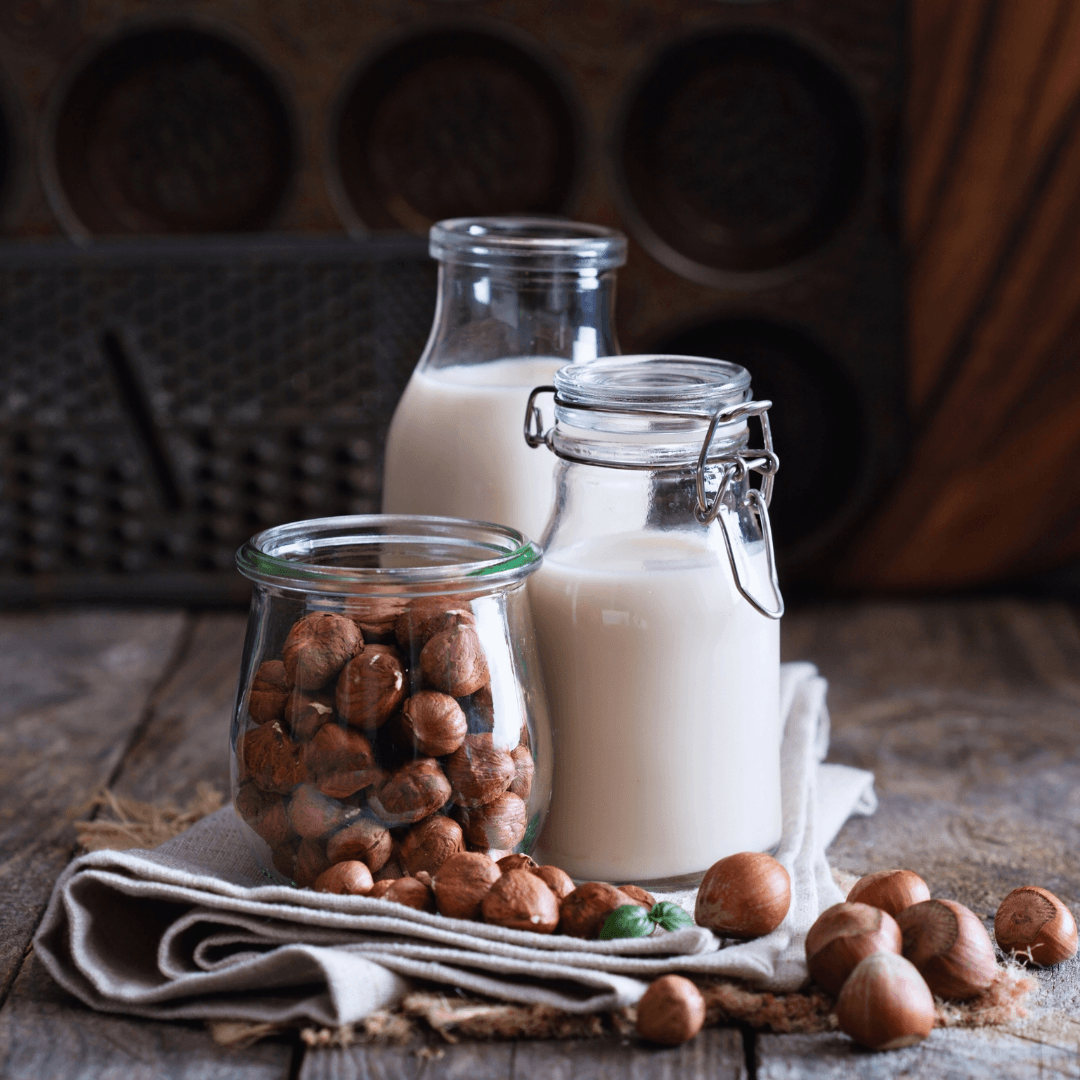

12. Hazelnut Milk
Hazelnut milk, created by blending hazelnuts with water, boasts a rich, nutty flavour and a creamy texture.
This indulgent milk alternative is lower in calories and carbohydrates than dairy milk. It can be fortified with extra nutrients and is perfect for drinking, adding to coffee, using in desserts, and cooking.
How Can I Make My Plant-Based Milk At Home?
Making your plant-based milk at home is easy and cost-effective. Here's a basic guide to making almond milk, but the process is similar for other nuts, seeds, or grains.
Ingredients
- 1 cup raw almonds (or other nuts/seeds/grains)
- 4 cups water
- Optional: sweeteners (like dates, maple syrup), flavourings (like vanilla extract), and a pinch of salt
Equipment
- Blender
- Nut milk bag or cheesecloth
- Large bowl
- Storage container
Method
- Put the almonds in a basin and add enough water to cover them. Soak them for eight to twelve hours, or overnight, to soften them and make blending simpler. Drain and rinse the almonds well under cold running water after soaking.
- Put 4 cups of fresh water and the soaked almonds in a blender. Blend high for one to two minutes until the mixture becomes creamy and the almonds are completely broken down. Pour the almond mixture into a big dish covered with cheesecloth or a nut milk bag.
- Gently squeeze and twist the bag or cloth to extract as much liquid as possible, which will be your almond milk.
- To add sweeteners or flavourings, pour the almond milk back into the blender, add the desired ingredients, and blend for a short time to combine everything.
- Refrigerate the almond milk after transferring it to a sanitized glass bottle or jar. Shake thoroughly before using, as it might gradually separate. For three to four days, keep homemade almond milk refrigerated.
Tips
- Pulp: The leftover almond pulp can be used in baking, smoothies, or as a base for homemade almond flour.
- Other Varieties: You can use the same method to make milk from other nuts (like cashews or hazelnuts), seeds (like hemp or sesame), or grains (like oats or rice). The soaking time and blending process are similar, though grains may require cooking before blending.
Enjoy your homemade plant-based milk in smoothies, cereal, coffee, or just by itself!
FAQ
1. Is Plant-Based Milk Nutritious?
Answer: Indeed, several plant-based milks are enriched with vital elements, including calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin B12, rendering them a wholesome substitute for cow's milk. It's important to check the labels for fortification and added sugars.
2. How Does Plant-Based Milk Compare To Cow's Milk In Taste?
Answer: The taste of plant-based milk can vary significantly depending on the type and brand. Some people find them a pleasant alternative, while others may need time to adjust. Many people enjoy the variety of flavours and textures available.
3. Can Plant-Based Milk Be Used In Cooking And Baking?
Answer: Yes, plant-based milk can be used in cooking and baking as a substitute for cow's milk. They work well in most recipes, including smoothies, soups, sauces, and baked goods.
Different types of plant-based milk may produce slightly different results, so that some experimentation might be needed.
4. Are There Any Allergens In Plant-Based Milk?
Answer: Some plant-based milk, such as almonds and soy, can be allergens for certain individuals.
It is important to choose milk that is safe for your dietary needs. Oats and rice milk are often good alternatives for nut or soy allergies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Vegans abstain from drinking milk for many reasons, from ethical concerns about animal welfare to environmental sustainability and personal health.
The rise of veganism has increased the variety and availability of plant-based milk alternatives, each with its unique flavour, texture, and nutritional profile.
Vegans have various choices available to meet their dietary needs and preferences while staying aligned with their principles, whether they opt for almond milk, soy milk, or other alternatives.
As awareness of plant-based milk alternatives grows, more people are discovering their benefits, contributing to developing a more sustainable and humane food system.
I trust you enjoyed reading the article about the Do Vegans Drink Milk? Please stay tuned. More blog posts will be posted very shortly.
JeannetteZ
Want To Learn How To Create Delicious, Cruelty-Free, Healthy AND 100% Vegan Meals? Try These Awesome Vegan Cooking Courses With A Free 7-DAY MEMBERSHIP
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I would love to hear from you. Please leave me your questions, experiences, and remarks about this article on Do Vegans Drink Milk in the comments section below. You can also email me at Jeannette@LivingTheVeganLifestyle.org.
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. I earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate and other affiliate programs. Please read my full disclosure.
Here are the links to some of my favourite articles:
How To Celebrate Your Veganniversary
Best Vegan Foods With Vitamin B12